CoQ10 and Ubiquinol Supplements Review
Find the Best CoQ10 and
Ubiquinol Supplements and Learn What They Do
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Last Updated![]() : 11/29/2021 | Initially Posted:
09/11/2021Latest Update: CoQ10 and Heart Failure
: 11/29/2021 | Initially Posted:
09/11/2021Latest Update: CoQ10 and Heart Failure

Recent Reviews
·
Aloe Juices, Gels, and Supplements
Review
·
NAD Booster Supplements Review
(NAD+/NADH, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN)
·
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone) Supplements
Review
Table of Contents
Summary
·
What does CoQ10 do? People often take CoQ10 to offset a
decline in natural levels that occurs with the use of statin
(cholesterol-lowering) medication. Some take it to feel more energized or for a
variety of other purposes. It may also modestly help with elevated cholesterol
levels, migraine, and other conditions. The evidence supporting these uses
remains preliminary, although it does benefit people with congestive heart
failure (see What It Does). After being absorbed into the
body, more than 90% of CoQ10 is converted to its active form, known as
ubiquinol (CoQH2-10), which is also available as a supplement and appears to
have greater bioavailability (i.e., it raises blood levels more) (see What It Is).
·
How much CoQ10 should I take? CoQ10 and ubiquinol are typically taken
at a dose of 50 to 200 mg per day, although higher doses have been used
(see Dosage).
·
What did CL's tests of CoQ10 show? In laboratory
testing, all of the products were shown to provide their listed amounts of
CoQ10 or ubiquinol, which is an improvement over the results of our previous
review. Cost comparisons, based on a 100 mg dose, showed you could spend as
little as 8 cents to over $6 for an equivalent amount of CoQ10, and from 34
cents to $1.18 for ubiquinol (see What CL Found).
·
Best CoQ10 supplement? Among 33 CL Approved products, CL
selected four Top Picks for
regular as well as bioavailability-enhanced CoQ10 and ubiquinol supplements,
each providing high quality CoQ10 or ubiquinol at very good value.
·
How to take CoQ10? Gastrointestinal side-effects may occur
but can be minimized by breaking up the dose throughout the day, although it
may interfere with sleep if taken before bed. CoQ10 and ubiquinol are best absorbed
when taken with or shortly after a fatty meal, although certain forms can be
taken without fats (see Absorption and Bioavailability Enhancers).
·
CoQ10 safety and side effects: At typical doses, CoQ10 and ubiquinol
appear to be generally safe, but there are possible interactions with blood
thinners and diabetes medications (see Concerns and Cautions).
What It Is:
Coenzyme
Q10 (CoQ10), also known as ubiquinone or ubidecarenone, is a naturally
occurring antioxidant compound used for energy production within cells. It's
manufactured in the heart, liver, kidney and pancreas. The body normally
produces sufficient CoQ10, although some medications such as statins may
interfere with this process and CoQ10 levels in the body may decline with age
and heart disease. Only small amounts of CoQ10 are available from food, mainly
beef and chicken. Consequently, dietary supplements are the most common way to
increase the body's CoQ10 levels. After being absorbed into the body (See Absorption and Bioavailability Enhancers), more
than 90% of CoQ10 is converted to its active form, known as (CoQH2-10) or
ubiquinol. Ubiquinol has strong antioxidant properties. Conditions that cause
oxidative stress on the body, such as liver disease, decrease the ratio of
ubiquinol to CoQ10. In the body, blood levels of CoQ10
steadily rise from young adulthood through middle-age, peaking at around age
60, when levels then decrease — although they do not fall below levels of early
adulthood. However, levels of CoQ10 in tissue of the brain,
heart and pancreas do decrease with age. Perhaps of greater significance
though, is that, after age 60, the body seems to convert less CoQ10 into its
active form (ubiquinol), resulting in a decreased ratio of ubiquinol to CoQ10
and indicating a higher level of oxidative stress (Niklowitz, J Clin Biochem Nutr 2016; Claessens, Ann Clin Biochem 2016).
Like CoQ10, ubiquinol is
available as a dietary supplement. (For more information about forms sold,
see ConsumerTips™.)
