NAD Booster Supplements Review (NAD+/NADH,
Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
How Important Is Boosting
NAD+ Levels? Find Out and Learn How Booster Supplements Compare.
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Last Updated![]() : 12/10/2021 | Initially Posted:
11/02/2021Latest Update: 64% of NMN Supplements Fail Tests
: 12/10/2021 | Initially Posted:
11/02/2021Latest Update: 64% of NMN Supplements Fail Tests
Recent Reviews
·
Aloe Juices, Gels, and Supplements
Review
·
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
Supplements Review
·
Choline and Lecithin Supplements Review
(Including Phosphatidylcholine, CDP-Choline, and Alpha-GPC)
Table of Contents
Summary
·
What Are NAD Boosters and Do They Help? Most cells in your
body use NAD as a coenzyme in the production of energy from glucose. The
thinking behind supplements that boost NAD levels is that they can, therefore,
boost energy and have other positive effects in the body. Conditions for which
they have been tried in small studies include chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS),
improving cognitive function, dementia, Parkinson's disease, depression,
cholesterol-lowering, and blood sugar control. However, there is no good
clinical evidence (based on the studies reviewed in this report) to support
these uses despite some interesting laboratory findings. It is not even clear
that taking these supplements will increase NAD in cells in
organs such as the brain, even though they raise NAD levels in the blood and
blood cells. Furthermore, if you have adequate intake of vitamin B3 (as niacin, niacinamide, or nicotinamide),
you are already getting the basic building block for NAD, which is
nicotinamide. (See What It Is)
·
What Did ConsumerLab's Tests Show? We purchased and
tested the quality of several types of NAD boosting supplements: NAD, NADH,
nicotinamide riboside, and NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) supplements. While
we found each to provide its listed amount of key ingredient, and none was
contaminated with lead, arsenic, or cadmium, we found many of these products to
be relatively expensive, although you can save a lot (as much as 67%) by
carefully comparing products to choose the right brand. (See What CL Found)
In addition, it's important to know that the amount of nicotinamide riboside in
a supplement is typically not shown on the label and includes the weight of the
attached salt (which is needed to stabilize the compound). This is a
significant amount and differs depending on the salt, e.g., chloride or
hydrogen malate). In this report, we've made it easy to compare actual amounts
of nicotinamide riboside.
·
Which NAD Boosters Are CL's Top Pick? In each category of
NAD booster, NAD/ NADH, nicotinamide riboside, and NMN, we chose a Top Pick,
based on high quality and low cost.
·
Concerns with NAD Boosters? In addition to the strong possibility
that these supplements will not provide a benefit and tend to be expensive, be
aware that some provide amounts of vitamin B-3 above the established daily
upper tolerable intake level. There is also a theoretical safety concern that
compounds that raise NAD+ levels like, nicotinamide riboside, as well as NAD,
NADH, and possibly NMN, may promote the growth of existing cancers. (See Concerns and
Cautions).
What It Is:
"NAD Boosters"
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), is a substance needed as a coenzyme in
the production of energy in the mitochondria of cells throughout the body. It
exists as either NAD+ or NADH ,
depending on whether it is in its oxidized state (which has a positive charge)
or reduced state (in which a hydrogen atom is attached, making it neutral).
Your cells convert niacin
(vitamin B-3)
and its derivatives, including nicotinamide and nicotinamide riboside, into
NAD, which is why vitamin B-3 is essential. Some NAD is stored in red blood
cells, increasing levels in the blood. Excess amounts of NAD are broken down in
the liver and excreted in urine.
In addition to vitamin
B-3, NAD, and NADH, other nicotinamide compounds may act as "NAD
boosters" such as nicotinamide riboside and nicotinamide mononucleotide
(NMN). Due to the focus on raising NAD levels, products that contain these
ingredients often have the name "NAD" in their names.
If you already get
adequate amounts of vitamin B-3 (14 to 16 mg daily for adults) from your diet
(which is not hard to do as B-3 is in many foods) and/or supplements, it is unclear
if any of the NAD Boosters in this review are important to take.
NAD and NADH:
These supplements contain NAD or, if in the reduced form, NADH. The name of the
ingredient may read, in its longest form, "beta-nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide-coenzyme vitamin B-3." If it is in the NADH form, it may say
"reduced" before the name.
Nicotinamide riboside
(NR): This is sold in various forms, including:
·
Nicotinamide riboside chloride (branded as Niagen, as found the product Tru
Niagen)
·
Nicotinamide riboside hydrogen malate
·
Crystalline nicotinamide riboside (as found in the product Basis)
Nicotinamide
mononucleotide (NMN):
This is typically marketed as NMN or beta-NMN, which are the same.
