Holy Basil Supplements Review
Find the Best Holy Basil
(Tulsi) Supplements. Tests and Reviews of Popular
Holy Basil Supplements & CL's Top Pick.
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Initially Posted:
03/14/2020

Recent Reviews
·
Aloe Juices, Gels, and Supplements
Review
·
NAD Booster Supplements Review
(NAD+/NADH, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
·
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
Supplements Review
Table of Contents
Summary
·
What is holy basil? Holy basil (Ocimum
sanctum or Ocimum tenuiflorum) is a shrub in the basil family. Holy basil
is also called by its Ayurvedic name, "tulsi".
The leaves of holy basil contain compounds call triterpenes, including
oleanolic and ursolic acid, that laboratory tests
show to have anti-inflammatory, blood-sugar lowering and immune system effects.
Holy basil leaves also contain eugenol, which may have analgesic effects. In
supplements, holy basil is typically sold as a leaf powder (whole, dry crushed
leaves) or as an extract (powder or liquid) (see What It Is).
·
What does holy basil do? Preliminary clinical studies
suggest holy basil may reduce symptoms of stress and anxiety and may modestly
lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. However, the chemical
make-up of holy basil extracts and powders used in some of these studies was
not well defined, and more research is needed to confirm these findings
(see What It Does).
·
What did CL's tests of holy basil find? Most of the holy
basil supplements ConsumerLab tested failed to
contain even the minimum amount of total triterpenes
expected or claimed on the label. Amounts of triterpenes in holy basil
supplements varied widely — from as little as 0.43 mg to 34.8. mg per suggested
serving, and only 3 of the 8 products tested contained their expected amounts.
In addition, one product was found to be contaminated with lead (see What CL Found).
·
Which is the best holy basil supplement? Among the products
that passed all tests and were Approved, ConsumerLab
selected one that provided the best quality and value as its Top Pick for
Holy Basil.
·
Safety and side effects of holy basil: Holy basil may
cause nausea or diarrhea. Due to its potential blood sugar lowering effect, it
should be used with caution in people with hypoglycemia and those taking blood
sugar lowering medications. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not
take holy basil. (See Concerns and
Cautions).
What It Is:
Holy
basil (Ocimum sanctum or Ocimum tenuiflorum)
is a shrub in the basil family, thought to have originated in India. In
traditional Ayurvedic medicine, holy basil is called "tulsi,"
"The Queen of Herbs" and "the elixir of life" (Cohen, J Ayurveda Integr Med
2014).
The leaves and stems of holy basil contain a wide variety of compounds
including the triterpenes oleanolic acid and ursolic
acid as well as saponins, flavonoids, and phenols such as eugenol.
Eugenol is thought to be responsible for analgesic effects and, to some extent,
blood-sugar lowering effects (Jamshidi, Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med 2017). It comprises approximately 40%
to 70% of essential oil derived from holy basil leaves (Prakash, Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2005; Khanna, J Ethnopharmacol
2003). Ursolic acid, which is found in
other herbs such as lavender, oregano, thyme, cloves, and in apple peels, has
been shown in laboratory and animal studies to have anti-inflammatory,
tumor-inhibiting and blood-sugar lowering effects (Lee, EXCLI J 2016).
Holy basil supplements are typically sold as leaf powder (whole, dry, crushed
leaves) or as an extract (liquid or powder). Extracts may be standardized to
amounts of triterpenes (oleanolic acid and/or ursolic
acid), or, less commonly, eugenol. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has
established the identity and quality of holy basil leaf based on the weight of
these two triterpenes, which should represent at least 0.5% of the weight of
the ingredient. Although extracts would typically be expected to have a higher
concentration of these triterpenes than a leaf powder, the USP has not yet
established such a standard for holy basil leaf extract, other than it should
provide 90% to 125% of the claimed amount of
triterpenes. (Nevertheless, ConsumerLab expects
extracts to not only meet the 90% to 125% requirement, but also the minimum
requirements of leaf powders.)
Holy basil seed oil does not appear to be widely available. The seed oil
contains linoleic acid (52%), linolenic acid (17%), oleic acid (14%), palmitic
acid (12%), and stearic acid (3%) and has been shown in laboratory and animal
studies to have antibacterial and blood-sugar lowering effects (Singh, Indian J Exp Biol 2005; Pattanayak, Pharmacogn Rev 2010; Sarkar Ind, J Physiol Pharmae 1989).