What It Does:
Taken orally, coenzyme Q10 may help treat congestive
heart failure, a disease in which the heart doesn't adequately maintain
circulation. CoQ10's role in cell energy production may be the mechanism by
which it assists the heart. An analysis of 13 clinical studies found that
taking coenzyme Q10 (usually 100 mg daily) significantly improves how well the
heart pumps blood (i.e., ejection fraction) by about 3.7% compared to placebo
in people with mild-to-moderate heart failure (Fotino, Am J Clin Nutr 2013). The largest and
longest clinical study to date found that taking 100 mg three times daily of
coenzyme Q10 for 2 years significantly reduced the chance of an adverse
cardiovascular event (e.g., hospitalization, worsening heart failure, or death)
by almost 50% compared to placebo in people with moderate-to-severe heart
failure and significantly improved measures of quality of life such as activity
levels, fatigue, and shortness of breath. It's important to note that these
benefits from CoQ10 may require long-term supplementation (2 years); when
researchers checked after just 3 months of supplementation, no significant
improvements were found (Mortensen, JACC Heart Failure 2014).
Further supporting the theory that short-term
supplementation may not be adequate to provide benefit is a study in Israel
among 32 men and women (average age 75) with mild to severe diastolic
heart failure (also known as heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction). The study found that 100 mg of stabilized ubiquinol (by Kaneka
Corporation, which funded the study) taken three times daily for four months in
addition to standard treatment did not improve diastolic function or decrease
levels of a blood marker typically elevated in people with heart failure
(NT-proBNP) compared to standard treatment plus placebo. In addition, there was
no significant improvement in ejection faction (which was, on average, low but
within normal range among participants) with ubiquinol compared to placebo (Samuel, Drugs R D 2021). In all of these
studies, coenzyme Q10 was used in addition to prescription heart failure
treatment, not in place of it.
Ubiquinol
may help protect the heart around the time of aortic valve replacement,
as demonstrated in a study of 50 elderly people (average age 78) who took 200
mg of ubiquinol (QH Absorb, Jarrow Formulas Inc.) or placebo twice daily
for 7 days before and 5 days after aortic valve replacement surgery. People
taking ubiquinol showed lower blood levels of troponin I and CK-MB (markers of
heart muscle damage) at 1 and 5 days after surgery, respectively, compared to
placebo. Taking ubiquinol also curbed the decline in how well the heart pumps
after surgery (i.e., ejection fraction) by about 5% at 6-months follow-up
compared to placebo. However, ubiquinol did not improve heart function as
measured by NYHA classification or reduce the rate of major adverse events
after surgery -- although rates of most of these events was low (Orlando, Aging 2020).
CoQ10
might help reduce side effects caused by "statins," drugs
used to lower high cholesterol, although this has not been well established due
to conflicting results. Some of the side effects reportedly reduced with CoQ10
include myalgia (muscle pain), fatigue, dyspnea, memory loss and peripheral
neuropathy. In a study among people reporting muscle pain associated with
taking statins, a dose of 50 mg of CoQ10 twice daily (100 mg per day) for 30
days reduced the intensity of mild to moderate muscle pain by 33.1% and the
interference with daily activities by 40.3%, while no improvement occurred
among people treated with placebo. Symptoms improved among seventy-five percent
of those treated with CoQ10 (Skarlovnik, Medical Science Monitor 2014).
Some studies using somewhat higher daily doses of CoQ10 (120 mg to 200 mg) have
not shown benefit for muscle pain (Bookstaver, Am J Cardiol 2012; Young, Am J Cardiol 2007). Nevertheless, a
review of twelve randomized placebo-controlled studies involving CoQ10
(including those cited above) concluded that, overall, CoQ10 improved
statin-associated muscle symptoms, i.e., pain, weakness, cramps, and tiredness
(Qu, J Am Heart Assoc 2018). On the other hand, a later analysis of several studies from
the same time period concluded that CoQ10 "did not demonstrate" a
benefit for patients with statin-associated muscle pain or improved adherence
to statin therapy (Kennedy, Atherosclerosis 2020).
One study suggests that
CoQ10 in combination with a reduction in statin dose can help people
considered statin-intolerant (due to muscle-related side effects) more
than lowering the statin dose alone. In the study, conducted in Italy,
participants reduced their statin dose by half for a month and then, for three
months also took either 100 mg daily of CoQ10 or placebo. Among those who took
the CoQ10, 46.6% reported having significantly less muscular pain than before
starting the CoQ10 compared to just 6.6% of those who took the placebo. In
addition, the CoQ10 prevented a worsening in lipid profiles that occurred in
the placebo group (Derosa, Drug Des Devel Ther 2019).