What It Does:
Interest in NAD-boosting compounds was sparked by preliminary
laboratory research suggesting that NAD+ declines with age (Massudi, PLoS One 2012; Gomes, Cell 2013), raising the hope that
increasing NAD+ levels could provide an anti-aging effect. However,
a subsequent study in people found no significant difference in
NAD+ levels between older people compared to younger people (Elhassan, bioRxiv 2019 —
preprint), making it less likely that taking nicotinamide riboside
(or NMN) to raise NAD+ levels would provide an anti-aging effect.
NAD+/NADH:
NADH, but not NAD+, has been evaluated in several clinical studies, although
both forms are sold. As discussed below, limited evidence suggests that
supplementing with NADH may improve some symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome.
Taking NADH along with CoQ10 may also help, although results are mixed. NADH
has also been evaluated for Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and
depression, but results are even more limited and some are inconsistent. In all
cases, any benefits appear to be small. Daily dosage used in studies has ranged
from 5 mg to 20 mg of NADH (the "reduced" form of NAD. NADH is 99.85%
NAD).
Chronic fatigue syndrome
(CFS) has
been associated with increased activity of certain enzymes that deplete ATP,
the main compound in cells that stores and transfers energy. Since NADH is
involved in ATP generation, there has been interest in using it to help
increase energy and reduce fatigue in people with CFS.
A crossover study among
26 people with CFS who were given 10 mg of stabilized NADH (ENADA) or
placebo daily for 4 weeks showed that 31% of those given NADH experienced a
clinically meaningful improvement in symptoms (defined as an improvement of at
least 10%) compared to only 8% of those given placebo. No between-group
comparison was made to determine if the between-group difference was
statistically significant. One person in the study reported feeling overly
stimulated while receiving NADH (Forsyth, Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol
1999).
Another small study among
20 people with CFS — 12 of whom received 5 mg of NADH daily (increased to 10 mg
daily if symptoms did not improve) and eight of whom received nutritional
supplements and psychological therapy for up to 24 months — showed that
symptoms improved for both groups during the first 3 months of the study
compared to baseline, but there was no significant between-group difference and
neither group showed improvement in symptoms in subsequent months (Santaella, P R Health
Sci 2004).
Taking NADH in
combination with coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has shown mixed results in people with
CFS. One study among 73 people with CFS showed that taking 20 mg of NADH along
with 200 mg of CoQ10 daily for 8 weeks modestly improved overall Fatigue Impact
Scale (FIS-40) scores by about 7.5 points (out of 160) compared to baseline,
and this improvement was significant compared to placebo (Castro-Marrero, Antioxid Redox
Signal 2015). However, another slightly larger study among 144
people with CFS showed the same combination of NADH and CoQ10 taken daily for 8
weeks did not improve physical functioning, psychosocial
symptoms, overall Fatigue Impact Scale (FIS-40) scores, or sleep quality,
compared to placebo. Although the NADH/CoQ10 group showed modest improvement in
perception of cognitive fatigue (improvement of about 1.1 points out of 40) compared
to baseline, the improvement was not significant compared to the placebo group
(Castro-Marrero, Nutrients 2021).
Based on the limited
available evidence, the European Network on Myalgic
Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (EUROMENE) has stated that NADH may
be tried by people with CFS to relieve fatigue or cognitive dysfunction (Nacul, Medicina (Kaunas) 2021).
One small, uncontrolled
study among 19 people with mild to moderate dementia (Alzheimer's,
vascular, and fronto-temporal types) found that
taking 10 mg of NADH (ENADA) daily for 3 months did not improve
measures of cognition compared to baseline (Rainer, J Neural Transm
(Vienna) 2000). Although a subsequent study among 24 people
with probable Alzheimer's disease showed that those who took
the same dose (10 mg) of the same NADH product (ENADA) daily for 6
months experienced no cognitive decline and had higher scores on the Mattis
Dementia Rating Scale compared to the placebo group, there was no between-group
difference in measures of attention or memory, nor was there between-group
difference in clinician rating of dementia severity (Demarin, Drugs Exp
Clin Res 2004).
NADH is a coenzyme
involved in the synthesis of L-DOPA, a precursor of dopamine — a chemical in
the brain that is deficient in people with Parkinson's disease.
While two open-label studies (i.e., no placebo control) suggested modest
benefit with NADH in Parkinson's patients, a placebo-controlled clinical trial
found no benefit. These studies are discussed below.
An open-label study among
885 people with Parkinson's disease already being treated with conventional
medication found that taking 5 mg of enteric-coated NADH by mouth or receiving
12.5 mg of NADH by 30-minute infusions every other day for 2 weeks improved
disability score based on the Birkmayer-Neumayr
disability scale by similar amounts (19.8% vs. 20.6%, respectively) (Birkmayer, Acta Neurol Scand
Suppl 1993). Another open-label study showed that receiving
10 mg of NADH by 30-minute infusion for a period of 7 days along with 100 mg of
levodopa improved scoring on the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale
(UPDRS) by 9.3 points (out of 199) and slightly increased blood levels of
levodopa compared to baseline (Kuhn, J Neural Transmission 1996). However, a
placebo-controlled clinical study showed that infusions of 25 mg of NADH for 4
days, then intramuscular injections of 25 mg of NADH on days 20 and 35 did
not improve UPDRS score compared to placebo, although both groups
showed improvement compared to baseline (7.6 and 5.3 point improvement,
respectively) (Dizdar, Acta Neurol Scand 1994).