What It Does:
Preliminary clinical studies suggest holy basil
may reduce symptoms of stress and anxiety and may modestly lower blood sugar
levels in people with type 2 diabetes. However, the chemical make-up of holy
basil extracts and powders used in some of these studies was not well defined,
and more research is needed to confirm these findings. In traditional Ayurvedic
medicine, holy basil, or "tulsi," is used
to boost general health, well-being and longevity and assist in dealing with
the stresses of daily life (Cohen, J Ayurveda Integr Med
2014).
Anxiety and stress
A double-blind, placebo-controlled study among 40 healthy young men found that
300 mg of holy basil leaf extract (standardized to 2.7% ursolic
acid) taken once daily (i.e., 8.1 mg of triterpenes) for one month improved
certain measures of cognition, such as reaction time and
short-term memory, but did not decrease anxiety or
levels of salivary cortisol (a "stress" hormone), compared to
placebo. One participant taking the extract experienced nausea and subsequently
discontinued supplementation (Sampath, Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2015).
In a study among 158 men and women (average age 47) who reported suffering from
three or more symptoms of stress (such as headache, fatigue,
forgetfulness, avoiding people, or sleep disturbances), a branded holy basil
leaf extract taken once daily for six weeks improved self-reported measures of
overall stress by 39% compared to placebo. None of the participants reported
any adverse effects. The extract (OciBest,
Natural Remedies Pvt. Ltd., India) was taken twice daily (400 mg with breakfast
and 800 mg with dinner — a daily total of 1,200 mg). OciBest is
standardized to contain >2.5% w/w triterpene acids (oleanolic acid and ursolic acid) (i.e., at least 30 mg of triterpenes per day)
and >0.1% w/w ociglycoside-I, >0.2% w/w rosmarinic acid (Saxena, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012).
(OciBest does not appear to be sold as a
single ingredient product in the U.S. but is one of several ingredients
in LifeExtension Adrenal Energy
Formula — not tested in this Review -- which lists 600 mg of OciBest per 2 capsule serving, to be taken
twice daily, i.e., yielding a similar amount used in the described study.)
A study among 35 men and women (average age 38) with generalized
anxiety disorder (GAD) who were not taking antidepressants or
anti-anxiety medications found that a capsule containing 500 mg of holy basil
leaf extract taken twice daily after a meal for two months reduced symptoms of
anxiety, stress and depression compared to before supplementation, but this
study did not include a control or placebo group, so it is not possible
to draw conclusions from this study. The amount of ursolic
acid and eugenol in the extract was not provided (Bhattacharyya, Nepal Med Coll J
2008).
Diabetes and lowering blood sugar
In a study among men and women with type 2 diabetes, 2.5 grams of holy basil
leaf powder added to 7 ounces of water and consumed every morning for one month
reduced fasting blood sugar and blood sugar levels after eating by 17.6% and
7.3%, respectively, compared to placebo (Agrawal, Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 1996). Another study among men and women
with type 2 diabetes reported that those who took 500 mg of holy basil
leaf in addition to the anti-diabetes drug glibenclamide
(5 mg) daily for one month had modestly greater decreases than those who took
only glibenclamide with regard to fasting blood sugar
(- 40% vs - 34%) and HbA1c ( - 30% vs. - 36%).
However, the results were not analyzed to see whether these differences were
statistically significant, so it is not possible to draw conclusions
from this study. In addition, no details were provided about the holy basil
used in the study (i.e. whether it was a powder or an
extract, how much ursolic acid and or eugenol it
contained, etc.). One 250 mg capsule of holy basil leaf was taken 30 minutes
before breakfast, and a second capsule was taken 30 minutes before dinner daily
(Somasunaram, Int J Life Sci Pharma Res 2012).
Immune system
There do not appear to be published studies on the effects of holy basil on
illnesses such as colds and flu. However, a study among 22 healthy
adults (average age 26) found that taking 300 mg of holy basil leaf extract on
an empty stomach once daily for one month increased levels of immune system
proteins (interferon-y) and cells (T-helper cells and NK-cells) compared to
placebo (Mondal, J Ethnopharmacol
2011).
Arthritis pain and inflammation
Possibly due to its purported anti-inflammatory effects and the analgesic
effects of eugenol, holy basil leaf extract has been promoted to reduce the
pain and inflammation of arthritis. While several animal studies suggest it may
decrease pain (Khanna, J Ethnopharmacol
2003; Godhwani, J Ethnopharmacol 1987), there do not appear to be
studies on the effects of holy basil in people with arthritis or other
conditions that cause pain.
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
Neither
the FDA nor any other federal or state agency routinely tests holy basil
supplements, or other dietary supplements, for quality prior to sale. Quality
issues for holy basil supplements can include the following:
·
Labeled Amount — Does the product really contain the
labeled and/or expected amounts of triterpenes (ursolic
acid and oleanolic acid).
·
Purity — Does the product contain potentially dangerous amounts of
toxic heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and arsenic, which plants may be
absorbed from the soil in which they are grown. This is of particular concern
with products containing whole holy basil powders, as opposed to extracts,
since contaminants are often removed during the extraction process.
ConsumerLab.com, as part
of its mission to independently evaluate products that affect health, wellness,
and nutrition, purchased many leading holy basil supplements sold in the U.S.
Products listing whole herbs as ingredients were tested to determine whether
they were free of unacceptable levels of lead, cadmium, arsenic and mercury.
Products were also tested to determine if they possessed the specific compounds
expected of holy basil. Holy basil products should contain ursolic
acid and oleanolic acid, compounds thought to be responsible for some it the
herb's anti-inflammatory effects. The specific amounts to be expected of
these compounds has not been well defined although a minimum has been
established by the USP and was applied by ConsumerLab.
See Testing Methods and Passing Score for
more details.
What CL Found:
ConsumerLab.com's testing revealed
problems with over half of the products selected for review.
Only three of the eight supplements ConsumerLab
selected for testing passed our tests and were Approved.
The five products that failed testing are designated as "Not
Approved" in the results table. As shown in the table and
described below, each was found to contain a much lower amount
of total triterpenes and/or ursolic acid than claimed
or expected. One of these products was also contaminated with lead. These
results were confirmed in a second, independent laboratory.
·
Best Naturals Holy Basil Extract contained just 0.66
mg of ursolic acid per Vcap
instead of its claimed 10 mg — that's just 6.6% of what is promised! It was
also low in total triterpenes -- which should have been at least 10 mg (from
the claimed ursolic acid) but totaled only 1.1 mg. As
noted in the 3rd column of the
results table, the extract was only 0.22% total triterpenes on a weight/weight
basis, failing to meet even the minimum expected amount (0.5%) for a leaf powder.
·
Herb Pharm Holy Basil liquid extract contained only 0.43 mg of
total triterpenes per dropperful instead of a minimum expected amount of 1.2 mg
— so just 37% of what was expected. The expected amount
of total triterpenes was calculated from the claimed amount of herb equivalent
for the liquid extract.
·
Bulk-Supplements.com Holy Basil, a leaf powder,
contained only 1.2 mg of total triterpenes per ˝ teaspoon (500 mg) serving,
which is just under half the expected amount of 2.5 mg for leaf powder. This
product was also discovered to be contaminated with a small, but avoidable,
amount of lead. It contained 1.22 mcg per ˝ teaspoon. If taken twice daily,
this would be a total of 2.44 mcg of lead per day. According to the FDA, on
a long-term basis adults can tolerate up to 12.5 mcg of lead daily from
their total diet and children can only tolerate about 3 mcg.
·
Oregon's Wild Harvest Holy Basil leaf powder
contained only 2.9 mg of total triterpenes per 2-capsule serving instead of the
4 mg expected from this much leaf powder.
·
Organic India Tulsi-Holy Basil, a blended leaf powder
(holy basil leaf and East Indian basil leaf) contained just 1.8 mg of total
triterpenes per 3-capsule (900 mg) serving. This is much less than 4.5 mg to 9
mg expected from this combination. East Indian basil leaf (Ocimum
gratissimum) itself is supposed to contain 1% ursolic acid (Silva, Molecules 2008), so if this combination
were mostly East Indian basil leaf, 9 mg of ursolic
acid would be expected, but only 0.9 mg was found. If it were mostly holy basil
leaf one would expect 4.5 mg of total triterpenes, but only 1.8 mg was found.