CoQ10,
itself, may modestly lower elevated cholesterol levels. A
study among middle aged people in China with high cholesterol levels who
were not taking statins or other cholesterol-lowering drugs
found that 60 mg of CoQ10 taken twice daily after meals (120 mg per day) for 5
½ months decreased LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels,
although not total cholesterol levels, compared to placebo. Among those who
took CoQ10, average LDL cholesterol decreased by 6.5% and average triglyceride
levels decreased by nearly 20%. In addition, average fasting blood
sugar and insulin levels decreased by 6% and 21%, respectively, and
average systolic and diastolic blood pressure decreased by 4% and 5%,
respectively, compared to placebo (Zhang, J Clin Lipidol 2017).
(However, as noted in Concerns and Cautions, a review clinical
studies concluded that CoQ10 does not have a clinically significant effect on
lowering blood pressure). CoQ10 does not, however, appear to
further lower cholesterol levels in people taking a statin drug.
This was shown in a study in Denmark among 55 men and women who were already
taking the statin drug simvastatin (40 mg/day); adding 400 mg of ubiquinol (the
active form of CoQ10) daily for two months did not lower LDL, total cholesterol
or triglyceride levels compared to simvastatin with placebo (Hansen, Cytokine 2018).
Although
the above study suggested an effect of CoQ10 on blood sugar levels, a study in
China that focused on men and women (average age 61) with type 2
diabetes found 100 mg of liquid ubiquinol daily (taken as four drops
before breakfast, lunch and dinner) for three months did not significantly
decrease fasting blood sugar levels, HbA1c (a measure of blood sugar over
several months) or improve insulin resistance, compared to placebo.
Nevertheless, at the end of the study, those who took the ubiquinol used less
diabetes medication than those who took the placebo (Yen, Br J Nutr 2018).
A study
in Switzerland among 42 men and women with migraine (with or
without aura) found that 100 mg of CoQ10 taken as liquid drops three times
daily (total daily dose of 300 mg CoQ10) for three months modestly decreased
the frequency of attacks by about one migraine per month and slightly decreased
the number of days with nausea but did not decrease the duration of episodes,
compared to placebo. The improvements were noticeable only after the first
month of supplementation (Sandor, Neurology 2005). A study in Iran among 45 men and women (average age 32)
with migraine found that those who took 200 mg of ubiquinol (Ubiquinol
Active CoQ10, Natural Factors Inc. Canada) as capsules twice daily with
meals (total daily dose of 400 mg) for three months had greater reductions in
the frequency (- 6 vs. - 3 migraines per month), duration (- 7 vs. - 4 hours),
and severity of episodes (-3.4 vs. -2.4 points on a scale of 1 to 10) compared
to placebo. CoQ10 supplementation also reduced blood levels of lactate and
nitric oxide, both of which may be elevated in people with migraine (Nattagh-Eshtivania, Eur J Integr
Med 2018).
CoQ10 may reduce symptoms
of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. It may also help
prevent pre-eclampsia (a complication of pregnancy) and reduce
the likelihood of more heart problems in some people who've
had a first heart attack. CoQ10 may also be useful in treating diseases
including muscular dystrophy, AIDS, and hypertension.
There is also evidence that it may increase sperm motility.
Although CoQ10 is sometimes touted for enhancing athletic performance this
use hasn't been well demonstrated.
CoQ10, both topical and
oral, is sometimes promoted to help treat gum disease, although the
evidence is limited. One small study reported a benefit with the application of
CoQ10 gel (PerioQ) in addition to non-surgical cleaning treatment, compared to
treatment alone (Sale, J Indian Soc Periodontol 2014).
Another small study in India, among 30 men and women with periodontitis who
received traditional treatment (deep cleaning with scaling and root planing),
found that those who took 120 mg of CoQ10 daily for three months after
treatment had a modest decrease in gum inflammation compared to those who took
a placebo after treatment, but there were no improvements in other measures of
disease, such as plaque or pocket depth (gaps between teeth and gums that can
deepen and allow for bacteria that cause gum disease to grow) (Manthena, J Clin Diagn Res 2015).