Preliminary evidence
suggests that L-DOPA medication may improve depression symptoms and, as
previously noted, NADH plays a role in the production of L-DOPA. One open-label
study among 188 people with depression found that taking 5 mg
of NADH by mouth or receiving injections providing 12.5 mg of NADH daily for up
to about 10 months improved symptoms in 93% of participants, with 32% of people
showing marked improvement (defined as improvement of disability greater than
half the original value) (Birkmayer, New Trends
Clin Neuropharmacol 1991). However, no conclusions can be
made based on these results due to the lack of control group.
Nicotinamide riboside:
Many studies that have shown that nicotinamide riboside can raise NAD+
levels in the blood. However, in terms of providing a therapeutic benefit,
evidence is largely limited to laboratory studies. There is no good clinical
evidence that nicotinamide riboside provides a therapeutic benefit. Daily
dosage used in studies has ranged from 100 mg to 2,000 mg. This is often
divided over two doses.
Among the studies showing
that nicotinamide riboside can raise NAD+ levels are the following:
·
A study by ChromaDex, the maker
of Niagen, among 11 healthy men and women
showed that a one-time dose of Niagen
of 100 mg, 300 mg or 1,000 mg increased NAD+ levels without any serious adverse
events, although two people reported flushing at the 300 mg dose and two others
reported "feeling hot" at the 1,000 mg dose (Trammell, Nat Commun 2016).
·
A study in which these same doses were given daily for 8 weeks
to overweight, but otherwise healthy men and women, showed that whole blood
NAD+ levels increased by 22%, 51% and 142%, respectively, within two weeks, and
these increases were maintained throughout the remainder of the study. There
were no reports of flushing and no significant differences in adverse events
between the Niagen and placebo-treated groups, and no
elevation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ("bad cholesterol")
which, as noted further below, has been reported with a combination of
nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene (Conze, Sci Rep, 2019).
·
A study among 24 healthy older men and women (ages 55 to 79)
found that 500 mg of Niagen taken twice daily for six
weeks significantly increased average blood levels of NAD+ by 60% compared to
placebo; flushing was reported in one participant when taking Niagen, and in two participants while taking placebo. Nausea,
leg cramps and increased bruising were each reported in one participant while
taking Niagen (Martens, Nat Commun 2018).
(Supplements typically provide about 250 mg nicotinamide riboside per daily
dose.)
·
A study of the effects of a combination of nicotinamide riboside
and pterostilbene (Basis,
Elysium Health) among 120 older people found that those who took one capsule
(providing 250 mg of nicotinamide riboside and 50 mg of pterostilbene — the
recommended amount on the product label) or two capsules daily with breakfast
for two months had average increases in blood levels of NAD+ of 40% and 55%,
respectively. There was a slight but significant increase in
LDL ("bad") cholesterol with two capsules and among overweight people
taking one capsule. There were no significant changes in total cholesterol,
triglyceride levels, or blood pressure -- except for a slight but significant
decrease in diastolic blood pressure among those who took 2 capsules per day (Dellinger, NPJ Aging Mech Dis 2017). Six of
the 80 people taking Basis reported experiencing nausea, mild
fatigue, or moderate abdominal discomfort. [Note: The maker of Niagen claims that the
nicotinamide riboside in Basis is not the same as in Niagen, which has been generally recognized as
safe].
Due to the role of NAD in
energy production in cells, it had been hoped that supplementing with
nicotinamide riboside would, therefore, improve one's energy levels. However,
this has not been proven in clinical studies: Clinical studies
evaluating nicotinamide riboside for physical performance in older people have
been small and short-term, and results have been mixed (Cusodero, Exp Gerontol 2020). In fact, the maker of Niagen, ChromaDex, had
claimed that Niagen increased
energy, but removed that claim in 2021 following a challenge by a division of the
Better Business Bureau (BBB) National Programs. The energy boosting
claim was apparently based only on laboratory research showing that it may
increase cellular energy but not necessarily at a functional
level.
Studies in mice have
shown nicotinamide riboside to reduce a main component of amyloid plaque
associated with Alzheimer's disease and improve cognitive function (Gong, Neurobiol Aging 2013)
and to improve stem cell function (Zhang, Science 2016).
Nicotinamide riboside has
been promoted for lowering cholesterol levels in the liver,
although this has only been shown in laboratory and animal studies (Lee, J Med Food 2015) and not in clinical studies.
Although animal and
laboratory studies have suggested nicotinamide riboside may help to
improve blood sugar control (Lee, J Med Food 2015), a study in Denmark
among 40 overweight men with insulin resistance (HOMA-IR ≥ 2.5) found
that 1,000 mg of nicotinamide riboside (Niagen) taken
twice daily for three months did not decrease fasting blood
sugar levels or HbA1c (a measure of blood sugar levels over several months), or
improve insulin sensitivity compared to placebo. There were no improvements in
body composition (body fat, lean mass or total body mass) compared to placebo.
Side effects were generally mild but included itching, excessive sweating,
bloating and changes in stool (Dollerup, Am J Clin Nutr 2018).
Be aware that the FDA
sent a warning letter to ChromaDex, the manufacturer of Niagen, in November 2020 that it cannot be promoted as
preventing or treating COVID-19. According to the FDA, ChromaDex made claims that having low NAD+ levels can
worsen COVID-19 and promoted Niagen products with
statements such as "early preclinical data suggests that increasing
cytoplasmic NAD levels through a NAD precursor, such as NR, may support innate
immunity to coronaviruses and other viruses…"
Nicotinamide
mononucleotide (NMN)
Like nicotinamide riboside, NMN is a precursor to NAD and may boost levels
of NAD+ in the body (Shade, Integr Med (Encinitas)
2020). A few studies have assessed the clinical effects of NMN in
humans, but results from these studies are limited. Overall, there is no good
evidence that NMN has any significant clinical benefits in humans. Daily dosage
used in studies has ranged from 250 mg to 1,200 mg. The larger dosage is
typically divided over two doses.
A study among overweight
or obese postmenopausal women with prediabetes found that taking 250 mg of NMN
daily for 10 weeks increased NAD+ content in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
(immune cells in the blood) by about 43% compared to placebo. Skeletal muscle
content of NAD+ was not increased (Yoshino, Science 2021).
One study in China among
48 recreational runners (average age 36) showed that taking 300 mg or 600 mg of
NMN twice daily for 6 weeks while participating in 40- to 60-minute training
sessions five to six times weekly increased the time until breathing begins to
increase during exercise (VT1) and improved power at the time point during exercise at which
the person becomes out of breath (VT2) compared to placebo, with the effects being dose-dependent.
However, neither dose increased maximum oxygen consumption, nor did it improve
the ratio of oxygen consumption to heart rate. Based on these results, the
researchers speculated that NMN may improve the use of oxygen by
skeletal muscles, but NMN does not appear to have
a cardiac benefit (Note: NMN is frequently touted as have
cardiovascular benefits). A lower daily dose of NMN (150 mg twice daily) did
not improve any outcome measures. No adverse effects were reported for the NMN
groups (Liao, J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2021).
A study among overweight
or obese postmenopausal women with prediabetes found that
taking 250 mg of NMN daily for 10 weeks increased muscle insulin
sensitivity by 25% compared to baseline. There was no improvement in
muscle insulin sensitivity in the placebo group, and neither group showed
improvement in liver insulin sensitivity (Yoshino, Science 2021). While these results
suggest that NMN may have some benefit for improving insulin sensitivity in
people with prediabetes, this study has been criticized by another researcher
(the Chief Scientific Advisor for ChromaDex) because,
at the start of the study, the placebo group had 2.35 times the level
of liver fat as those in the treatment group, and other research has
shown that liver fat reduces muscle insulin sensitivity. Consequently, it is
unclear if the difference between the treatment and placebo group was due to
NMN supplementation or differences in liver fat content (Brenner, Science 2021).
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
No U.S.
government agency is responsible for routinely testing dietary supplements,
such as NAD+, NADH, nicotinamide riboside, or nicotinamide mononucleotide for
their contents or quality. In this review, ConsumerLab.com selected, purchased
and tested such products to determine whether they contained the amounts of key
ingredients stated on their labels. In addition, all were tested for potential
contamination with lead, cadmium and arsenic. All regular tablets were also
tested to determine if they would properly disintegrate. (See How Products Were Evaluated for
information on testing methods and passing score.)
UPDATE: (12/9/2021): Twenty-two
brands of NMN with the highest market share on Amazon were recently tested by ChromaDex, which sells the nicotinamide riboside ingredient
Niagen and the product Tru Niagen and is an indirect competitor of these brands.
Single samples were tested using HPLC, similar to what ConsumerLab
applied in this review. ChromaDex found that only
three products contained their claimed amounts of NMN or slightly higher
amounts: Infinite Age NMN, ProHealth Longevity NMN Pro 300,
and maac10 NMN 250M (which also passed ConsumerLab
testing), and another five contained 88-99% of claimed amounts (ForestLeaf NMN, GeneX
Formulations NMN, Jarrow Formulas NMN, Toniq NMN, and Double Wood NMN (which
also passed ConsumerLab testing).
Fourteen
products tested by ChromaDex contained
less than 1% of their claimed NMN. These were Komprocha
NMN & Resveratrol, monoHerb NMN, Paragon Health
NMN 500, VIVALIFER NMN, and the following ten products all from the same
distributor (SerumLab S&C International LLC,
Oregon) and having similar labeling: ChriBubble
NNM, EliteHealth NMN, Energecko
NMN Longevity, LIVEMAX NNM, NMN MAX 500 mg, NMN PLUS 500 mg, NMN Star 500 mg, Starhonor NMN, VitaBlossom NMN
Refresh, and Vitamin Shower NMN 500 mg.
Interestingly,
many of the products found to contain virtually no NMN have hundreds or
thousands of positive reviews on Amazon and some display images of certificates
of analysis indicating that they provide their claimed amounts of NMN.
What CL Found:
All eight of the supplements that ConsumerLab.com selected,
purchased and tested for this review were found to contain their listed amounts
of nicotinamide compounds, and none was found to be contaminated with lead,
arsenic, or cadmium.
What was most striking in
our review was the wide range in dosage among NAD+ and NADH products, the
difficulty a consumer could have in comparing amounts of nicotinamide riboside
from different chemical forms, and the range in cost among products in each
category, most of which are relatively expensive, as discussed below.
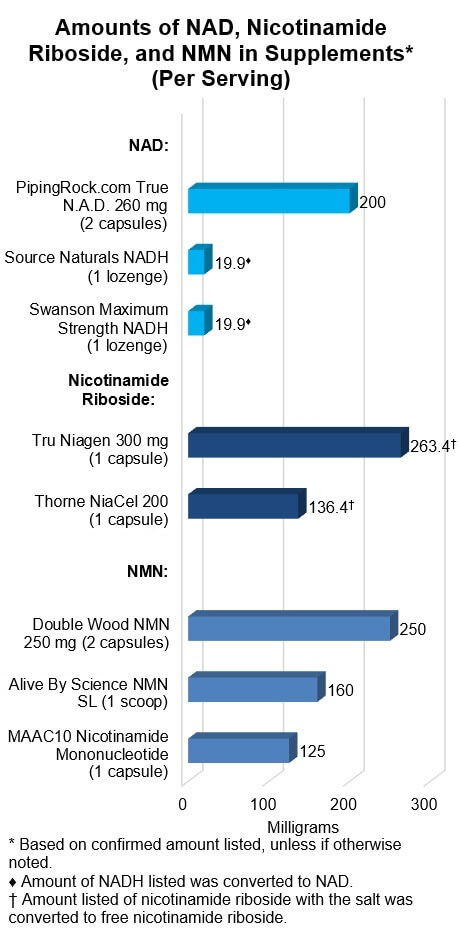
Amounts of Ingredient
As shown in the graph below, among NAD/NADH products there was a 10-fold
difference in dosage, with PipingRock.com True N.A.D providing
200 mg of NAD per 2-capsule serving, while each of the NADH lozenges provided
one-tenth that amount — about 20 mg. However, published clinical studies have
tended to use the lower amount, in the NADH form.
The differences in dose
per serving were less than two-fold for the other two categories, although, for
nicotinamide riboside products, consumers should be aware that the chloride
form (in Tru Niagen)
is 87.5% nicotinamide riboside while it is only 65.7% in the hydrogen malate
form (in Thorne NiaCel). To make it easy
to compare, we've done the calculations to show the amounts of just
nicotinamide riboside in the products in the graph below.
Among NMN products, Double
Wood and MAAC10 provide the same amount (125 mg) per
capsule, although Double Wood lists a serving as two capsules
while MAAC10 lists one.
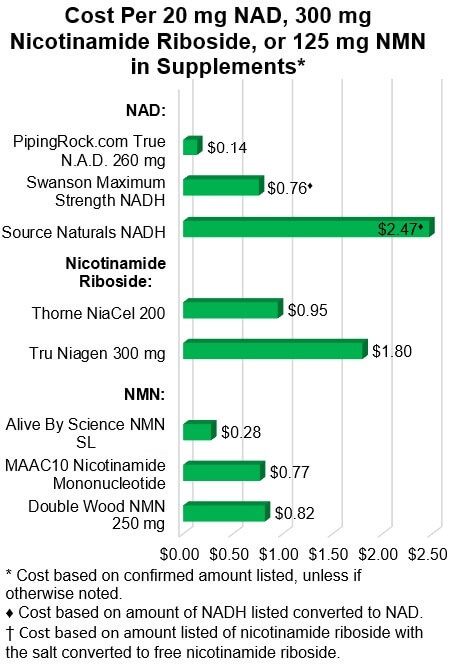
Cost
In all three supplement categories shown below, there was a large difference in
the cost to get an equivalent amount of active compound.
This was most striking
with NAD and NADH products, with the cost for 20 mg of NAD ranging from about
14 cents to $2.47, and between two lozenges there was a three-fold difference
in cost: $2.47 from two Source Naturals lozenges versus 76
cents from one Swanson lozenge.
The cost to get 300 mg of
nicotinamide riboside was nearly double with Tru
Niagen ($1.80) versus Thorne NiaCel (95 cents).
The cost to get NMN was
similar from the two products sold as capsules (Double Wood and MMAC10),
while the powder (Alive By Science) was much
less expensive.
Top Picks:
NAD/NADH:
Although Piping Rock True N.A.D. provides much more NAD (260
mg per 2-capsule serving) than the 10 mg and 20 mg lozenges from,
respectively, Source Naturals and Swanson, and at
a lower cost for NAD, the dose in Piping Rock is much higher
than has been used in clinical trials, which have used just 5 to 20 mg of NAD
(as NADH) daily. It would seem more prudent to use the lower amounts in the
lozenges despite the fact they are more expensive sources of NAD, as discussed
above.
Each Source
Naturals NADH lozenge provides 10 mg of NADH (9.9 mg of NAD) -- a dose
more commonly used in clinical trials than the 20 mg in Swanson. On
the other hand, Swanson's 20 mg lozenge costs much less (76
cents) than Source Naturals 10 mg lozenge ($1.23) —
making Source Naturals more than 3 times as expensive as
a source of NADH than Swanson. Since these lozenges can be easily
broken in half, it would be more economical to purchase the Swanson lozenges
and break them as needed to get the dose you want. For this reason, our Top
Pick for NAD/NADH is Swanson Maximum Strength NADH.
Of course, if you don't
want to break lozenges and are okay with paying a much higher price, Source
Naturals NADH is a fine alternative — in fact, some of the clinical
trials with NADH have been conducted with the ENADA brand of NADH listed
in Source Naturals but not in Swanson.
Nicotinamide Riboside:
Both nicotinamide riboside supplements that we tested met our quality
standards. If you are looking to purchase one, you need to consider the fact
that there is a large amount of clinical information around the chloride form
(branded as Niagen) in Tru
Niagen and little information about the
hydrogen malate form in Thorne Niacel 200,
although it is half the cost to get nicotinamide riboside.
While it is possible that
any effects would be the same with an equal dose of nicotinamide riboside from
either product, Tru Niagen is our Top Pick for
nicotinamide riboside because it is better studied and the FDA did not object in 2016 to
a filing by Niagen's maker, ChromaDex,
that Niagen should be "generally recognized as
safe" (GRAS) for use in foods, while there does not appear to be a public
record of any filing with the FDA for the hydrogen malate form of nicotinamide
riboside in Niacel. The FDA also did not
object to ChromaDex's New Dietary Notification in 2018 on Niagen at 300 mg per day.
It should be noted that
nicotinamide riboside is a source of vitamin B-3, and both Tru Niagen and Niacel exceed the U.S. tolerable upper intake
level for B-3 of 35 mg. European limits are higher — 500 mg to 900 mg
(see Concerns and Cautions), but the European Food
Safety Authority has also raised concern with high doses of nicotinamide
riboside and other nicotinamide compounds, writing that "Experimental data
indicate several pathways by which intakes of nicotinamide that are
substantially higher than the physiological requirement, or its precursors, might
cause adverse effects." (EFSA 2021).
Another supplement
containing nicotinamide riboside, in crystalline form, is Elysium Basis,
which was tested by ConsumerLab.com in 2019 as part of its B Vitamin Supplements Review. It passed
testing, providing its claimed 250 mg of nicotinamide riboside per 2-capsule
serving (costing $2.00), making it a more expensive source of nicotinamide
riboside than Tru Niagen and NiaCel.
NMN:
Alive by Science NMN SL, a powder, provides 160 mg of NMN at about 1/3
the cost (28 cents) of the other two Approved products (Double Wood and MAAC10)
which each provide less NMN (125 mg per capsule) at higher cost (respectively,
82 and 77 cents). Due to this large savings, Alive by Science is
our Top Pick for NMN. However, if you don't care for the
overly sweet and sour taste of the powder (which, the label suggests, be placed
under the tongue, perhaps to stimulate salivation to dissolve the powder) and
you don't mind paying more, you next best choice would be MAAC10 capsules,
as they cost a little less than capsules from Double Wood.
Be aware that the Alive
by Science company was previously named Alive by Nature. The change in name
took place after it received a Warning Letter from the FDA on May 5,
2020, indicating that its NAD+ and NMN sublingual gel products were being sold
as unapproved and misbranded drugs based on primarily claims made by the
company suggesting that these products could treat COVID-19. The FDA cited
statements on the company's website such as "NMN shows great promise in
case studies of humans with COVID-19... The NMN mixture lead [sic] to a
surprisingly rapid and thorough reversal of COVID-19."
Test Results by Product:
Listed
below are the test results for eight products alphabetically within their
respective category. ConsumerLab.com selected all of these products. Shown for
each product are the labeled amounts of the various forms of nicotinamide per
listed serving. Products that exceed the tolerable upper intake level for
vitamin B-3 are indicated with a with a ">UL" symbol. Prices paid
for each product and the costs per daily serving are shown in the fourth to
last column. Listed in the second to last column are other notable ingredients
and features, and the last column shows a full listing of labeled ingredients.
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of NAD Boosters Supplements
(NAD+/NADH, Nicotinamide Ribose, and NMN)
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Approval Statusⓘ
Product Name
Claimed Amount of Nicotinamide Ingredientⓘ
Heavy Metals
Pill Sizeⓘ
Suggested Serving on Label
Cost for Suggested Serving
Price
Notable Features
Full List of Ingredients Per Serving
NAD/NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide/Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide):
APPROVED
PipingRock.com® True N.A.D. 260 mg
Mfd. by Piping Rock Health Products
2 capsules
200 mg NAD
NAD: 200 mg ✔
Metals: Pass
Medium/large capsule
For adults, take two (2) quick release capsules daily, preferably with a meal.
$1.43/2 capsules
[$0.14 per 20 mg NAD]
$42.99/60 capsules
No Gluten, Wheat, Milk, Lactose, Soy, Artificial
Color, Artificial Flavor, Artificial Sweetener, Preservatives.
2 capsules
Nicotinamide Rejuvenator™ NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) 260 mg.
Other Ingredients: Cellulose (Plant Origin), Gelatin Capsule, Vegetable
Magnesium Stearate, Silica.
APPROVED
Source Naturals® NADH
Dist. by Source Naturals, Inc.
2 lozenges
20 mg NADH
NADⓘ: 19.9 mg ✔
Metals: Pass
Medium circular lozenge
1 to 2 lozenges daily.
Taste: Mild peppermint-flavored lozenge tablet.
$2.47/2 lozenges
[$2.47 per 20 mg NAD]
$36.99/30 lozenges
Sodium 10 mg per 2 lozenges
Contains no yeast, dairy, egg, gluten, soy or wheat. Contains no sugar,
preservatives, or artificial color, flavor or fragrance.
2 lozenges
Sodium 10 mg, ENADA® NADH (Reduced β-Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide-Coenzyme Vitamin B-3) 20 mg.
Other Ingredients: D-Mannitol, sodium bicarbonate, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, natural peppermint flavor, and magnesium
stearate.
APPROVED
Top Pick
for NAD/NADH
Swanson® Maximum Strength NADH
Dist. by Swanson Health Products
1 lozenge
20 mg NADH
NADⓘ: 19.9 mg ✔
Metals: Pass
Medium circular lozenge
Place one lozenge under the tongue and allow to dissolve.
Taste: Mild peppermint-flavored lozenge tablet.
$0.76/lozenges
[$0.76 per 20 mg NAD]
$22.88/30 lozenges
Dairy Free. Soy Free. Vegetarian. Nut Free.
1 lozenge
NADH (reduced β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) 20 mg.
Other Ingredients: Xylitol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, crospovidone,
rice extract, natural peppermint flavor, sodium copper chlorophyllin.
Nicotinamide Ribosides:
APPROVED
Thorne® NiaCel 200®
Mfd. by Thorne Research
1 capsule
207.5 mg nicotinamide riboside hydrogen malate
nicotinamide riboside
expectedⓘ: 136.4
mg>UL ✔
(Found: 145 mg nicotinamide riboside, calculated as 221 mg nicotinamide
riboside hydrogen malate)
Metals: Pass
Large capsule
Take 1 capsule one to two times daily or as recommended by your health-care
practitioner.
$0.43/capsule
[$0.95 per 300 mg nicotinamide riboside]
$26.00/60 capsules
Betaine anhydrous 42.5 mg per capsule
Gluten Free.
1 capsule
Nicotinamide Riboside Hydrogen Malate 207.5 mg, Betaine Anhydrous (Trimethylglycine) 42.5 mg.
Other Ingredients: Hypromellose (derived from cellulose) capsule,
Microcrystalline Cellulose, Calcium Laurate, Silicon Dioxide.
APPROVED
Top Pick
for nicotinamide riboside
Tru Niagen®
300 mg
Dist. by ChromaDex,
Inc.
1 vegetarian capsule
300 mg nicotinamide riboside chloride
nicotinamide riboside
expectedⓘ: 263.4
mg>UL ✔
(Found: 303 mg nicotinamide riboside, calculated as 345 mg nicotinamide
riboside chloride)
Metals: Pass
Large vegetarian capsule
Adults, take one capsule daily or as recommended by your healthcare
professional.
$1.58/vegetarian capsule
[$1.80 per 300 mg nicotinamide riboside]
$47.30/30 vegetarian capsule
NSF Certified Sport seal. Halal. Kosher.
1 vegetarian capsule
NIAGEN® (nicotinamide riboside chloride) 300 mg.
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Hypromellose (vegetarian
Capsule), Vegetable Magnesium Stearate.
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide):
APPROVED
Top Pick
for NMN
Alive By Science NMN SL
Dist. by Alive By
Science, LLC
1 scoop [250 mg]
160 mg NMN
✔
Metals: Pass
Take one (1) level scoop, 2 times per day under
the tongue and allow to completely dissolve.
Taste: Extremely sweet, citrus-flavored powder with strong sugar
alcohol aftertaste from mannitol. Elicits saliva, which dilutes the powder in
the mouth.
$0.36/scoop
[$0.28 per 125 mg NMN]
$31.95/22 g (approx. 88 servings)
Betaine anhydrous 30 mg per scoop
No artificial colors, preservatives or additives. Gluten-free. Non-GMO.
Suitable for vegans.
1 scoop
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide 160 mg, Betaine Anhydrous (TMG) 30 mg.
Other Ingredients: Mannitol, Monk Fruit, Citrus Burst™.
APPROVED
Double Wood® NMN 250 mg
Dist. by Double Wood LLC
2 capsules
250 mg NMN
✔
Metals: Pass
Medium/large capsule
Take 2 capsules per day.
$1.63/2 capsules
[$0.82 per 125 mg NMN]
$48.95/60 capsules
Non-GMO. Gluten Free.
2 capsules
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide 250 mg.
Other Ingredients: Gelatin (capsule), organic rice flour.
APPROVED
MAAC10® Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
Dist. by MAAC10, LLC
1 capsule
125 mg NMN
✔
Metals: Pass
Medium/large capsule
Take 1-4 capsules per day or as directed by your healthcare professional.
$0.77/capsule
[$0.77 per 125 mg NMN]
$22.99/30 capsules
Does Not Contain: Milk, eggs, fish, shellfish,
tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, GMO, or preservatives.
1 capsule
NMN (beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide) 125 mg.
Other Ingredients: Cellulose (capsule), rice fiber, and rice hulls.
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's
ingredients differ from what is listed above, it may not necessarily be of the
same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
Concerns and Cautions:
All of
the NAD boosters in this review are sources of vitamin B-3 which has an established
upper tolerable intake level of 35 mg per day for adults in the
U.S. Nearly all of the products exceed this limit. However, it
should be noted that this limit based on causing flushing of the skin, which is
not thought to be a side effect of the nicotinamide form of vitamin B-3.
Nevertheless, more serious toxicities can occur with much higher intakes
nicotinamide (also known as niacinamide), which has prompted government
agencies in Europe to set tolerable upper intake levels of 500 mg in the UK and 900 mg in the European Union for
adults. Toxicities at high levels include liver injury, damage
to the macula (part of the retina of the eye), gout, declines
in platelet counts. High doses may also impair glucose control and
increase blood levels of anticonvulsant drugs (See "Upper
Limit" for vitamin B-3 in the B Vitamins Review.)
There is a theoretical
concern that compounds like nicotinamide riboside, as well as NADH and possibly
NMN, that raise NAD+ levels may promote the growth of existing cancers (Poljsak, J Clin Exp Oncol 2016). In fact, one
group of researchers suggested that reducing NAD+ levels
(rather than raising them) may be a promising approach to a cancer treatment (Gujar, PNAS 2016; Wash U Sch Med news 2016).
Furthermore, one CL member reported (6/17/2019) that "After one year
taking Elysium Basis [which provides nicotinamide riboside]
supplements, I experienced a sharp rise in PSA levels from 1.8 to 4.9. After
stopping these supplements for one month my PSA returned to 1.9."
[Increases in PSA may indicate prostate cancer.] He told us he contacted
Elysium Health, but was told they have no data "that point to a
correlation or interaction between Basis and PSA levels" although they did
acknowledge that "a handful of people" have "reached out to us
about positive changes to their PSA levels." While there is no current
evidence of nicotinamide riboside causing or fostering cancer, it would seem
prudent to avoid this form of niacin if you have been diagnosed with cancer. [ConsumerLab tested Basis in its B Vitamin Supplements Review in
2019, in which it passed tests and was Approved for quality.]
Information on this site
is provided for informational purposes only. It is not an endorsement of any
product nor is it meant to substitute for the advice provided by physicians or
other healthcare professionals. The information contained herein should not be
used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease. Consumers should
inform their healthcare providers of the dietary supplements they take.
Latest Clinical Research Updates for NAD Boosters (NAD+/NADH,
Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
64% of NMN Supplements Fail Tests
12/10/2021
Fourteen of the 22 most
popular NMN supplements (which can boost NAD+ levels) on Amazon were recently
discovered to contain no detectable NMN. See the results in the Update to our NAD Boosters Review, which
includes CL's tests of additional NMN, NADH, and nicotinamide riboside
supplements, as well as our Top Picks.