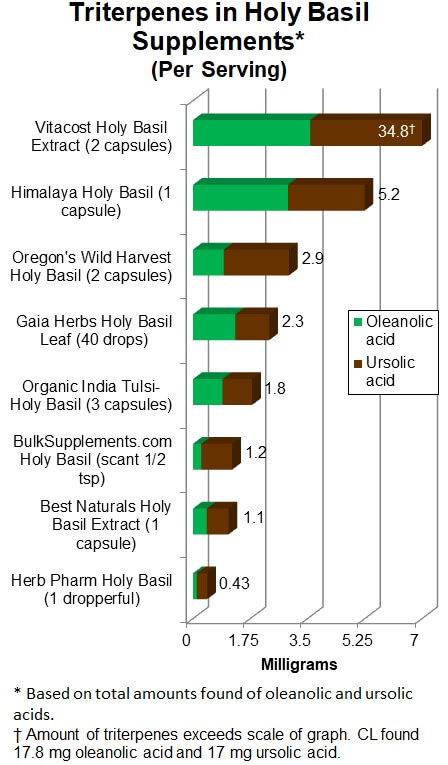
Wide range of
triterpenes, oleanolic and ursolic acids
Amounts of total triterpenes per serving varied widely across all of the
products, from as much as 34.8 mg in 2 capsules of Vitacost
Holy Basil Extract to as little as 0.43 mg per dropperful of Herb
Pharm Holy Basil (to be taken 2 to 4 times daily) as shown in the
graph below. Total triterpenes were calculated as the amounts of oleanolic acid
(shown in green) and ursolic acid (shown in brown)
combined.
As the chemical components of the holy basil powders and extracts used in
clinical studies have not always been well defined, it's difficult to say what
amounts of oleanolic acid, ursolic acid and total
triterpenes are needed for beneficial effects. However, based on our analysis
of the placebo-controlled studies presented in the What It Does section, a daily dose of
holy basil providing about 8 mg of triterpenes showed some benefit on cognition
but not anxiety, while a dose of 30 mg per day appeared to reduce symptoms of
stress.
Two of the three Approved products provided these amounts of total triterpenes
when taken at their suggested daily servings: Himalaya Holy Basil provides
10.4 mg (one capsule twice daily) and Vitacost
Holy Basil provides 34.8 mg in its suggested 2 capsule serving. The
third Approved product, Gaia Herbs Holy Basil Leaf, comes close at
6.9 mg from its suggested daily serving of 40 drops (added to water) taken three
times daily.
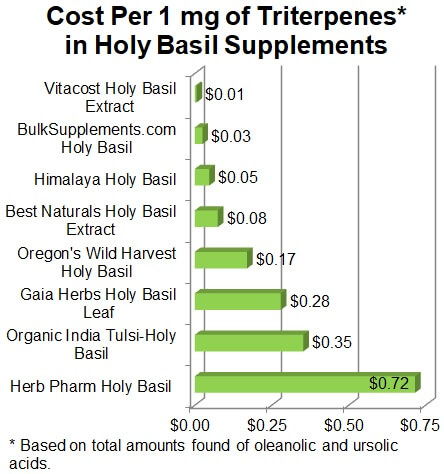
Cost
As shown in the graph below, the cost to get 1 mg of triterpenes ranged among
products from as little as 1 cent from Vitacost
Holy Basil Extract to as much as 72 cents from Herb Pharm Holy
Basil (which was Not Approved).
Top Pick:
ConsumerLab's Top Pick among holy
basil supplements is Vitacost
Holy Basil Extract. It provides 34.8 mg of total triterpenes (17.8 mg
oleanolic acid and 17 mg ursolic acid) per 2-capsule
serving for 20 cents.
Himalaya Holy Basil is another good option, providing 10.4 mg of
triterpenes from one capsule taken twice daily, but it is considerably more
expensive (50 cents per day) for a lower amount of
triterpenes. It is a combination of two types of extracts and a leaf powder, so
may provide a broad range of compounds.
If you prefer a liquid, Gaia Herbs Holy Basil Leaf Extract provides
6.9 mg of triterpenes in a daily serving (40 drops or 1.33 ml three times
daily) but is much more expensive at 65 cents per serving and $1.95 per day.
Test Results by Product:
Listed
below are the test results for eight holy basil supplements selected for
testing by ConsumerLab. They are listed
alphabetically within three categories: 1) extracts, 2) leaf powders, and 3)
extract/leaf powder combinations. Shown for each product is the claimed amount
of holy basil extract or leaf powder, the serving size recommended on the
label, the amounts of total triterpenes as well as ursolic
and oleanolic acids found in testing, and whether or not the product passed
heavy metal testing. Products listed as "Approved" met their label
claims and ConsumerLab.com's quality criteria
(see Passing Score). Those
that did not are listed as "Not Approved" with an explanation of the
problem found. Price comparisons are in the fourth column, special features per
daily serving and pill size are listed in the fifth column, and the full list
of ingredients is in last column.
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of HOLY BASIL SUPPLEMENTS
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Product Name
(Suggested Serving on Label)
Suggested Serving and Claimed Amounts of Holy
Basil and Triterpenesⓘ
Directions
TEST RESULTS:
Plant Compounds Per Suggested Servingⓘ
Heavy Metalsⓘ
Cost per Serving
[Cost per 1 mg Total Triterpenes Found]
Price & Sizeⓘ
Notable Features
Full List of Ingredients Per Serving
Holy Basil Extracts:
NOT APPROVED
Best Naturals® Holy Basil Extract
Dist. by Best Naturals
1 Vcap
500 mg extract
10 mg ursolic acid
✗
Take one (1) capsule one to two times daily, preferably with food or as
directed by your qualified healthcare professional.
1 Vcap
Found:
Total
triterpenes: 1.1 mg (Expected at least 10 mg based on claimed ursolic acid. Only 0.22% wt/wt of extractⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 0.42 mg
Ursolic acid: 0.66 mg (only 6.6% of listed amount)
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.08/Vcap
[$0.08]
$9.79/120 Vcaps
Large Vcap
No Artificial Color, Flavor or Sweetener, No
Preservatives, No Sugar, No Starch, No Milk, No Lactose, No Soy, No Gluten, No
Wheat, No Yeast, No Fish, Sodium Free.
1 Vcap
Holy Basil Extract (Tulsi Extract) (Leaves (Ocimum Tenuiflorum)
(Standardized to min. 2% Ursolic Acid) 500 mg.
Other Ingredients: Vegetarian Capsule, Silica, Vegetable Stearate.
APPROVED
Gaia® Herbs Holy Basil Leaf
Dist. by Gaia Herbs, Inc.
40 drops [1.33 ml]
1.33 ml extract (equal to 442.9 mg of herb)
Adults take 30-40 drops in a small amount of water 3 times daily between meals.
40 drops [1.33 ml]
Found:
Total triterpenes: 2.3 mg (0.7% wt/wt of claimed herbⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 1.3 mg
Ursolic acid: 1 mg
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.65/40 drops
[$0.28]
$14.99/1 fl oz [30 ml] bottle (approx. 23 servings)
Liquid from bottle
USDA Organic seal.
40 drops
Organic Holy Basil (Ocimum sanctum)
leaf extract 1.33 ml.
Other Ingredients: Organic USP (70-80%) and water. 333 mg/ml Herb Equivalency.
NOT APPROVED
Herb Pharm® Holy Basil
Dist. by Herb Pharm
1 dropperful [0.7 ml]
612 mg extract (equal to 233 mg of herb)
Add 1 full squeeze of the dropper bulb to 2 oz. of water or juice, 2 to 4 times
per day.
1 dropperful [0.7 ml]
Found:
Total
triterpenes: 0.43 mg (Expected 1.2 mg. Only 0.19% wt/wt of claimed herbⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 0.11 mg
Ursolic acid: 0.32 mg
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.31/dropperful
[$0.72]
$13.05/1 fl oz [30 ml] bottle (approx. 42 servings)
Liquid from bottle
USDA Organic seal. Gluten-Free.
1 dropperful
Holy Basil herb [(Ocimum tenuiflorum) extract 612 mg].
Other Ingredients: Certified organic cane alcohol (91-81%) & distilled
water. Extraction rate 233 mg herb per 0.7 ml.
APPROVED
Top Pick
Vitacost Holy Basil Extract
Dist. by Vitacost.com
2 capsules
800 mg extract
16 mg ursolic acid
✔
Take 2 capsules daily with food or as directed by a healthcare professional.
2 capsules
Found:
Total triterpenes: 34.8 mg (4.4% wt/wt of extractⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 17.8 mg
Ursolic acid: 17 mg
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.20/2 capsules
[$0.01]
Lowest cost for triterpenes from holy basil
$18.19/180 capsules
Large capsule
Free of: Milk, Eggs, Peanuts, Tree Nuts,
Crustacean Shellfish, Fish, Soy, Gluten, Titanium Dioxide. Vegetarian.
2 capsules
Holy Basil Extract (leaf) [standardized to 2% ursolic
acid (16 mg)] 800 mg.
Other Ingredients: Maltodextrin, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose,
microcrystalline cellulose, vegetable stearic acid and vegetable magnesium
stearate.
Holy Basil Leaf Powders (i.e.,
whole leaf, not extract):
NOT APPROVED
Bulk-
Supplements.com Holy Basil
Dist. by Bulk-
Supplements.com
Scant 1/2 tsp [500 g]
500 mg leaf powder
Take 500 mg (scan 1/2 tsp) once or twice daily, or as directed by a physician.
Scant 1/2 tsp [500 g]
Found:
Total
triterpenes: 1.2 mg (Expected 2.5 mg. Only 0.24% wt/wt of leaf powderⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 0.25 mg
Ursolic acid: 0.94 mg
Heavy
metals:
Found 1.22 mcg to 2.44 mcg lead per daily serving (2.44 mcg per g)
$0.03/scant 1/2 tsp
[$0.03]
$14.96/8.82 oz [250 g] pouch (approx. 500 servings)
Powder in container
Free of: Sugar, soy, dairy, yeast, gluten or
additives.
Scant 1/2 tsp
Holy Basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum)
(leaf) 500 mg.
Other Ingredients: None.
NOT APPROVED
Oregon's Wild Harvest Holy Basil
Mfd. by Oregon's Wild Harvest
2 capsules
800 mg leaf powder
Take two capsules daily or as directed by your healthcare professional.
2 capsules
Found:
Total
triterpenes: 2.9 mg (Expected 4 mg. Only 0.37% wt/wt of leaf powderⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 0.94 mg
Ursolic acid: 2 mg
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.50/2 capsules
[$0.17]
$14.96/60 capsules
Large capsule
Verified Non-GMO Ingredients. Free from: Dairy,
wheat, peanuts, soy, gluten and corn allergens.
2 capsules
Organic Holy Basil leaf (Ocimum sanctum)
800 mg.
Other Ingredients: Non-GMO bovine gelatin capsule and nothing else.
NOT APPROVED
Organic India™ Tulsi-Holy
Basil
Dist. by Organic India USA
3 capsules
900 mg leaf powder blend (holy basil leaf and East Indian basil leaf powders)
3 capsules once daily with food and water.
3 capsules
Found:
Total
Triterpenes: 1.8 mg (Expected at least 4.5 to 9 mg depending on mix of basil
leaf in blendⓘ.
Only 0.2% wt/wt of total
leaf powder blendⓘ)
Oleanolic Acid: 0.9 mg
Ursolic Acid: 0.9 mg (Expected at least 4.5 to 9 mg depending on mix of
basil leaf in blendⓘ)
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.64/3 capsules
[$0.35]
$19.12/90 veg caps
Large veg cap
Kosher. Non GMO Project
Verified seal. USDA Organic seal. Vegan. Vegetarian. Gluten Free.
3 capsules
Proprietary Organic Blend [Holy Basil leaf (Ocimum
sanctum) (Krishna Tulsi and Rama varieties), East
Indian Basil leaf (Ocimum gratissimum) (Vana Tulsi
variety)] 900 mg.
Other Ingredients: Organic Vegetable Pullulan Capsules.
Holy Basil Extract and
Leaf Powder Combination Product:
APPROVED
Himalaya® Holy Basil
Dist. by The Himalaya Drug Company
1 capsule
160 mg extract
60 mg supercritical CO2 extract
500 mg leaf powder
Adults take 1 capsule twice daily before meals.Found:
1 capsule
Found:
Total triterpenes: 5.2 mg (0.73% wt/wt of all forms of holy basilⓘ)
Oleanolic acid: 2.9 mg
Ursolic acid: 2.3 mg
Heavy metals: Pass
$0.25/capsule
[$0.05]
$14.99/60 vegetarian capsules
Large vegetarian capsule
Non GMO Project Verified seal. Gluten
Free. Vegan Friendly. No Wheat. No Corn. No Soy. No Dairy. No ingredients of
animal origin.
1 capsule
Organic holy basil powder (leaf) (0.4% Ursolic acid
and Oleanolic acid, 2.0 mg) 500 mg, Organic holy basil extract (leaf) 160 mg,
Organic holy basil supercritical CO2 extract (leaf) (Ocimum
tenuiflorum) (2.5% Ursolic
acid and Oleanolic acid, 1.5 mg) 60 mg.
Other Ingredients: Plant based cellulose (capsule).
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's
ingredients differ from what is listed above, it may not necessarily be of the
same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
ConsumerTips™:
Dosage
Unfortunately, few studies of holy basil have provided detailed information
about chemical composition of the products. In general, holy basil leaf powders
(crushed and powdered leaf) have been taken in daily doses of about 2,500 mg,
and extracts (as powders or liquids) in daily doses ranging from 250 mg to
1,200 mg.
Below are dosages based on available clinical trials, with details provided
where possible.
For generalized anxiety — 500 mg of holy basil leaf extract taken
twice daily after a meal (Bhattacharyya, Nepal Med Coll J
2008). (This size serving should provide at least 2.5 mg of
triterpenes twice daily.)
For stress — 1,200 mg of holy basil extract (standardized to
contain >0.1% w/w ociglycoside-I, >0.2% w/w rosmarinic acid, and >2.5% w/w triterpene acids
(oleanolic acid and ursolic acid) taken as 400 mg
with breakfast and 800 mg with dinner (a daily total of 1,200 mg) may improve
symptoms such as headache, fatigue, and forgetfulness (Saxena, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012).
(This size serving should provide 30 mg of triterpenes.)
For lowering blood sugar — 250 mg of holy basil leaf/ leaf powder
taken one to two times daily (30 minutes before breakfast and/or dinner) may
reduce fasting blood sugar, blood sugar levels after eating and/or HbA1c in
people with type 2 diabetes — although this was not a placebo-controlled study
(Agrawal, Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 1996; Somasunaram, Int J
Life Sci Pharma Res 2012).
Consult your health care provider if taking insulin or other anti-diabetes
drugs before using so that effects/dosage can be monitored. (This size serving
should provide at least 1.25 mg to 3 mg of triterpenes.)
For immune system health — In healthy adults, 300 mg of holy basil
leaf extract on an empty stomach once daily for one month may increase blood
levels of some immune system proteins — although this was not a
placebo-controlled study (Mondal, J Ethnopharmacol
2011). (This size serving should provide at least 1.5 mg of
triterpenes.)
How to Take
For most uses, holy basil is typically taken with food, possibly to reduce the
risk of nausea. When taken to reduce fasting blood sugar and/or HbA1c, it has
been taken 30 minutes before a meal.
Storage
Holy basil supplements should be stored in a cool, dry place.
Concerns and Cautions:
In
small, short-term clinical trials (lasting up to three months), few side
effects have been reported with the use of holy basil, but occasionally, holy
basil leaf may cause nausea or loose stools (Mondal, J Ethnopharmacol
2011; Jamshidi, Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med 2017). Studies are needed to determine
the long-term safety of holy basil leaf and its extract.
Preliminary studies in animals suggest that high doses of holy basil leaf
extract may interfere with implantation of embryos or otherwise disrupt
pregnancy (Khanna, Indian J Exp Biol 1986). To be
safe, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not use holy basil
leaf extract.
Be aware that, in animal studies, holy basil leaf extract has been shown to
decrease blood levels of thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) (Panda, Pharmacol Res 1998).
It is not known if it has this effect in people.
Holy basil seed oil has been shown to have anti-platelet effects and to lower
blood pressure in animals (Singh, J Ethnopharmacol
2001); however, holy basil leaf extract did not lower blood
pressure in a study among healthy adults (Mondal, J Ethnopharmacol
2011).
Eugenol found in holy basil may be toxic to the liver (Thompson, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1998). However, there do not appear to
be reports of liver toxicity with holy basil. Eugenol-related liver toxicity
has been reported in infants and children given clove oil, which contains
higher concentrations of eugenol (70 — 90%) than holy basil extract (Hartnoll, Archives of Disease in Childhood 1993, Eisen, J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 2004). Interestingly, a study in animals
found that holy basil leaf extract (% eugenol not provided) seemed to have a
protective effect on paracetamol (Tylenol)-induced liver damage (Chattopadhy, Ind J Pharmacol 1992).
Acute allergic and skin reactions to eugenol oil when used
topically or as an analgesic during dental procedures have been reported (Barkin, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984; Tammannavar, BMJ Case
Rep 2013).
Related CL Answers (1)