In children with trisomy
21 (Down syndrome), ubiquinol supplementation has been shown to increase
the ratio of ubiquinol to CoQ10 to normal levels -- although it is unknown if
this provides medical benefit.
A
small, placebo-controlled study in veterans in their forties and early fifties
with Gulf War illness found that taking 100 mg of CoQ10 (in
oil from a softgel) daily for 3 to 4 months appeared to improve physical
function and symptoms of the illness (such as recalling words and
names, impatience, irritability, headache, fatigue with exertion, low energy to
do things, and muscle pain). There was no improvement with sleep problems —
possibly due to an "activation" effect of CoQ10. Self-rated health
status also improved among men, although not among women. These effects,
however, were not found with a larger, 300 mg dose (Golomb, Neural Computation 2014).
A study
in Japan among 62 healthy men and women (average age 42) experiencing fatigue in
daily life showed little benefit with either 100 mg or 150 mg of ubiquinol
taken daily after breakfast. Despite both dose amounts causing significant
increases in blood levels of CoQ10, there was no significant improvement,
relative to placebo, in nerve function, blood markers of oxidative stress, or
on most tests of cognitive function and fatigue. At four weeks into the study
there was improvement at both dosage levels in self-reported fatigue and
sleepiness after cognitive testing, but the improvement was no longer
significant relative to placebo at the end of the study. The study was funded
by Kaneka, a manufacturer of ubiquinol supplements (Mizuno, Nutrients 2020).
A study in Spain among 69 men and women (average age 72)
with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) found that 200 mg of
ubiquinol (Kaneka Corp) taken as a capsule once daily with breakfast for one
year improved cerebral vasoreactivity (the ability of blood vessels to expand
and contract to allow proper blood flow in the brain) and reduced a blood
marker of inflammation (lipopolysaccharide) in men, but not in women, compared
to placebo. However, there were no improvements in cognition or
measures of neurological function compared to placebo (Garcia-Carpintero, Antioxidants 2021).
A small, preliminary study in Spain among middle- aged adults
with fibromyalgia (chronic, wide-spread muscular pain and
fatigue) found that 100 mg of CoQ10 taken three times daily for 40 days
significantly improved measures of interpersonal sensitivity, depression,
anxiety, hostility, and symptoms of somatization and obsessive-compulsion
compared to placebo (Alcocer-Gomez, CNS Neurosci Ther
2017). A reduction in inflammation and clinical symptoms, including
sleep quality and tender points, was also noted by the researchers, but,
unfortunately, data was not provided for these findings. Another small
study, among middle-aged men and women in Thailand with fibromyalgia, found
that taking 300 mg of CoQ10 in addition to 150 mg of the common fibromyalgia
medication pregabalin (Lyrica) daily for 40 days significantly reduced pain,
anxiety, and certain measures of inflammation compared to the decreases in
these measures with pregabalin plus placebo. The study also found that those
who took CoQ10 had greater decreases in brain activity in regions of the brain
associated with pain perception and modulation (including emotional, cognitive
and motor control responses to pain) compared to pregabalin taken with placebo
(Sawaddiruk, Free Radic Res 2019).
CoQ10
may help people with trigeminal neuralgia (nerve pain in the
face and jaw). A small study in Thailand among men and women being treated with
standard medication (carbamazepine e.g. Tegretol, Carbatrol)
for trigeminal neuralgia found that 100 mg of CoQ10 taken three times daily for
two months significantly reduced self-reported nerve pain and certain measures
of oxidative stress compared to placebo (Khuankaew, Free Radic Res 2018).
Although
preliminary research had suggested CoQ10 might delay the progression of Parkinson
disease, a large, placebo-controlled clinical study found no benefit from
high-doses of CoQ10 (1,200 mg or 2,400 mg daily) in people with early Parkinson
Disease (Parkinson Study Group, JAMA Neurol 2014). In
fact, over the course of the 16+ month study, symptoms worsened more among
those given CoQ10, particularly at the higher dose, than in the placebo group,
although these differences were not statistically significant. All patients in
the study also received high-dose (1,200 mg daily) vitamin E. An earlier,
smaller study had suggested benefit with a daily dose of 1,200 mg of CoQ10
(also with 1,200 mg of vitamin E), although not at lower doses (300 mg and 600
mg) (Shults, Arch Neurol 2002).
Although some studies have found CoQ10 to lower elevated
blood pressure, a critical review of these studies concluded that CoQ10
does not have a clinically significant effect in lowering blood pressure (Ho, Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016).
Interestingly, one physician found that CoQ10 helped maintain blood pressure in
seven older people with orthostatic hypotension (low blood
pressure upon standing) who were also using traditional treatments (clonidine,
salt tablets, compression stockings etc.). The patients were given 257 mg of
CoQ10 daily for approximately eight months. This apparently reduced the drop in
systolic blood pressure upon standing from 30 mmHg to just 7 mmHg, although the
study lacked controls and can only be considered preliminary. Three of the
individuals had signs of multiple system atrophy, an neurodegenerative disease
that can affect the autonomic nervous system (and therefore, blood pressure)
and is associated with mutations in an enzyme involved in CoQ10 synthesis (Rembold, Am J Med 2017).
A clinical study in India suggested that taking 100 mg of CoQ10
daily for two months could significantly lower elevated homocysteine
levels. However, the study had no placebo control, so the results area
inconclusive (Ritu, J Clin Trials Cardiol 2014).
In a placebo-controlled study in China, neither a low (60 mg) nor higher (150
mg) dose of CoQ10 taken daily for three months had a significant effect on
homocysteine levels (Lee, Nutrition 2012).
Furthermore, a study among healthy older men and women in Japan (average age
59) whose homocysteine levels were not elevated found that supplementation with
100 mg to 120 mg of ubiquinol for six to twelve months had no effect on
homocysteine levels in men and slightly increased levels in women — although
this study did not include a control group, making the results inconclusive (Kinoshita, Funct Foods Health Dis 2016). In
short, there is no solid evidence that CoQ10 or ubiquinol lowers homocysteine
levels. Also, keep in mind that although elevated homocysteine is associated
with a higher risk of heart disease, lowering homocysteine levels have not been
shown to be beneficial.
A preliminary study
suggested that CoQ10 (200 mg three times a day for 60 days) improved ovarian
response to gonadotrophin stimulation in young women with low ovarian
reserve (Xu, Reprod Biol Endorinol 2018),
although no such benefit was reported when adding CoQ10 (amount not published)
to treatment with DHEA (Ryan, Fert Steril 2013 - abstract).
Skin
A preliminary study among 33 healthy, middle-aged women found that 150 mg of
water-soluble CoQ10 (Q10Vital® from Valens Intl.) taken daily for three months
significantly reduced visible wrinkles around the eyes, nose
and lips compared to placebo. However, there were no improvements in wrinkles
on the forehead or frown lines between eyebrows, nor were there improvements in
skin thickness or hydration, and there was no evidence of increased protection
from UV damage. A lower dose (50 mg) had more limited effectiveness (Zmitek, Biofactors 2016).
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
No U.S.
government agency is responsible for routinely testing CoQ10 or ubiquinol
supplements for their contents or quality. Research by ConsumerLab.com in most
years since it began testing CoQ10 supplement in 2000 has revealed that not all
CoQ10 supplements contain their claimed amounts of active ingredient. In this
review, ConsumerLab.com again evaluated CoQ10 products, as well as ubiquinol
products, to determine whether they contained the amounts of CoQ10 or ubiquinol
stated on their labels. Any product containing whole herb and/or 250 mg or more
of minerals per daily serving was tested for potential contamination with lead,
cadmium and arsenic. In addition, all regular tablets were tested to determine
if they would properly disintegrate. (See How Products Were Evaluated for
information on testing methods and passing score.) [Note: In past reviews,
ConsumerLab.com has checked CoQ10 and ubiquinol products for idebenone, a
potential manufacturing by-product, but none has been found. Consequently,
products were not tested for idebenone.]
The majority of products
tested in this Review are from popular and, generally, well-established brands,
as we are guided in our product selection by our readers' interests in brands
as conveyed in our annual survey. However,
it was brought to our attention in March, 2020 that an established brand, NOW
Foods, conducted its own tests of selected competing brands of CoQ10 sold
on Amazon.com in February, 2020. These brands are generally not popular among
our readers. Those tests suggested that products from several companies (NasaBe'Ahava,
Healthy Way, aSquared Nutrition, Mental Refreshment Nutrition, We Like Vitamins,
and NusaPure) contained less than 8% of their listed CoQ10, with
some having no detectable amount. ConsumerLab.com was not involved in this
testing and cannot vouch for its accuracy but was made aware of the results
from an online merchant, iHerb.com, which is an established online vendor
that posted the results as a PDF on
its own site.
What CL Found:
All 15
of the CoQ10 and ubiquinol products ConsumerLab.com selected for review
(including one CoQ10 product for pets) passed quality testing and label review.
An additional 18 products that underwent the same testing and review were
Approved through ConsumerLab.com's voluntary Quality Certification Program.
A high approval rate was also seen in 2019, when all but one
product passed testing in our review (the one product that did not pass,
contained nearly twice as much CoQ10 as labeled). With that said, there is a
great amount of diversity among products in terms of dose, cost, and additional
ingredients — primarily bioavailability enhancers -- as discussed below.
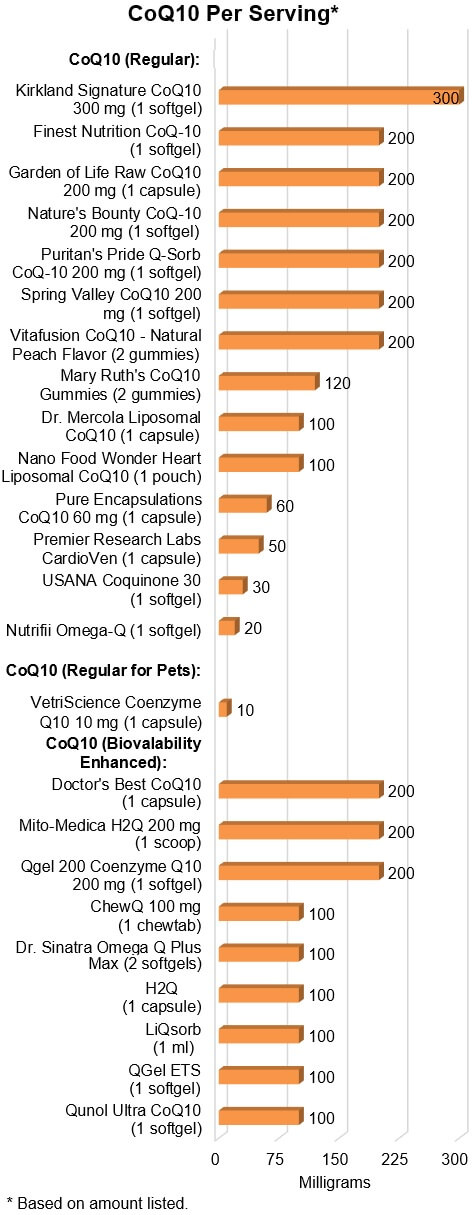
CoQ10:
As shown below, amounts of CoQ10 in the tested products ranged from ten-fold,
from 20 mg (or just 10 mg in a product for pets) to 300 mg per serving
(typically from one or two pills or other dosage units). It's important to know
the dose of CoQ10 that's appropriate for your particular use -- see ConsumerTips for dosage information.
There were major differences in cost among the CoQ10 products.
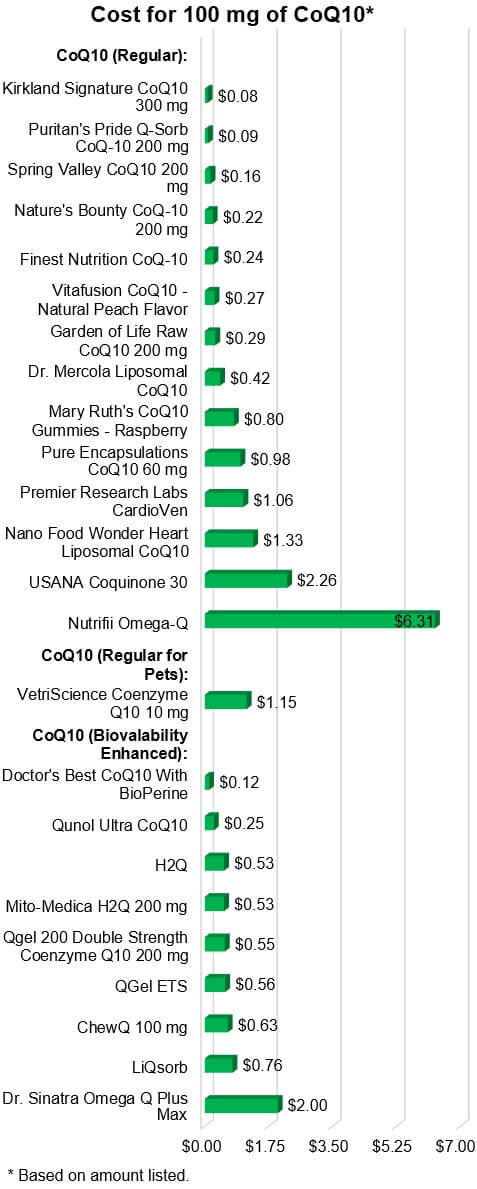
As shown in the graph below, the cost to obtain 100 mg of CoQ10 ranged from 8
cents to over $6. Lower-priced products tended to provide CoQ10 alone in oil
without other ingredients that may enhance absorption/bioavailability. More
expensive products tended represent delivery vehicles other than capsules and
softgels or include bioavailability enhancers and/or additional ingredients.
These differences are discussed further below, as they should be considered
when buying and using these supplements.
Absorption and
Bioavailability Enhancers:
Before focusing on specific Approved products, it is important to note that
only a small amount of CoQ10 is actually absorbed, although it can still
significantly increase CoQ10 blood levels. CoQ10, especially the dry dosage
form (tablet or capsule), is best absorbed when fats or oils are
present in the gastrointestinal tract, such as during a meal. The small
amount of oil (typically less than 1 gram of rice bran oil, soybean oil,
sunflower oil, vitamin E, or medium chain triglycerides listed as "Other
Ingredients") in softgels and some other formulations may slightly improve
absorption, although not nearly as much as a fat- or oil-containing meal, which
could easily provide 5 to 40 grams (or 1 to 8 teaspoons) of fats. These fats
stimulate the release of bile into the intestine, greatly facilitating
absorption of fat-soluble compounds, such as CoQ10 and ubiquinol.
Supplements with special absorption enhancers, such as
polysorbate 80 or cyclodextrin can make CoQ10 and ubiquinol more absorbable.
These formulations tend to cost more, but you may be able to use a lower dose.
On the other hand, if you will be taking the supplement with meals containing
fats/oils, solubility enhancers like polysorbate 80 may not be as necessary.
- Formulations designed to be water-soluble
Greater absorption may be achieved with CoQ10 that has been solubilized
with polysorbate 80 (such as "Q-Gel") or formulated
as water-soluble beadlets (sold as "All-Q"). These
formulations reduce the need for fats, as they make the product water soluble.
Bioavailability tests in people with softgels containing Q-Gel, for example,
showed that it achieved CoQ10 blood levels more than twice that
of softgels containing CoQ10 in oil, capsules containing CoQ10 powder, or
tablets made with CoQ10 powder. Another human bioavailability test showed All-Q
to be nearly equal to Q-Gel and both to be superior to Q-Sorb (which is not a
solubilized formula but does include rice bran oil).
Be aware that some people have sensitivity to polysorbate 80 and it can affect metabolism of other compounds including certain
prescription medications.
Another water-soluble form of CoQ10 is a cyclodextrin
complex (sold as "Chew-Q" and "Hydro-Q-Sorb")
which has been associated with increased absorption in laboratory models.
Water-soluble formulas do not have to be taken with fats or oils. However, it
is still best to take them with food because food slows down the transit time
through the small intestine, which is where CoQ10 and ubiquinol (and all
vitamins and minerals) are absorbed. Longer time in the intestine creates more
opportunity for absorption. Water-soluble formulas of CoQ10 and ubiquinol
should, obviously, also be taken with water. A study in older people given a
CoQ10 cyclodextrin complex in syrup form (Q10Vital from Valens
Int., Slovenia) found that a 5 mL dose (containing 100 mg of CoQ10) increased
ubiquinol levels in the blood 144% more than taking the same amount of CoQ10
from a standard capsule and was statistically equivalent to taking 100 mg of
ubiquinol from a standard capsule. However, all products were taken with a
light breakfast that may have contained little fat, so it is possible that
results for the two CoQ10 products would have been more similar if both had
been taken with a fatty meal (Pravst, Nutrients 2020).
"Nano" formulations are those in which very small
amounts of CoQ10 are microencapsulated with substances to make CoQ10 more
dispersible in water and improve absorption (Zhou, Biomed Res Int 2014; Cheuk, