Digestive Enzyme Supplements Review
Big Differences in
Strength Found Among Digestive Enzyme Supplements. CL Tests Reveal Which Are
Best.
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Last Updated![]() : 09/21/2021 | Initially Posted:
05/04/2019Latest Update: Enzyme Supplements for Eye Floaters?
: 09/21/2021 | Initially Posted:
05/04/2019Latest Update: Enzyme Supplements for Eye Floaters?
Recent Reviews
·
Aloe Juices, Gels, and Supplements
Review
·
NAD Booster Supplements Review
(NAD+/NADH, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
·
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
Supplements Review
Table of Contents
Summary
·
What are digestive enzyme supplements? Digestive enzyme
supplements can help you digest specific foods when you do not naturally
produce enough enzymes. (See "What They Are" for a list of
enzymes and the foods they break down.) They may also have other beneficial
effects.
·
How to choose a digestive enzyme supplement: Choose a digestive
enzyme supplement that lists enzyme activity units (such as PU, HUT, FIP,
etc.), not just the amount of enzyme (such as milligrams) since that won't tell
you how potent the enzyme is (See "What They Do"). Also, check that
ConsumerLab.com or another reputable independent 3rd party has verified the
enzyme activity. As found in this Review, some products don't provide what they
list (See "What CL Found")
·
Best digestive enzyme supplements? See our Top Pick among
products "Approved" by ConsumerLab.com.
·
Digestive enzyme supplements safety and side effects: Digestive enzymes
are generally well-tolerated but people with allergies to a specific enzyme
source, certain medical conditions, or who take medications such as
blood-thinners or diabetes drugs may need to avoid specific enzymes. Rarely,
nausea and allergic reactions have been reported with the use of lactase (See
"Concerns and Cautions").
What They Are:
Digestive
enzymes break down specific parts of food (such as fats or carbohydrates) to
make them available for absorption. These enzymes are typically named by the
part of the food which they break down, as shown in the table below. For
example, proteases break down protein, lipases break down lipids (fats),
lactase breaks down lactose, alpha-galactosidase breaks down complex sugars (galactosides) in foods like beans and broccoli and
cellulase breaks down parts of cell walls in plant-based foods. Some enzyme
materials are named for their source. For example, papain and bromelain, which
contain proteases, are, respectively, from papaya and pineapple (Bromeliaceae). Pancreatin, which is produced in the
pancreas, is a combination of amylase, lipase and protease enzymes.
The body naturally secretes enzymes throughout the gastrointestinal tract
during digestion. Nutrients that we can't absorb (such as plant fiber) are
often fermented by the bacteria in our guts, creating gas which can lead to
abdominal discomfort. Most of the supplements tested in this review are
digestive enzyme blends, which contain a combination of enzymes to help break
down multiple components of a meal. These enzymes may be animal-derived (such
as pancreatin from pigs or cows) or from plants (such as bromelain and papain),
bacteria, or fungi.
Be aware that enzymes are not only specific to the compounds they break down,
but they have optimal activity under specific conditions. Consequently, many
different types of enzyme assays are used to measure their activity, resulting
in a plethora of units of measurement — as indicated in the table below. For
more about what to look for on an enzyme supplement label, see the ConsumerTips™ section.
|
Enzyme |
Breaks down: |
Unit to Look For on
Label |
Effective Serving Size |
|
Protease (peptidase, dipeptidyl-peptidase, nattokinase, papain, bromelain) |
Protein |
HUT, DPP, PU, PC, SAP, FIP, USP (if referring
to pancreatin), GDU |
Bovine or porcine protease: 15,625 - 150,000 USP per day1 |
|
Lipase |
Fat (in butter, rich sauces) |
FIP, LU, USP (if referring to pancreatin) |
Bovine or porcine derived lipase: 5,000 - 40,000 USP1 |
|
Amylase, glucoamylase |
Starch (in beans, lentils, grains, bread,
corn) |
DU, AGU, USP (if referring to pancreatin) |
Bovine or porcine derived amylase: 16,600 - 149,400 USP1 |
|
Invertase |
Table sugar (sucrose) |
SU, INVU |
(4,200 SU or 3,000 INVU per day) |
|
Alpha-galactosidase |
Complex sugars (found in grains, beans, nuts
and certain vegetables like broccoli and cabbage) |
GalU |
240 — 1,200 GalU |
|
Lactase (See Review of Lactase Enzyme
Supplements) |
Milk sugar (lactose) |
ALU |
3,000 — 6,000 ALU |
|
Cellulase, hemicellulase |
Plant fiber (in fruits and vegetables) |
CU, HCU |
(110,000 CU or 45,000 HCU per day) |
|
Pectinase |
Plant fiber |
PGU |
(180 endo-PG per day) |
|
Xylanase |
Plant fiber |
XU |
(3,300 XU per day) |
|
Beta-glucanase |
Plant fiber |
BGU |
(210 BGU per day) |
|
Phytase |
Phytic acid (in wheat and other grains, beans,
nuts, seed oils) |
FTE, FTU |
20 - 75 FTU |
1Effective dose or maximum dose in activity
units established by Health Canada
What They Do:
For people with medical conditions that prevent them from
normally producing certain digestive enzymes, taking medication or supplements
that provide digestive enzymes can certainly help. For example, people
with pancreatic disease or impaired pancreatic function due
to cystic fibrosis do not produce sufficient pancreatin. In
these cases, animal-derived pancreatin is helpful, particularly for the
digestion of fats. (Be aware that some supplements include a combination of
amylase, lipase and protease enzymes from plant or fungal sources and refer to
this as "pancreatin alternative "or "vegetarian pancreatin
analog.")
Some studies have found that the body's own production of pancreatic enzymes
such as amylase, lipase and chymotrypsin may decrease with age; however, the
evidence for this is mixed (Keller, Gut 2005).
Digestive discomfort
Some, but not all, studies have shown that digestive enzymes can improve digestive
symptoms in people without pancreatic disease. For example, a small
clinical study of healthy men and women found that taking one capsule of a
prescription animal-derived pancreatin containing lipase (10,000 USP), amylase
(33,200 USP), and protease (37,500 USP) enzymes (Creon, Solvay
Pharmaceutical) immediately before a high fat, high calorie meal, and two more
capsules immediately after the meal, significantly reduced bloating, gas and
fullness compared to placebo (Suarez, Dig Dis Sci 1999). On the other hand,
another study found that pancreatic enzymes did not improve symptoms of
indigestion (Kleveland, Scand J Gastroenterol 1990). More recently, a small study in India by the makers of
a branded enzyme blend (DigeZyme, Sabinsa/Sami Labs) found that taking a 50 mg capsule
of DigeZyme three times daily for
two months significantly reduced the severity of self-reported and
physician-assessed symptoms such as stomach pain, indigestion, heartburn,
burping and nausea compared to placebo in healthy men and women with functional
dyspepsia (indigestion) who consumed their regular diet. No adverse
events or changes in blood pressure, heart rate, blood cell counts or liver
enzymes were reported in those who took the enzyme blend (Majeed, J Med Food 2018). DigeZyme, which has also been found to reduce pain after exercise, provides 1,200 DU
alpha-amylase, 55 CU cellulose, 10 FIP lipase, 200 ALU lactase and 300 PC
protease per 50 mg capsule and is typically taken after meals.
Lactase has been shown to improve the digestion of lactose (milk sugar) and
decrease the symptoms of lactose intolerance such as gas,
bloating and diarrhea (Gao, Nagoya J Med 2002; Lami,
Am J Gastr 1988). A dose
between 3,000 and 6,000 ALU can help those with lactose intolerance digest
about 20 grams of lactose from milk (Lin, Dig Dis Sci 1993). See the Review of Lactase Enzymes and
Lactose-Free Milks for more information and our tests and
reviews of products.
A small clinical study found that a dose of 1,200 GalU of alpha-galactosidase taken during a meal rich in
fermentable carbohydrates (420 grams of cooked beans)
significantly reduced the severity of flatulence compared to placebo (Di Stefano, Dig Dis Sci 2007). Measures of
bloating, abdominal discomfort and pain were also lower in the group taking
alpha-galactosidase but did not reach statistical significance. A clinical
study of a branded supplement (Beano) containing alpha-galactosidase
derived from Aspergillus niger found
that a lower dose of alpha-galactosidase (240 GalU
from 8 drops of the supplement) also significantly reduced flatulence compared
to placebo (Ganiats, J Fam Pract 1994). Another small study of men and
women with type 2 diabetes (average age 56) who were taking the
glucose-lowering drug acarbose found that 15 drops of Beano taken
with a test meal significantly reduced self-reported measures of flatulence
compared to eating a test meal without the enzyme supplement (Lettieri, Clin Ther 1998).
However, the supplement also appeared to reduce the effectiveness of acarbose
(See Cautions and Concerns for more about
this).
A study among 52 children (average age 8) showed that
taking alpha-galactosidase derived from Aspergillus niger (Sinaire, Promefarm) three
times daily at the start of a meal for two weeks reduced the percentage
of children with flatulence from 59% to 19%, which was
significant compared to the placebo group, which showed no improvement. Also,
children taking alpha-galactosidase experienced fewer days of bloating during
the study compared to placebo (5.4 days vs. 3.4 days, respectively). However,
there was no significant improvement in abdominal distension, abdominal spasms,
or daily bowel movements compared to placebo. The dose given was based on
weight: four drops for children weighing less than 20 kg (44 lbs), 8 drops for children weighing 20 to 40 kg (44 to 88 lbs), or one tablet for children weighing more than 40 kg
(88 lbs) (Di Nardo, BMC Gastroenterol
2013).
A very small clinical study found that 160 mg of a patented enzyme blend
of carbohydrases derived from Aspergillus
niger and Aspergillus oryzae and containing amylase, cellulase and hemicellulase (Carbogen, Triarco
Industries) taken with a meal replacement bar (providing approximately 50 grams
of carbohydrate) significantly increased glucose levels compared
to ingestion of the meal replacement bar without the enzyme, which could be
useful for athletes during training or competition when they need to quickly
replenish glucose (Frank, Int J Sport Nutr Excer Metabol
2002).
Supplementation with bromelain was reported to decrease
diarrhea and other symptoms in two women with ulcerative colitis who
were taking medication but still experiencing significant symptoms, (Kane, Ann Intern Med 2000) — although dosage
and enzyme activity were not described. There is one report of papain
supplementation (one 1,800 mg enteric coated tablet taken with each meal)
improving nutrient absorption and eliminating loose stools in a patient
with celiac disease (Messer, Lancet 1976).
If you feel that you are having trouble digesting particular foods, it may be
best to choose a supplement that provides an enzyme or enzymes specific to the
food causing your digestive symptoms. For example, if you find you feel too
full or have gas or bloating after a high-fat meal, choose a supplement with
higher lipase activity. If protein seems to cause symptoms, choose a supplement
with more protease activity.
Nutrient absorption
In addition to reducing digestive discomfort, by breaking down foods into
absorbable nutrients, enzymes increase your absorption of
nutrients in foods.
Phytates, a component in many grains, beans, nuts and certain potatoes, can
inhibit the absorption of minerals like iron and zinc. A
review of clinical studies found that a dose between 20 and 320 FTU
significantly improved iron absorption from consumption of flour (100 grams) (Troesch, Food Nutr Bull 2013).
Preliminary studies with a product containing lipase, amylase, protease,
cellulase and lactase derived from Aspergillus niger and
bromelain (AbsorbAid, Nature's Sources)
suggest that it may reduce stool frequency and water content in patients
with short bowel syndrome and that one teaspoon of AbsorbAid added four times daily to an enteral
feeding solution given to elderly nursing home patients increased
protein absorption compared to giving the same solution without the enzyme
blend (Glade, Nutrition 2001). According to its
label, AbsorbAid contains lipase 381
FIP, amylase 2772 SKB/DU, protease (from bromelain) 12 GDU, cellulase 99 CU,
and lactase 300 ALU per two-capsule serving; however, it's not known whether
the same formulation with the same activity units were used in the studies
above.
A small clinical trial found that the addition of 2.5 to 5 grams (activity
units not identified) of a patented blend of proteases derived from Aspergillus
niger and Aspergillus oryzae (Aminogen,
Triarco Industries) taken with 50 grams of whey
protein concentrate significantly increased serum amino acid
levels in young healthy men compared to the same amount of whey
protein ingested without added proteases (Oben, J Int Soc Sports
Nutr 2008).
Inflammation/muscle pain/bruising
Proteases, like bromelain, have been promoted to reduce inflammation or pain in
muscles and joints, although the evidence for this is mixed and far from
convincing.
Osteoarthritis
A 3 month clinical study of 400 mg bromelain taken twice daily found no benefit
in moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the knee compared to placebo (Brien, QJM 2006). However, a study of an
enteric coated combination product, Wobenzym (Mucos Pharma), found that taking two tablets 3 times daily
on an empty stomach for 3 months significantly reduced pain in men and women
with knee osteoarthritis compared to placebo. This treatment
also worked as well as 150 mg of diclofenac sodium (a prescription NSAID) to
reduce pain, but only diclofenac produced a significant improvement in
stiffness and joint function, although patients taking Wobenzym reported
less heartburn, stomach pain and nausea (Bolten, Arthritis 2014).
The six tablets of Wobenzym provided
540 mg bromelain, 288 mg trypsin (from porcine or bovine pancreas) - units of
enzyme activity not listed - and 600 mg rutoside
trihydrate (which is not an enzyme). A study in Germany among 90 men and women
(average age 52) with osteoarthritis of the hip found that the
same daily dose of the same formula (sold as Germany as Phlogenzym) taken for six weeks reduced pain and
stiffness, and improved function just as well as a daily dose of diclofenac
sodium (100 gm). Both treatments had similar tolerability, with the most common
side effect reported for each being gastrointestinal complaints (Klein, Clin Exp Rheumatol 2006).
One weakness of this study, however, was the lack of a placebo control.
Muscle pain
There have been mixed results with proteases for delayed onset muscle
pain. One study found no decrease in muscle pain when 300 mg of bromelain
was taken 3 times daily following weight lifting exercises (Stone Clin J Sport Med 2002). Interestingly,
in this study, ibuprofen also had no effect on muscle pain. However, a small
study found that supplementation with two protease tablets (each providing 325
mg pancreatic enzymes, 75 mg trypsin, 50 mg papain, 50 mg bromelain, 10 mg
amylase, 10 mg lipase, 10 mg lysozyme, 2 mg chymotrypsin — activity units not
given) (Enzymatic Therapy Corporation) taken four times a day 1 day before a
downhill running test and for 3 days after the running test, significantly
reduced self-reported soreness in young healthy men compared to placebo (Miller, J Sport Sci 2003). The supplement was
taken on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before a meal, with an 8 oz.
glass of water. Another small study investigating the
effects of a branded enzyme blend (DigeZyme,
Sami Labs) in healthy men found those who took one capsule (providing 1,200 DU
alpha-amylase, 55 CU cellulose, 10 FIP lipase, 200 ALU lactase and 300 PC
protease) three times daily, one day before a treadmill running test and for
two days after the running test, significantly reduced self-reported pain
and tenderness 3 days after the test, compared to placebo (Vuppala, Sports Nutr Ther 2016). No adverse events were noticed
in the study.
Protease enzymes have also been proposed for reducing inflammation in a number
of other conditions such as sinusitis, recovery from surgery and
bruising (Ryan, Headache 1967; Zatuchni, Obstet Gynecol 1967; Blonstein,
Practitioner 1969).
Blood pressure lowering
In men and women with untreated high systolic blood pressure (130 to 159 mmHg)
one capsule containing 2,000 FU nattokinase taken
daily for 8 weeks was shown to reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure, by
5.55 mmHg and 2.84 mmHg, respectively (Kim, Hypertens
Res 2008).
Eye floaters
Eye floaters — the small specs or lines that sometimes appear to float in one's
field of vision — are typically caused by tiny fibers of collagen or clumps of
cells that become loose within the gel-like portion of the eye (i.e., the
vitreous). A study in Taiwan among 160 adults (average age 48) with eye
floaters for at least 3 months showed that taking one, two or three capsules
each containing 190 mg of bromelain, 95 mg of papain, and 95 mg of ficin daily
for 3 months eliminated eye floaters (assessed by indirect ophthalmoscopy) in
65%, 70% and 75% of the participants, respectively, compared to only 5% of
those in a placebo group. According to the researchers, the enzymes promoted
the breakdown and absorption of the substances causing the eye floaters (Takeuchi, Appl Sci 2020). However, the
researchers did not test to confirm that the enzymes were absorbed into the
vitreous of the eye, and there was no mention of enzymatic activity levels of
the enzymes in the capsules. There was also no significant improvement in best
corrected visual acuity.
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
Neither
the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) nor any other federal or state agency
routinely tests supplements for quality prior to sale. In order to help consumers identify products of better quality,
ConsumerLab.com purchased and tested digestive supplements to determine whether
they contained their labeled amount of enzyme activity for amylase, lipase, and
protease. As the FDA only requires supplements to list the amounts of enzyme
ingredients, for products listing only amounts and not enzyme activity,
activity levels were determined by ConsumerLab.com. Non-chewable tablets were
tested for their ability to properly break apart (disintegrate) in solution.
Products were also tested for potential contamination with lead, cadmium, and
arsenic if they contained whole herb and/or 250 mg of minerals per daily
serving. See How Products Were Evaluated for
more information on testing.
What CL Found:
Our tests of enzyme products showed that most provide their
listed activities of key enzymes and that these activities range enormously
from product to product. Eight products that CL selected for testing were
Approved for their quality, as were three products tested though ConsumerLab.com's voluntary Quality Certification Program.
The one product that failed to pass our tests was ZenWise Health Daily Digestive Enzymes With
Prebiotics + Probiotics. Despite listing "lipase" as the second
of 10 enzymes in its "Advanced Enzyme System," no quantifiable lipase
activity was found. In addition, relative to other products it provided little
activity for amylase (429 DU vs. 1,693—24,000 DU) and protease (1,166 HUT while
most provided 10,000-100,000 HUT). It did, however, provide one of the highest
levels of bromelain and papain activity (1,014,225 PU).
Enzyme Activities:
The enzyme product that you choose should relate to the types of enzyme
activities you desire. The graphs below compare the products on their
activities in digesting specific types of nutrients found in foods:
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
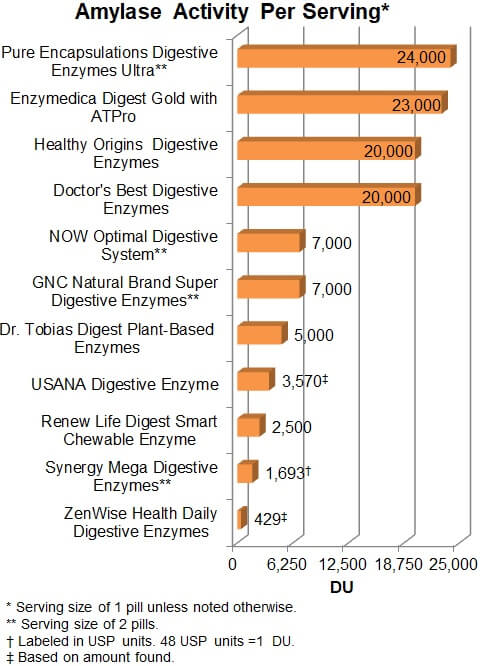
Carbohydrate digestion - Amylase activity
The digestion of carbohydrates is by the enzyme amylase and its activity can be
measured in DU. As shown below, the greatest amount of amylase activity was
24,000 DU with Pure Encapsulations Digestive Enzymes Ultra (at
the suggested 2 capsules per meal). This is in the known range of desirable
activity for a meal rich in carbohydrates and below the tolerable limit of
34,000 DU per dose, 150,000 DU per day. Enzymedica, Healthy
Origins, and Doctor's Best also provide significant doses.
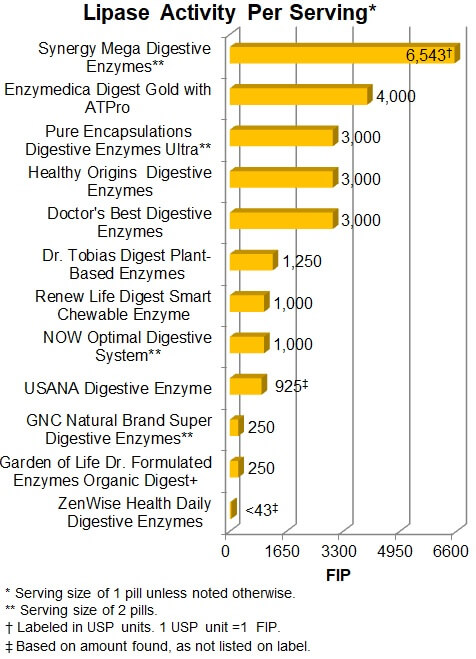
The digestion of fats and oils is by the enzyme lipase and its activity can be
measured in FIP. As shown below, the greatest amount of lipase activity was
6,543 FIP with Synergy Mega Digestive Enzymes (at the
suggested 2 capsules per meal). This is in lower end of the range of desirable
activity (5,000 FIP - and up) for a meal rich in fats and below the tolerable
limit of 11,880 FIP per dose, 45,000 FIP per day. The next most active products
for amylase activity were among those noted above as being most active for
lipase -- Enzymedica, Pure
Encapsulations, Healthy Origins, and Doctor's Best —
ranging from 4,000 FIP down to 3,000 FIP.
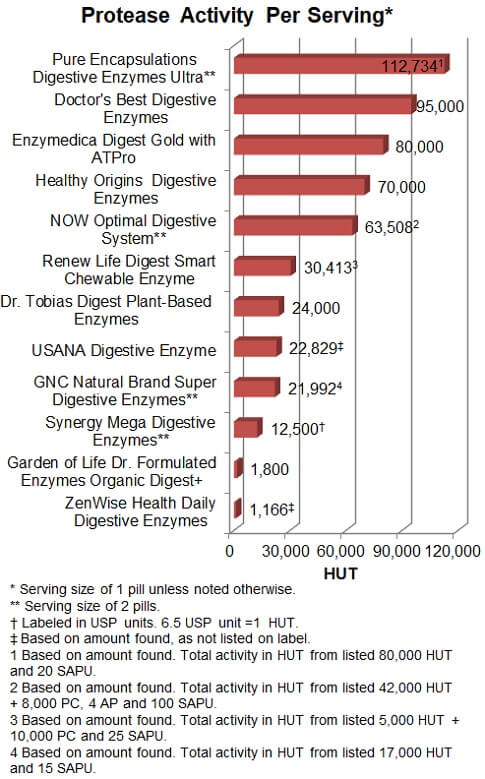
Protein digestion - Protease activity
The digestion of proteins is by protease enzymes and can be measured in HUT. As
shown below, the greatest amount of protease activity was 112,734 HUT with Pure Encapsulations (at the
suggested 2 capsules per meal) and results from a combination of proteases. It
lists protease (60,000 HUT), protease 6.0 (20,000 HUT), and protease 3.0 (20
SAPU). The numeric symbols indicate the pH at which the protease is most
active, such that protease 3.0 is likely more active in the stomach which has a
low pH (very acidic), while protease 6.0 is more active in the intestine
(mildly acidic). The HUT assay is conducted at a moderate pH of 4.5 — in
between the two. Pure Encapsulations' protease activity seems
to be below the desirable activity (about 500,000 HUT) for a meal rich in
protein, although it is likely quite safe.
Products that were the next most-active for protease HUT activity were Doctor's
Best, Enzymedica, Healthy
Origins, and Now — ranging from 95,000 HUT down to 6,508
HUT. However, as footnoted in the graph below, several products (Now, Renew
Life, and GNC) list proteases that are measured in units other
than HUT and those activities are not necessarily reflected in
the HUT values that are shown.
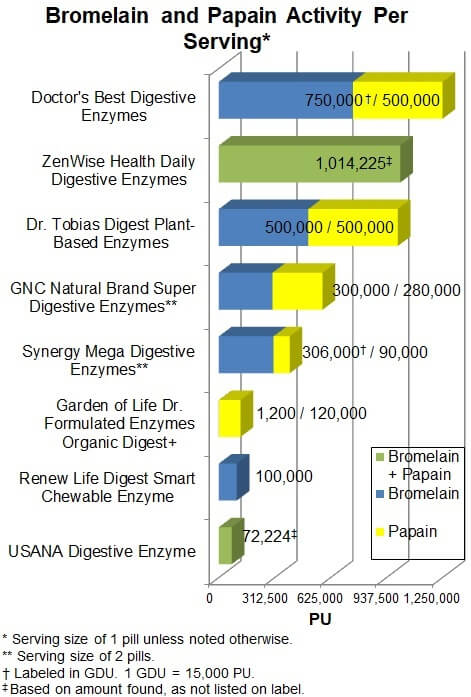
Protease activity from Bromelain and Papain
Bromelain and papain contain proteases that are active in a broad range of pH
levels, although their activities are typically measured at pH 6.0 and listed
in PU.
Only some of the products in this review contained bromelain and/or papain as
these ingredients are not typically used to digest food in the digestive tract.
As discussed in the What They Do section, bromelain and
papain may have effects on other parts of the body after they are absorbed into
the bloodstream, although the evidence of their benefits is mixed.
As shown below, the greatest amount of bromelain and papain activity was a
combined 1,250,000 PU with Doctor's Best Digestive Enzymes (at
the suggested one capsule per meal). Other products with 1,000,000 PU or more
were Zenwise Health Daily Digestive
Enzymes (which, for other reasons, was Not Approved, as discussed above) and Dr. Tobias Digest
Plant-Based Enzymes. It is difficult to know if these levels provide a
benefit but they are generally safe, as they are well below the upper tolerable
levels per dose of 10,125,000 PU for bromelain and 2,400,000 PU for papain.
Top Pick:
If you
are looking for an all-around digestive enzyme supplement of high quality with
substantial activity in digesting carbohydrates and fats, as well as some
protein action, four products stand out based on our analyses: Pure
Encapsulations Digestive Enzymes Ultra (62 cents per 2 capsule
serving), Enzymedica Digest Gold with ATPro (40 cents per 1 capsule serving), Doctor's
Best Digestive Enzymes (22 cents per 1 veggie cap serving), and Healthy
Origins Digestive Enzymes (16 cents per 1 veggie cap serving).
However, Pure Encapsulations requires twice the number of
pills as the others, and it and Enzymedica cost
significantly more per serving than the other two. Between Doctor's
Best and Healthy Origins, Doctor's Best has
somewhat more protease (protein-digesting) activity and contains bromelain and
papain, but these are of questionable additional benefit and Healthy
Origins is two-thirds the cost of Doctor's Best, so
our Top Pick is Healthy Origins Digestive
Enzymes.
Note that all four of these products include some lactase (900 to 1,600 ALU),
which helps digest lactose in dairy products, but at lower strengths than
in lactose-specific supplements which
tend contain 9,000 ALU per chewable tablet. If you are lactose intolerant and
want to eat dairy, you're better off with a lactose-specific supplement, which
can cost as little as 8 cents per serving.
Test Results by Product:
Listed
below are the test results for 12 digestive enzyme products. Nine products were
selected by ConsumerLab.com and three (denoted with a CL flask) are included
for having passed the same evaluation through the ConsumerLab.com's
voluntary Quality Certification Program.
The products are listed alphabetically.
Also shown are the labeled amounts and types enzymes, claimed enzyme activities
per suggested daily serving, and, when claimed amounts were not listed or were
incorrect, activity found. Products listed as "Approved" contained
their claimed amounts of tested enzyme activity (column 2) and met ConsumerLab.com's other criteria for quality (see Passing Score). The full
list of ingredients is available for each product by in the last column,
although some notable features are listed in the 3rd column. Price and cost
comparisons are in the 4th column.
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of DIGESTIVE ENZYMES
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Product Name
(Suggested Serving on Label)
Contained Claimed Activity of Tested Enzymes Per
Suggested Daily Serving
Additional Enzymes
(Not
Tested)
Notable Features
Suggested Daily Serving on Label
Cost
Full List of Ingredients
(Per Serving)
APPROVED
Doctor's Best® Digestive Enzymes
Dist. by Doctor's Best, Inc.
✔
1 veggie capsule:
Amylase: 20,000
DU (2 strains)
Lipase: 3,000 FIP
Protease: 95,000 HUT (fungal)
Papain: 500,000 PU
Bromelain: 50 GDU (equivalent to 750,000 PU)
1 veggie capsule:
Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV 250 DPP-IV, Invertase 100 INVU, Cellulase 3,250 CU,
Beta-glucanase 65 BGU, Alpha-galactosidase 500 GaIU, Hemicellulase 750 HCU,
Xylanase 650 XU, Phytase 10 FTU, Glucoamylase 50 AGU, Lactase 1,000 ALU
Non-GMO/ Gluten Free/ Vegetarian.
"Take 1 capsule with each meal, or as recommended by a
nutritionally-informed physician."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large veggie cap
$0.22/veggie cap
$20.00/90 veggie caps
1 veggie capsule:
Digestive Enzyme blend [Amylase Blend (2 strains) 20,000 DU, Protease SP Plus
Blend (4 strains) 95,000 HUT, Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV 250 DPP-IV, Bromelain 50
GDU, Papain 500,000 FCC PU, Invertase 100 INVU, Cellulase 3,250 CU, Beta-glucanase 65 BGU, Alpha-galactosidase 500 GaIU, more...
APPROVED
Dr. Tobias® Digest Plant-Based Enzymes
Dist. by DTI GmbH
✔
1 veggie capsule:
Amylase: 5,000 DU
Lipase: 1,250 FIP
Protease 1: 20,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease 2: 4,000 HUT (fungal)
Papain: 500,000 PU
Bromelain: 500,000 PU
1 vegetable capsule:
Aspergillopepsin 100 SAPU, Amylase 5,000 DU, Lipase
1,250 FIP, Cellulase 500 CU, Glucoamylase 50 AGU, Invertase 200 SU, Alpha
Galactosidase 50 GaIU, Beta Glucanase
65 BGU, Pectinase 16.9 PGU, Xylanase 250 XU, Phytase 10 FTU, Hemicellulase 1,000 HCU, Lactase 500 ALU, Bromelain 500,000
PU, more...
"1 capsule, take 1 to 2 times at the beginning of each meal
as a dietary supplement, or as directed by a health care professional."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large vegetable capsule
$0.30/vegetable capsule
$17.97/60 vegetable capsule
1 vegetable capsule:
Protease 1 20,000 HUT, Protease 2 4,000 HUT, Aspergillopepsin
100 SAPU, Amylase 5,000 DU, Lipase 1,250 FIP, Cellulase 500 CU, Glucoamylase 50
AGU, Invertase 200 SU, Alpha Galactosidase 50 GaIU,
Beta Glucanase 65 BGU, Pectinase 16.9 PGU, Xylanase
250 XU, Phytase 10 FTU, Hemicellulase 1,000 HCU, more...
APPROVED
Enzymedica® Digest Gold™ with ATPro™
Mfd. by Enzymedica,
Inc.
✔
1 capsule:
Amylase: 23,000 DU
(Thea-blend™)
Lipase: 4,000 FIP (Thea-blend™)
Protease: 80,000 HUT (fungal)
(Thea-blend™)
1 capsule:
Glucoamylase 50 AGU, Alpha Galactosidase 450 GaIU,
Cellulase Thera-blend™ 3,000 CU, Lactase 900 ALU, Beta Glucanase
25 BGU, Maltase 200 DP, Xylanase 550 XU, Invertase 240 SU, Pectinase (w/
Phytase) 45 Endo-PGU, Hemicellulase 30 HCU
No Fillers Added. Vegan & Kosher. Non GMO. , more...
"1 capsule with each meal."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large capsule
$0.40/capsule
$35.99/90 capsules
1 capsule:
Amylase Thera-blend™ 23,000 DU, Protease Thera-blend™ 80,000 HUT, Glucoamylase
50 AGU, ATPro™ (ATP, Magnesium citrate, Phytase,
CoQ10) 25 mg - 300 Million LCU, Alpha Galactosidase
450 GaIU, Cellulase Thera-blend™ 3,000 CU, Lipase
Thera-blend™ 4,000 FCCFIP, Lactase 900 ALU, Beta Glucanase
25 BGU, more...
APPROVEDⓘ
Garden of Life® Dr. Formulated Enzymes Organic
Digest+ - Tropical Fruit Flavor![]()
Dist. by Garden of Life
✔
1 chewable tablet:
Lipase: 250 FIP
Protease: 1,800 HUT (fungal)
Papain: 120,000 PU
Bromelain: 1,200 PU
1 chewable tablet:
Aspergillopepsin 11 SAPU, beta-Glucanase
2 GBU, Cellulase 180 CU, Phytase 5 FTU, Lactase 150 ALU, Peptidase 210 HUT,
Pectinase 5 endo-PGU, Xylanase 40 XU, Hemicellulase
190 HCU
Certified Vegan Vegan.org Seal. USDA Organic Seal. Non GMO
Project Verified Seal. Gluten Free. Dairy Free. Soy Free.
"Adults chew 1 tablet after each
meal or snack."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Medium/large circular chewable tablet
$0.24/chewable tablet
$21.69/90 chewable tablets
1 chewable tablet:
Calories 5, Total Fat 0 g, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 1 g, Sugars less
than 1 g, Whole Food Enzyme Blend [Organic Carrot (root), Organic Apple
(fruit), Organic Broccoli (stalk & flower), Organic Acai (fruit), Organic
Parsley (leaf), Organic Sweet Potato (tuber), Organic Pineapple (fruit),
Organic Banana (fruit), Organic Cranberry (fruit), Organic Mango (fruit), more...
APPROVED
GNC Natural Brand Super Digestive Enzymes![]()
Dist. by General Nutrition Corporation
✔
2 capsules:
Amylase: 7,000 DU
Lipase: 250 FIP
Protease 4.5: 15,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease 3.0: 15 SAPU (fungal)
Protease 6.0: 2,000 HUT (fungal)
Papain: 280,000 PU
Bromelain: 300,000 PU
Found:
Total Protease: 21,992 HUTⓘ
2 capsules:
Glucoamylase 11 AGU, Cellulase 100 CU, Malt diastase 125 DP
No Artificial Colors, No Artificial Flavors, Sodium Free, Yeast Free.
Precaution: Contains: Milk, Soybeans and Wheat.
"As a dietary supplement, take two capsules after each
meal."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large capsule
$0.36/2 capsules
$17.99/100 capsules
2 capsules:
n-zimes® Proprietary Blend [Amylase 7,000 DU,
Protease 4.5 15,000 HUT, Lipase 250 FIP, Glucoamylase 11 AGU, Protease 3.0 15
SAPU, Bromelain 300,000 FCCPU, Protease 6.0 2,000 HUT, Papain 280,000 FCCPU,
Cellulase 100 CU, Malt diastase 125 DP] 291 mg, more...
APPROVED
Top Pick
Healthy Origins® Digestive Enzymes
Dist. by Healthy Origins®
✔
1 veggie cap:
Amylase: 20,000 DU
Lipase: 3,000 FIP
Protease 4.5: 60,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease 6.0: 10,000 HUT (fungal)
1 veggie cap:
Peptidase 10,000 HUT, Alpha-galactosidase 500 GaIU,
Glucoamylase 30 AGU, Pectinase 35 endo-PGU, Cellulase 2,500 CU, Beta-glucanase 35 BGU, Lactase 1,000 ALU, Diastase 150 DP,
Invertase 250 SU, Hemicellulase 200 HCU
Non-GMO. Does not contain Wheat, Gluten,
Soy, Fish, Shellfish, more...
"As a dietary supplement for adults; take one (1) vegetarian
capsule with every meal, or as directed by a physician."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large veggie cap
$0.16/veggie cap
$14.17/90 veggie caps
1 veggie cap:
Enzyme Blend [Amylase 20,000 DU, Protease 4.5 60,000 HUT, Peptidase 10,000 HUT,
Alpha-galactosidase 500 GaIU, Glucoamylase 30 AGU,
Pectinase 35 endo-PGU, Protease 6.0 10,000 HUT, Cellulase 2,500 CU, Lipase
3,000 FIP, Beta-glucanase 35 BGU, Lactase 1,000 ALU,
Diastase 150 DP, Invertase 250 SU, more...
APPROVED
NOW® Optimal Digestive System
Dist. by NOW Foods
✔
2 veg capsules:
Amylase: 7,000 DU
Lipase: 1,000 FIP
Protease: 42,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease: 8,000 PC (plant)
Protease: 4 AP (fungal)
Protease: 100 SAPU (fungal)
Found:
Total Protease: 63,508 HUTⓘ
2 veg capsules:
Glucoamylase (from Aspergillus niger) 10
AGU, Invertase (from Saccharomyces cerevisiae) 800 SU, Diastase
(from Aspergillus oryzae) 3,000 DP
Vegetarian/Vegan. Not manufactured with wheat, soy, egg, fish, shellfish or
tree nut ingredients.
"Take 2 capsules with or before each meal."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Medium/large veg capsule
$0.22/2 veg capsules
$10.10/90 veg capsules
2 veg capsules:
BioCore Optimum™ [Amylase (from Aspergillus oryzae) 7,000 DU, Protease (from Aspergillus oryzae) 42,000 HUT, Protease (from Aspergillus oryzae) 8,000 PC, Protease (from Aspergillus oryzae) 4 AP, Protease (from Aspergillus niger) 100 SAPU, more...
APPROVED
Pure Encapsulations® Digestive Enzymes Ultra
Mfd. by Pure Encapsulations
✔
2 capsules:
Amylase: 24,000 DU
Lipase: 3,000 FIP
Protease: 60,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease 6.0: 20,000 HUT (fungal)
Protease 3.0: 20 SAPU (fungal)
Found:
Total Protease: 112,734 HUTⓘ
2 capsules:
Glucoamylase 30 AGU, Lactase 1,600 ALU, Beta-glucanase
20 GGU, Invertase 900 SU, Cellulase 800 CU, Alpha-galactosidase 120 GaIU, Phytase 10 FTU, Hemicellulase
200 HCU
Gluten-free & Non-GMO.
"As a dietary supplement, take 2 capsules with each meal, or
as directed by a health professional."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Medium/large capsule
$0.62/2 capsule
$27.70/90 capsules
2 capsules:
Proprietary enzyme blend [providing: Amylase 24,000 DU, Protease 60,000 HUT,
Protease 6.0 20,000 HUT, Glucoamylase 30 AGU, Lactase 1,600 ALU, Lipase 3,000
FIP, Beta-glucanase 20 GGU, Invertase 900 SU,
Cellulase 800 CU, Alpha-galactosidase 120 GaIU,
Protease 3.0 20 SAPU, more...
APPROVED
Renew Life® Digest Smart® Chewable Enzyme -
Mixed Berry Flavor
Dist. by Renew Life Formulas
✔
1 chewable tablet:
Amylase: 2,500 DU
Lipase: 1,000 FIP
Protease A: 10,000 PC (plant)
Protease B: 5,000 HUT (fungal)
Acid Protease: 25 SAPU (fungal)
Bromelain: 100,000 PU
Found:
Total Protease: 30,413 HUTⓘ
1 chewable tablet:
Lactase 500 ALU, Alpha-Galactosidase 50 GaIU, Phytase
10 FTU, Glucoamylase 5 AGU, Cellulase 100 CU, Hemicellulase
500 HCU
Precaution: May contain traces of soy, milk, and wheat from
ingredients used in fermentation process to make enzymes.
"Chew one (1) tablet before each meal."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Medium/large chewable tablet
$0.30/chewable tablet
$26.99/90 chewable tablets
1 chewable tablet:
Calories 3, Total Carbohydrate <1 g, Sugar Alcohol <1 g, Plant Enzyme
Blend [Protein Enzyme Activity Values [Bromelain 100,000 PU, Protease A 10,000
PC, Protease B 5,000 HUT, Acid Protease 25 SAPU], Carbohydrate Enzyme Activity
Values [Amylase 2,500 DU, Lactase 500 ALU, Alpha-Galactosidase 50 GaIU, more...
APPROVED
Synergy® Mega Digestive Enzymes
Dist. by Vitacost.com
✔
2 capsules:
Amylase: 81,250 USP (from
pancreatin 10x USP) (equivalent to 1,693 DU)
Lipase: 6,500 USP (from pancreatin 10x USP)
Lipase: 42.5 FIP
Protease: 81,250 USP (from pancreatin 10x USP) (equivalent to
12,500 HUT)
Papain: 90,000 PU
Bromelain: 40.8 GDU (equivalent to 306,000 PU)
2 capsules:
Trypsin 5,625 USP, Lysozyme 9,500 MCG, Chymotrypsin 2,000 USP
Free of: Milk, Peanuts, Tree Nuts, Crustacean Shellfish, Fish, Soy, Gluten,
Titanium Dioxide.
Precaution: Contains: Eggs.
"As a dietary supplement, take 2 capsules before each meal or
as directed by a healthcare professional."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large capsule
$0.13/2 capsules
$18.98/300 capsules
2 capsules:
Pancreatin 10X USP (protease [81,250 USP], amylase 81,250 USP], lipase [6,500
USP]) 325 mg, Trypsin (5,625 USP) 75 mg, Papain (90,000 USP) 50 mg, Bromelain
(40.8 GDU) 17 mg, Amylase (50 FCC) 10 mg, Lipase (42.5 FCC FIP) 10 mg, Lysozyme
(9,500 MCG) 10 mg, Chymotrypsin (2,000 USP) 2 mg., more...
APPROVED
Mfd. by USANA Health Sciences
✔
1 tablet:
Enzyme activities not
listed
Found:
Amylase: 3,570 DU
Lipase: 952 FIP
Protease: 22,829 HUT (fungal)
Papain+Bromelain: 72,224 PU
1 tablet:
Lactase, Cellulase
No animal derived ingredients.
Precaution: Contains: Soy.
"Take one (1) to three (3) tablets with a meal or as
needed."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Medium circular tabletⓘ
$0.55/tablet
$30.95/56 tablets
1 tablet:
Natural Enzyme Blend (Alpha-Amylase, Bromelain, Protease, Lipase, Lactase,
Papain, Cellulase) 120 mg, Artichoke Extract (Cynara scolymus L.)
25 mg.
Other Ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Croscarmellose Sodium, more...
NOT APPROVEDⓘ
ZenWise Health® Daily Digestive
Enzymes With Prebiotics + Probiotics
Dist. by Zenwise
Health, LLC
✗
1 vegetarian capsule:
Enzyme activities not
listed
Found:
Amylase: 429 DU
Lipase: No quantifiable
activity (<43.3 FIP)
Protease: 1,166 HUT (fungal)
Papain+Bromelain: 1,014,225 PU
1 vegetarian capsule:
Glucoamylase, Invertase, Maltase, Cellulase, Lactase
"Take one capsule immediately before each meal, or as
directed by a healthcare professional."
Pill sizeⓘ:
Large vegetarian capsule
$0.12/vegetarian capsule
$21.97/180 vegetarian capsules
1 vegetarian capsule:
Advanced Enzyme System [Amylase, Glucoamylase, Lipase, Protease, Invertase,
Maltase, Cellulase, Bromelain, Lactase, Papain] 350 mg, Green Papaya 30 mg,
Apple Pectin 30 mg, Ginger (Rhizome) 20 mg, Turmeric (Rhizome) 15 mg, Fennel
(Seed) 15 mg, Peppermint (Herb) 10 mg, Sea Vegetable Complex, more...
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's
ingredients differ from what is listed above, it may not necessarily be of the
same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
ConsumerTips™:
What to
look for on the label
Choose a product that lists activity and correct units for each enzyme
ingredients. As discussed in Quality Concerns, the FDA only requires
supplement labels to list the weight of each enzyme (i.e. milligrams), but this
will not tell you activity -- how much it can digest in certain period of time,
which is the true measure of how well an enzyme will work. For example,
"Amylase 40,000 DU" will tell you more than "Amylase 400
mg," because there are different versions of amylase available as
ingredients and some digest more than others.
Activity units should be listed as a number which represents the measured
activity, followed by the abbreviation of the unit for that specific enzyme (i.e. HUT, PU, CU, ALU). (See the table in What They Are for common enzyme names,
what foods they help to digest, and what activity unit they should be labeled
with. Watch out for products which list enzymes only in terms of FCC (i.e. "Lipase 375 FCC"), as these are not defined
units. (For more information about enzyme units, see the definitions published
online by the enzyme company Deerland).
Digestive enzyme supplements may contain enzymes from animal sources (such as
porcine pancreatin) — although these are active in the narrow, alkaline pH
range (7.2 — 9.0) of the small intestine and they generally require enteric
coating to prevent them from being destroyed in the acid environment of the
stomach.
Enzymes from plants such as papaya and pineapple (like papain and bromelain),
or from fungi (such as Aspergillus) or bacteria are more stable and
active in the much broader pH range (3.0 — 11) found throughout the digestive
tract, so they can work in the stomach as well as the small intestine.
How to take
Digestive enzymes work best when taken immediately before, or during a meal,
although there may still be a benefit when taken immediately after eating.
Enzymes taken for other reasons, such as proteases taken for pain and
inflammation, should be taken on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before a
meal.
Dosage:
Pancreatin: Taking one capsule (containing lipase 10,000 USP, protease 37,500
USP and amylase 33,200 USP) of a prescription, animal derived pancreatin
formula (Creon, Solvay Pharmaceutical) immediately before a high fat,
high calorie meal, and two more capsules immediately after the meal
significantly reduced bloating, gas and fullness compared to placebo (Suarez, Dig Dis Sci 1999).
Amylase: 33,200 USP of porcine-derived amylase taken immediately before a high
fat meal, and 66, 400 USP lipase taken immediately after the meal may help to
reduce gas, bloating and fullness (Suarez, Dig Dis Sci 1999).
Lipase: For people with general malabsorption disorders, 25,000-40,000 USP
(porcine-derived) or 18,750-30,000 LU (fungal derived) per meal (Roxas, Alt Med Rev 2008). In healthy people, 10,000 USP
lipase taken immediately before a high fat meal, and 20,000 USP lipase taken
immediately after the meal, may help to reduce gas, bloating and fullness (Suarez, Dig Dis Sci 1999).
Bromelain: For digestion, a dose of 2,000 MCU or 1,200 GDU is recommended (Roxas, Alt Med Rev 2008). (Other uses: 540 mg bromelain
taken 3 times daily on an empty stomach pain from knee osteoarthritis.)
Fungal derived proteases: 2.5 grams or 5 grams of a patented blend of proteases
derived from Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus
oryzae (Aminogen,
Triarco Industries) (enzyme activity units not
provided) added to 50 grams of whey protein concentrate may increase the rate
of absorption and increase amino acid absorption (Oben, J Int Soc Sports
Nutr 2008).
Lactase: A dose of 3,000 to 6,000 ALU can help people with lactose intolerance
digest about 20 grams of lactose from milk (the amount in about 1 ½ cups), with
the larger dose providing a greater benefit (Lin, Dig Dis Sci 1993).
Alpha-galactosidase: A does between 240 GALU and 1,200 GALU may help to reduce
gas from a meal rich in fermentable carbohydrates, such as beans (Ganiats, J Fam Pract 1994; Di Stefano, Dig Dis Sci 2007).
Phytase: A dose between 20 and 320 units FTU per 100 grams of flour may help to
increase iron absorption (Troesch, Food Nutr Bull 2013).
Storage
Digestive enzymes should be stored in their original container, in a cool, dry
place. Exposure to excessive heat can reduce potency.
Concerns and Cautions:
Digestive
enzymes are generally well-tolerated, however, as noted below, people with
allergies to a particular enzyme source, and people with certain conditions, or
who are taking certain medications, may need to avoid certain enzymes. In
addition, if you are experiencing digestive trouble, it is advisable to see a
physician to rule-out conditions which may require medical treatment.
Some people may be
allergic to the fungi from which certain enzymes are derived, such as Aspergillus
niger and Aspergillus oryzae, although this has typically been reported in
people with occupational exposure to large amounts of the fungus over time,
such as in breweries (Ishiguro, Clin Case Rep 2018; EPA 1998). However, one
case of an allergic reaction to a fungal-derived
enzyme supplement has been reported.
Pancreatin (amylase,
lipase and protease) and Other animal-derived enzymes:
Pancreatin may inhibit folic acid absorption; if you take pancreatin on a
regular basis, you may need extra folate (Russell, Dig Dis Sci 1980). People with a
known allergy to porcine (pig) protein should avoid enzymes derived from this
source, as allergic reactions can occur. In addition, porcine-derived enzymes
contain purines — organic compounds that can increase blood uric levels; therefore people with gout, renal impairment and
hyperuricemia should consult their healthcare provider before using.
Changes in blood sugar
levels (hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia) have been reported in people with
exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatectomy
taking a prescription pancreatin enzyme (containing animal-derived lipase,
amylase and protease enzymes) (Creon, Solvay Pharmaceutical) (Creon Prescribing Information 2015).
People taking the
diabetes drugs acarbose (Precose) or miglitol (Glyset) should not take digestive enzyme supplements
containing amylase or pancreatin (which contains amylase) (Precose Prescribing Information 2011; Glyset Prescribing Information 2012).
Proteases
Papain may cause itching, sweating, watery eyes, diarrhea or exacerbate asthma
in people who are allergic to papaya or fig (Ficus benjamina)
(Mansfield, Ann Allergy 1985; Diez-Gomez, Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1998).
It could also potentially increase bleeding risk and should be used with
caution in people taking blood-thinning medications such as warfarin (Shaw, Drug Saf 1997).
Bromelain may have anti-platelet activity, which could increase the risk of
bleeding or bruising when taken with blood-thinning drugs such as aspirin,
clopidogrel (Plavix) heparin, warfarin (Coumadin) etc. Some people may have an
allergic reaction to bromelain (Nettis, Allergy 2001 ).
Bromelain may also increase the effects of sedative drugs or certain
antibiotics, especially amoxicillin. High doses may increase heart rate, but
not blood pressure (Gutfreund, Hawaii Med J 1978).
Fungal proteases derived from Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus
oryzae and maltodextrin may cause stomach
upset, nausea and headache, but a 30-day study did not find it to cause adverse
effects on measures of metabolic and cardiovascular safety such as liver and
kidney function and blood pressures, although (Anderson, Food Dig 2013).
Alpha-glucosidase
Alpha-glucosidase may interfere with the
glucose-lowering effects of the diabetes drug acarbose (Precose),
which is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. One clinical study found that people with
type 2 diabetes taking acarbose, those who also took 15 drops of
alpha-galactosidase (Beano) with breakfast, lunch and dinner had blood
glucose levels that were higher than those who did not take the enzyme --
although blood glucose levels in the group taking acarbose and Beano were still
significantly lower than in those who took only a placebo (Lettieri, Clin Ther 1998).
Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV (DPP-IV)
People with type 2 diabetes who take DPP-IV inhibitors drugs (gliptins) such as
alogliptin (NESINA), linagliptin (Tradjenta),
saxagliptin (Onglyza) and
sitagliptin (Januvia) should not take digestive enzyme products containing
dipeptidyl-peptidase IV (DPP-IV).
Lactase
Very few side effects have been reported with the use of lactase supplements;
rarely, however, nausea and allergic reactions have been reported (see
the Concerns and Cautions section
of the Lactase Supplements Review for details).
Information on this site
is provided for informational purposes only. It is not an endorsement of any
product nor is it meant to substitute for the advice provided by physicians or
other healthcare professionals. The information contained herein should not be
used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease. Consumers should
inform their healthcare providers of the dietary supplements they take.
Latest Clinical Research Updates for Digestive Enzymes
Enzyme Supplements for Eye Floaters?
9/21/2021
Can enzyme supplements
(bromelain, papain and ficin) reduce eye floaters? Find out what a recent study
suggests in the What They Do section of our Digestive
Enzyme Supplements Review.
Also see our answer to the question: Do any supplements help prevent or reduce eye floaters?
12/15/2018
Will taking digestive
enzymes reduce indigestion? Although not all studies have shown a benefit, a
recent study suggested improvements with no adverse effects. For details, see
the Digestive Discomfort section
of the Digestive Enzyme Supplements Review. (Also see our top choices for
enzyme supplements).
1/14/2017
A blend of enzymes
reduced delayed-onset muscle soreness after exercise in healthy men. For
details, see the "What They Do" section of
the Digestive Enzyme Supplements Review >>
Related CL Answers (9)











