Milk Thistle Supplements Review
Find the Best Milk
Thistle Supplement. Tests and Reviews of Popular Milk Thistle Supplements &
CL's Top Picks.
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Last Updated![]() : 07/30/2021 | Initially Posted:
08/01/2020
: 07/30/2021 | Initially Posted:
08/01/2020

Recent Reviews
·
Aloe Juices, Gels, and Supplements
Review
·
NAD Booster Supplements Review
(NAD+/NADH, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
·
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
Supplements Review
Table of Contents
Summary
·
What does milk thistle do? For people with type 2 diabetes, milk
thistle may decrease blood sugar, hemoglobin A1c, and LDL cholesterol levels
when used with conventional therapy. The evidence is mixed as to whether it
improves liver function in people with chronic active hepatitis (see What It Does).
·
What is silymarin? Silymarin is the term for a specific
group of chemically-related compounds found in milk thistle. Silymarin is
thought to be responsible for some of the herb's effects and is used as a
marker of milk thistle strength (see What It Is).
·
What to look for with milk thistle? Milk thistle comes
in various forms and concentrations, but most clinical studies of milk
thistle's effectiveness have used extracts at a dose of about 200 mg of extract
taken 2 to 3 times per day. The amount of silymarin in these extracts is about
58% of its weight (although this has been reported as 80% when using a
non-specific, older method of testing known as UV-VIS) (see ConsumerTips™ for
dosage and other details).
·
What did CL find in its tests of milk thistle supplements? The amount of
silymarin per serving ranged from 61.2 mg to 202 mg. For most products, these
amounts were far less than a consumer might expect from labels, leading CL to
rate several products as having poor labeling (see What CL Found).
·
Which is the best milk thistle supplement? Among products
Approved for Quality by ConsumerLab.com one was chosen as CL's Top Pick for
providing a substantial amount of silymarin, appropriate usage instructions,
and superior value.
·
What are the side effects of milk thistle? Milk thistle is
generally well tolerated but, infrequently, can have a laxative or other
gastrointestinal side-effect. Allergic reactions can occur, especially in
people who are sensitive to related plants and it may interact with certain
medications (see Concerns and
Cautions for details).
What It Is:
The
ripe seeds of the milk thistle plant (Silybum marianum) are
used medicinally. One of the most important constituents of milk thistle is
silymarin, which itself has several chemical constituents of which most
prominent is silybinin (also referred to as silibinin or silybin).
What It Does:
Diabetes
The silymarin component of milk thistle may decrease blood sugar, hemoglobin
A1c, and LDL cholesterol levels when used with conventional therapy in people
with type 2 diabetes, as shown in a 4-month, placebo-controlled study in Iran
which 200 mg of a milk thistle extract was given 3 times daily (Huseini, Phytother Res 2006). A milk thistle extract also
appeared to reduce insulin resistance in people with coexisting diabetes and
alcoholic cirrhosis in a 12-month study in Italy in which an extract providing
200 mg of silymarin was taken 3 times daily given; however, the study was not
placebo-controlled (Velussi, J Hepatol
1997).
Hepatitis and Diseases of
the Liver
Silymarin is thought to act as a liver-protectant, although evidence of benefit
in liver disease has been mixed. One preliminary study of a specific silybinin preparation improved liver function in people
with chronic active hepatitis. However, most studies in patients with hepatitis
B or C have not shown an improvement in mortality or liver function using milk
thistle or preparations of milk thistle. Similarly, in alcoholic liver disease,
some preliminary clinical studies suggested that milk thistle might improve
liver function and mortality, but later studies did not show a significant
effect.
Some
research has shown benefit of milk thistle in people with nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis (NASH), a condition marked by excessive storage of fat in the
liver and ballooning of liver cells. However, the studies have been small and
short-term, so larger studies conducted over longer periods of time are needed
to confirm the effectiveness. A study in Iran among 64 people with NASH showed
that the silymarin component of milk thistle, taken in doses of 70 mg three
times daily for 8 weeks (Livergol, Goldaru Pharmaceutical Company), reduced markers of liver
injury compared to placebo, although these markers of liver injury improved in
the placebo group as well (Solhi, Caspian J
Intern Med 2014). Another small study in Malasia
among 89 people with confirmed NASH also showed that taking silymarin in much
higher doses, longer-term (700 mg three times daily for 48 weeks) reduced
markers of liver injury and reduced fibrosis compared to placebo. However,
taking silymarin did not increase the percentage of patients who showed at
least 30% improvement in liver injury based on NAFLD Activity Score, which was
the primary outcome of the study, nor did it improve steatosis or liver cell
ballooning or prevent the development of fibrosis (Kheong, Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017).
Liver
Protection from Chemotherapy and Other Drugs
Preliminary evidence suggests that milk thistle extract standardized to 70% -
80% silymarin may protect the liver against damage from certain toxins,
including drugs such as acetaminophen and phenytoin (Dilantin). Milk thistle
extract may also reduce liver toxicity associated with chemotherapy -- a
complication which can limit therapy. In a study of children with acute
lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) receiving maintenance chemotherapy, milk thistle
extract standardized to 33% silybinin was given at a
daily dose of 80 mg to 320 mg of silybinin (Ladas, Cancer 2010). Although no benefit was
seen during the short course of therapy (28 days), one month later the milk
thistle-treated children had reductions in levels of liver enzymes that
indicate toxicity compared to those who did not receive milk thistle.
Administered
intravenously (IV), silybinin may lessen liver damage
due to poisoning by Amanita phalloides mushroom (death cap) --
although this IV preparation is not readily available in the U.S.
Menopause
Milk thistle may help reduce the severity and frequency of hot flashes in
postmenopausal women, as shown in a placebo-controlled study in Iran, in which
200 mg of a milk thistle extract or placebo was given twice daily for 8 weeks
to 73 postmenopausal women (average age 52). After 8 weeks, women given milk
thistle extract reported about 3 fewer hot flashes per day compared to
baseline. This improvement persisted for 4 weeks after they stopped taking the
supplement. Women given milk thistle extract also reported less severe hot flashes
when they did occur. Women given milk thistle reported a 68% reduction in hot
flash severity after 8 weeks (from 5.25 points to 1.70 points based on a 10
point-scale). The frequency and severity of hot flashes remained unchanged for
women in the placebo group. The milk thistle extract was standardized to 80%
total silymarin (47.7% silibinin) (Saberi, Phytother Res 2020). Note that women with very
severe symptoms were excluded from the study, so it is uncertain if milk
thistle would be beneficial in such cases. See CL's Menopause Supplements Review, covering soy and red
clover isoflavones, black cohosh, and progesterone cream, for information about
other ingredients commonly used for menopause.
Other:
Silybinin is under investigation for use in
preventing or treating various forms of cancer, especially prostate cancer.
For information about
dosage, see What to Consider When Using section
below.
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
Most
clinical studies of milk thistle's effectiveness have used specific dry
extracts standardized to approximately 70% to 80% silymarin on a weight basis
based on non-specific testing methods or about 58% using a High
Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) specific for silymarin. Milk
thistle is also available in non-concentrated, seed powder form, which should
contain at least 2% silymarin. ConsumerLab.com purchased and tested milk
thistle products by HPLC to determine which products contained this level of silymarin
-- and/or other levels if claimed on labels.
Past testing by
ConsumerLab.com has revealed many milk thistle products that do not contain
these expected amounts. Any product containing whole herbs (including milled,
milk thistle seed powder) was also tested for contamination with the heavy
metals lead, cadmium and arsenic, as this can occur in herbal supplements —
although is less likely with extracts, and for yeast and mold contamination.
Testing of 19 milk thistle extract supplements purchased
from the U.S. and seven more from the Czech Republic found that seven from the
U.S., and three from the Czech Republic, contained detectable levels of one or
more of five synthetic pesticide-related ingredients (i.e., pirimiphos-methyl,
malathion, and chlorpyrifos, which are insecticides; carbendazim, a fungicide;
and piperonyl butoxide, a component added to enhance
the potency of certain pesticides) in amounts that would be considered unsafe
for infants and babies, as they exceeded the European Union (EU) maximum
residue levels of 10 mcg/kg. One of the products from the U.S. and one from the
Czech Republic contained levels that exceeded EU maximum residue levels for
adults. At least one of the pesticides (chlorpyrifos) detected in some of the
milk thistle products has been reported to cause liver and kidney toxicity when
given orally to mice. All of the evaluated milk thistle products (specific
brand names were not provided), which were purchased between 2016 and 2017,
contained milk thistle extract or seed extract. Some, although not all, of the
products also contained other herbal ingredients (Fenclova, Sci Rep 2019).
These results were not published until 2019, around the time of ConsumerLab's current review. In light of the findings,
ConsumerLab.com may evaluate pesticides in milk thistle products in its next
review.
What CL Found:
When choosing a milk thistle supplement made from an extract (as
most are), you want one that provides a significant amount of silymarin --
about 58% (or at least 52.2% allowing for acceptable variance) of the extract's
weight when measured with a highly specific test method known as HPLC. This is
the test method used by ConsumerLab and is the
official USP method (see How Products Were Evaluated).
What causes great confusion in the market is that many extracts are labeled as
providing 80% silymarin, likely based on an older, non-specific method of
testing known as UV-VIS. Finding 58% silymarin by HPLC is equivalent to finding
80% silymarin by UV-VIS because the UV-VIS method incorrectly counts some
non-silymarin compounds as being silymarin. The FDA allows manufacturers to use
any testing method they want.
Some manufacturers are clear about this and tell you, right on the label, the
percent silymarin and the method used. Others only tell you the percent
silymarin without the method. Since the only official compendial method is
HPLC, if a product claims 80% silymarin without disclosing that this is based
on the older method, we consider that to be poor labeling, although the product
itself may be fine to use and has not violated FDA labeling requirements.
Based on the amounts of silymarin that we found in testing among the nine milk
thistle supplements that we selected for review, here is what we found:
·
Approved: California Gold (claims 80% silymarin
flavonoids by UV-VIS and 58% by HPLC) and Jarrow
Formulas (claims 80% total flavonoids, which implies silymarin and
other flavonoids as included in UV-VIS).
·
Approved but with "Poor Labeling": (CVS Health,
Nature's Sunshine, Pure Encapsulations, and Swanson). These
products contain significant concentrations of silymarin — meeting our minimum
requirements, but did not state that their claimed "80% silymarin"
(or claims to that effect) were apparently based on a non-specific test method,
as we found the extracts in these products to provide 57.2%, 57.7%. 54.9%, and
53% silymarin, respectively.
·
Approved but with "Low Strength": TruNature
Premium Milk Thistle contains a much smaller amount than other
products of silymarin as confirmed by CL (and which is listed as silybin, the
basic chemical name for silymarin compounds), although it does include
phospholipids that may increase absorption.
·
NOT Approved: NOW Silymarin and Vitamin
Shoppe Milk Thistle Extract. NOW claims 280 mg of
silymarin but we found only 174.7 mg by HPLC, and Vitamin Shoppe claims
240 mg of silymarin but we found only 154 mg. This also means that these
extracts are less concentrated than the others, at 49.9% and 51.3% silymarin,
respectively — too far below our minimum of 58%. The amounts of silymarin they
provide, however, remain significant.
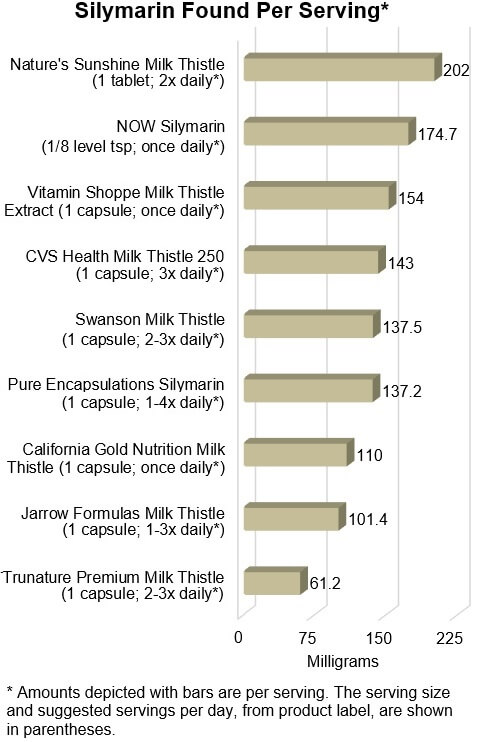
Amounts of silymarin
found in products
Although we didn't like the way that many milk thistle extracts were labeled
(as explained above), the graph below shows that most provided substantial
amounts of silymarin, although not as much as one might think from the claims
on the labels.
Unfortunately, the only two products that CL Approved without
qualification, California Gold and Jarrow,
provided among the smallest amounts of silymarin per serving.
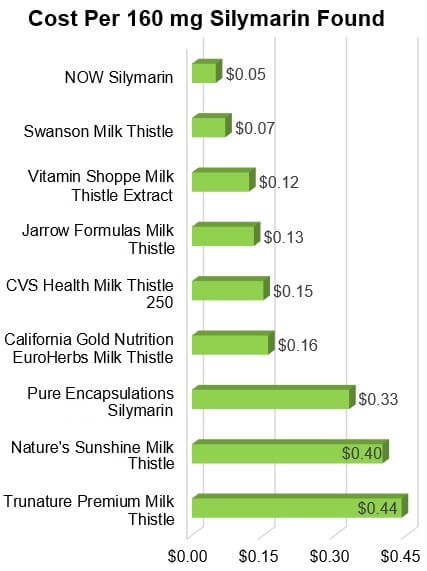
Cost to get silymarin
The cost to get 160 mg of silymarin (a substantial dose, in-line with what has
been used clinically per serving), ranged from just 5 cents to 44 cents among
the products, as shown in the graph below. The least expensive, Approved
product was Swanson Milk Thistle.
Top Pick:
California Gold could have been our Top Pick for
milk thistle if it were designed to provide somewhat more than its 175 mg of
extract per capsule, as, otherwise, it was the only product reviewed that
clearly stated its silymarin content — both in terms of HPLC (58%) and UV-VIS
(80%), and we found it to meet its claim based on our HPLC analysis. It also
had the second highest concentration of silymarin, at 62.9% based on the amount
we found (only Jarrow was higher at
67.6%). It is also reasonably priced at 11 cents per large capsule.
Our Top Pick, however, is Swanson Milk Thistle,
despite the fact that its claimed 80% silymarin (i.e.,
200 mg) from its extract was likely based on UV-VIS, as we found 137.5 mg based
on HPLC analysis, which included about 5 mg expected from its other ingredient,
milk thistle seed powder. This is still a substantial amount of silymarin per
capsule and 27.5 mg more per capsule than in California Gold, while
costing about half the price -- only 6 cents per large capsule. Swanson's suggestion
of taking two to three capsules per day with water is also consistent with how
milk thistle is best taken, while California Gold suggests
only one capsule daily with food, which is unusual.
Going forward, it would be great for consumers if Swanson and
other brands would list their silymarin content based on the official USP
method, HPLC, while optionally indicating the amount of silymarin by UV-VIS.
Test Results by Product:
Listed
alphabetically below are test results for nine milk thistle products selected
for testing by ConsumerLab.com. Products listed as "Approved" met
their label claim or minimum expected amount of silymarin and ConsumerLab.com's additional standards for milk thistle
supplements (see Passing Score).
Silymarin claims and amounts are shown in the 2nd column. Labeled serving suggestions and
a description of pill sizes are in the 3rd column. Cost and price comparisons are shown in the 4th column; notable features and precautions
are in the 5th column; and full
list of ingredients for each product is found in the final column.
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of MILK THISTLE SUPPLEMENTS
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Product Name
(Suggested Serving on Label)
Claimed Amount of Milk Thistle
Claimed or Expectedⓘ Amount of Silymarinⓘ
Pill Sizeⓘ
Suggested Serving on Label
Cost for Suggested Serving
[Cost Per 160 mg of Silymarin]
Priced
Notable Features
Full List of Ingredients Per Serving
Milk Thistle Extracts:
APPROVED
California Gold Nutrition® EuroHerbs™
Milk Thistle
Dist. by California Gold Nutrition®
1 veggie capsule
175 mg extract
101.5 mg silymarinⓘ (C)
✔
Met claim of 58% silymarin by HPLC (found 110 mg or 62.9% of
extract).
Large veggie capsule
Take 1 veggie capsule daily with food.
$0.11/veggie capsule
[$0.18 based on amount listed]
[$0.16 based on amount found]
$20.00/180 veggie capsules
This product is not manufactured with milk,
eggs, fish, crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy or gluten.
Precaution: Produced in a third-party, audited and registered cGMP
compliant facility that may process other products that contain these allergens
or ingredients.
1 veggie capsule
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum, seed/fruit) [Standardized to 80%
total silymarin flavonoids/ flavonoligans via UV-VIS;
58% via HPLC] 175 mg.
Other Ingredients: Veggie Capsule (Modified Cellulose, Chlorophyll [as Sodium
Copper Chlorophyllin]), Organic Rice Concentrate.
APPROVED
But Poor Labeling
CVS Health™ Milk Thistle 250
Dist. by CVS Pharmacy, Inc.
1 capsule
250 mg extract
200 mg silymarin (C)
Found
only 143 mg by HPLC (71.5% of listed amount)
[57.2% of extract]
Large capsule
For adults, take one (1) capsule three times daily, preferably with meals.
$0.13/capsule
[$0.11 based on amount listed]
[$0.15 based on amount found]
$26.99/200 capsules
No yeast, wheat, gluten, milk or milk
derivatives, lactose, sugar, preservatives, soy, artificial color, artificial
flavor, salt.
1 capsule
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum) (seed) (standardized to contain
80% Silymarin, 200 mg) 250 mg.
Other Ingredients: Gelatin (Porcine and Bovine), Dicalcium Phosphate,
Maltodextrin, Stearic Acid, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Magnesium Stearate,
Croscarmellose Sodium and Silica.
APPROVED
Jarrow Formulas® Milk Thistle
Dist. by Jarrow
Formulas®
1 veggie cap
150 mg extract
120 total flavonoids (C)
Found 101.4 mg silymarin by HPLC
[67.6% of extract]
Medium/large veggie cap
Take 1 to 3 capsules per day or as directed by your qualified healthcare
professional.
$0.08/veggie cap
[$0.13 based on amount found]
Lowest cost for silymarin among Approved products
$8.18/100 veggie caps
Suitable for vegetarians/ vegans. Gluten Free. Non GMO Certified by NSF® seal. No wheat, gluten, soybeans,
dairy, egg, fish/ shellfish, or peanuts/ tree nuts.
1 veggie cap
Milk Thistle Seed 30:1 Extract (Silybum marianum) (80% [120 mg] Total
Flavonoids) 150 mg.
Other Ingredients: Cellulose, magnesium stearate (vegetable source) and silicon
dioxide. Capsule consists of hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose.
APPROVED
But Poor Labeling
Nature's Sunshine® Milk Thistle
Dist. by Nature's Sunshine Products, Inc.
1 tablet
350 mg extract
280 mg silymarin (C)
Found
only 202 mg by HPLC (72.1% of listed amount)
[57.7% of extract]
Medium/large tablet
Take 1 tablet with a meal twice daily.
$0.51/tablet
[$0.29 based on amount listed]
[$0.40 based on amount found]
$30.50/60 tablets
Time Release.
1 tablet
Milk Thistle Seed Extract (Silybum marianum) [Silymarin 280 mg] 350 mg.
Other Ingredients: Dicalcium phosphate, cellulose, stearic acid (vegetable).
NOT APPROVED
NOW® Silymarin
Dist. by Now Foods
1/8 level tsp of powder [0.35 g]
350 mg extract
280 mg silymarin (C)
Found only
174.7 mg by HPLC (62.4% of listed amount)
[only 49.9% of extract]
Powder in container
Take 1/8 level teaspoon daily in juice or water, with food.
$0.05/0.125 level tsp
[$0.03 based on amount listed]
[$0.05 based on amount found]
$16.19/4 oz [113 g] bottle (approx. 323 servings)
Kosher. Non-GMO. Not manufactured with yeast,
wheat, gluten, soy, corn, milk, egg, fish, shellfish or tree nut ingredients.
1/8 level tsp
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum) (Fruit/Seeds) (Standardized to
280 mg Silymarin Flavonoids - equivalent 80%) 350 mg.
Other Ingredients: None.
APPROVED
But Poor Labeling
Pure Encapsulations® Silymarin
Mfd. by Pure Encapsulations
1 capsule
250 mg extract
200 mg silymarin (C)
Found
only 137.2 mg by HPLC (68.6% of listed amount)
[54.9% of extract]
Medium/large capsule
Take 1 capsule, 1-4 times daily, between meals.
$0.29/capsule
[$0.23 based on amount listed]
[$0.33 based on amount found]
$34.30/120 capsules
Gluten-Free.
1 capsule
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) extract (seed) (standardized to contain
80% silymarin) 250 mg.
Other Ingredients: Vegetarian capsule (cellulose, water).
APPROVED
But Low Strength
Trunature® [Costco] Premium Milk
Thistle
Dist. by Costco Wholesale Corporation
1 vegetarian capsule
160 mg phytosome
52 mg silybin (C)
✔
Met claim of 52 mg silybin but provides relatively small amount of
silymarin (61.2 mg by HPLC).
Medium/large vegetarian capsule
1 capsule per day. For additional liver support: 1 capsule 2-3 times per day.
$0.17/vegetarian capsule
[$0.44 based on amount found]
$19.99/120 vegetarian capsules
1 vegetarian capsule
Calcium 42 mg
No Soy. No Sugar. No Artificial Colors or Flavors. No Gluten. No Salt. No
Lactose.
1 vegetarian capsule
Calcium (dicalcium phosphate) 42 mg, Siliphos® Milk
Thistle Phytosome (Silybum marianum) extract
(seed); phospholipids (sunflower lecithin) [Silybin 52 mg] 160 mg.
Other Ingredients: Vegetarian capsule (hypromellose,
purified water), silica, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate (vegetable
grade).
NOT APPROVED
Vitamin Shoppe® Milk Thistle Extract
Dist. by Vitamin Shoppe, Inc.
1 capsule
300 mg extract
240 mg silymarin (C)
Found only
154 mg by HPLC (64.2% of listed amount)
[only 51.3% of extract]
Large capsule
Take one (1) capsule daily, preferably with a meal.
$0.11/capsule
[$0.08 based on amount listed]
[$0.12 based on amount found]
$22.90/200 capsules
Does not contain: Gluten, Sugar, Salt,
Artificial Colors or Flavors. Gluten free. Dairy free. Soy free. Nut free.
1 capsule
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum) (seed) (std. to contain 80% Silymarin
(240 mg)) 300 mg.
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, gelatin, magnesium stearate,
silicon dioxide.
Milk Thistle Extract and Powder Combination:
APPROVED
But Poor Labeling
Top Pick
Swanson® Milk Thistle
Dist. by Swanson Health Products
1 capsule
250 mg extract
250 mg powder
205 mg silymarin (C + M)ⓘ
Found
only 137.5 mg by HPLC (67% of expected amount)
[53% of extract, assuming 5 mg from powder]
Also, tested for heavy metalsⓘ,
mold & yeastⓘ
✔
Large capsule
Take one capsule two to three times per day with water.
$0.06/capsule
[$0.05 based on amount expected]
[$0.07 based on amount found]
$7.59/120 capsules
None.
1 capsule
Milk Thistle Seed Extract (Silybum marianum) (standardized to 80% silymarin)
250 mg, Milk Thistle Seed (Silybum marianum) 250 mg.
Other Ingredients: Gelatin.
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's
ingredients differ from what is listed above, it may not necessarily be of the
same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
ConsumerTips™:
What to
Consider When Buying:
Extracts vs. Seed Powder:
Dry milk thistle seed powder contains only 1.5% to about 3.0% silymarin (or 2%
when tested by HPLC according to the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP)), while
dry "extracts" are much more concentrated -- with silymarin
accounting for approximately 80% of their weight by UV-VIS but only about 58%
by HPLC. Consequently, pills made from seed powder contain relatively little
silymarin (about 10 mg per 200 mg of powder) while pills made from dry extracts
generally provide more than 100 mg of silymarin. People who prefer to use whole
herb products as opposed to concentrated extracts should be aware that much
larger doses of milk thistle will be necessary to get the same amount of
silymarin and, as found in a previous Review, may be more likely to be exposed
to contaminants, such as lead.
Be aware that "liquid extracts" are not necessarily concentrated
extracts. One liquid extract product tested by ConsumerLab
in a previous Review indicated that it was made from milk thistle
"seed" as opposed to a "seed extract." Products like this
are not concentrated -- this particular product was expected to contain only
7.5 mg of silymarin per mL (although testing showed it to actually provide less
than 2 mg).
Serving recommendations also range widely from 1 to 4 servings per day.
Other Ingredients in "Liver" Formulas:
Milk thistle is often used in "liver" formulations which include
additional ingredients. Be aware that, in most cases, these formulations (which
are typically more expensive that a straight milk thistle product) have not
been clinically tested. A common ingredient in such formulas is artichoke
extract, which may help relieve digestive pain by stimulating the gall bladder
and liver (Salem, Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2015; Holtmann, Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003).
Another is schizandra fruit extract (also spelled schisandra), for which
preliminary evidence suggests a liver benefit. Other common ingredients in
liver formulas include dandelion root extract -- a "liver tonic" in
traditional folk medicine with little supporting scientific evidence, and phyllanthus, which has been used in treating hepatitis B
but with questionable benefit.
What to Consider When Using:
The common dosage of milk thistle is 200 mg 2 to 3 times a day of an extract
standardized to 70% to 80% silymarin by UV-VIS, which is approximately 58% by
HPLC. The reason why it is taken more than once a day is the relatively short
half-life of silymarin of just 1-2 hours (Hawke, J Clin Pharmacol 2010).
Taking milk thistle extract without food may allow silymarin to be more quickly
absorbed, according to information from Floridis which
sells a form of milk thistle extract, Legalon, used
in clinical studies. Legalon is produced by the
German company, Madaus, and product information indicates
that the extract is at least 58% silymarin tested by HPLC.
For diabetes, the 200 mg is taken 3 times a day along with conventional
treatment. For cirrhosis of the liver, a daily dose of 420 mg has been used
(expected to contain about 300 to 330 mg of silymarin). For chronic active
hepatitis, 240 mg of silybinin (the major constituent
of silymarin) taken twice daily has been used. (Among the products tested in
this review, silybinin was generally found to account
for 30% to 65% of the total silymarin.) There is some evidence that
preparations containing phosphatidylcholine may increase absorption of active
ingredients of milk thistle. Phosphatidylcholine would be expected in the Trunature Premium Milk Thistle product
tested in this Review, as it contains lecithin, as source of
phosphatidylcholine.
As a liver-protectant during chemotherapy, milk thistle extract providing 80 mg
to 320 mg of silybinin per day has been used in
children, with the dosage based on weight (approximately 5.1 mg of silybinin daily per kilogram of body weight) (Ladas, Cancer 2010).
For treatment of mushroom poisoning with Amanita phalloides, 20 mg
to 50 mg of silybinin per kg of body weight has been
administered intravenously over 24 hours, divided into four infusions, each
administered over a two hour period. Intravenous silybinin,
however, is not available in the U.S.
Silymarin has a relatively short (1 to 2 hour) half-life
and low bioavailability. A short-term (7 day) study in non-cirrhotic patients
with hepatitis C showed that much higher doses of silymarin (as much at 700 mg
three times per day) could be given without causing adverse events. Plasma
levels of silymarin were dramatically increased. However, even these high doses
did not cause meaningful reductions in markers of hepatitis viral activity (Hawke, J Clin Pharmacol 2010).
Concerns and Cautions:
Milk
thistle and its extracts are generally well-tolerated but, infrequently, can
have a laxative effect and cause other gastrointestinal side-effects. Some
patients may have allergic reactions to milk thistle including itching, rash,
hives, eczema, and anaphylaxis. Allergic reactions may be more likely to occur
in patients sensitive to plants such as ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, and
daisies. Milk thistle might reduce the effectiveness of oral
contraceptives. Milk thistle may inhibit the enzyme CYP2C9, that is
involved in metabolizing (breaking down) certain drugs, thereby increasing the
levels of such drugs, including amitriptyline, diazepam, verapamil, and
warfarin. For example, approximately four weeks after taking a "liver
cleanse" supplement containing 200 mg of milk thistle, a man in his 30s
taking warfarin (36.5 mg per week) as a blood thinner experienced an increase
in his INR (a measure of blood clotting time) from 2.64 to 4.12 despite it
having been previously stable. His INR returned to its normal level one week
after stopping the supplement. The supplement contained other ingredients, none
of which are known to interact with warfarin (Lash, J Clin Pharm Ther 2019).
Milk thistle can be contaminated with yeast and mold (fungi)
which create potentially harmful toxins. These organisms are known to grow on
milk thistle if not properly dried and stored after harvest. An analysis of
milk thistle products in the U.S. (Tournas, Int J Food Microbio 2013) found that 100% of seed powders
(14 of 14 samples) and herb powders (7 of 7) were contaminated with yeast or
mold, as were 88% of whole seed products (30 of 34 samples), and 71% of cut
herb products (10 of 14). However, none of the milk thistle
supplements sold as tea bags, alcohol-based seed extracts, oil-based seed
extracts, capsules, or soft gels contained yeast or mold. A study which looked
for fungal toxins (mycotoxins) in supplements found that 28%
(9 of 32) contained about 30% to 75% of the daily tolerable intake amount. Four
of these were capsules (out of a total of 23 capsules/tablets), although all
were from the Czech Republic or Slovakia while products from other countries
(the U.S. was not included) had little or none (Veprikova, J Ag Food
Chem 2015). (In this Review, ConsumerLab.com tested any
products containing seed ingredients (such as seed powder) for yeast and mold.)
Since mycotoxins can affect the liver, it seems prudent for people with liver
disease to avoid milk thistle sold as whole seed, cut herb, or powders and to
use milk thistle supplements with caution, not taking more than the suggested
amount.
Information on this site
is provided for informational purposes only. It is not an endorsement of any
product nor is it meant to substitute for the advice provided by physicians or
other healthcare professionals. The information contained herein should not be
used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease. Consumers should
inform their healthcare providers of the dietary supplements they take.
Latest Clinical Research Updates for Milk Thistle Supplements
7/31/2021
Some milk thistle
products may be contaminated with pesticides, according to a study of more than
25 commercially available supplements. Learn more in the Quality Concerns section of our Milk
Thistle Supplements Review.
8/14/2020
Can taking milk thistle
relieve hot flashes during menopause? Learn what a new study showed in
the What It Does section
of the Milk Thistle Supplements Review. Also see our Top Pick among milk thistle supplements. (Also see
our Menopause Supplements Review for
information and reviews of products containing soy and red clover isoflavones,
black cohosh, or progesterone cream.)
10/22/2019
Milk thistle may interact
with certain drugs, as noted in a recent case report. For details see the Concerns and Cautions section
of the Milk Thistle Supplements Review. Also see our Top Picks for milk thistle.
Related CL Answers (8)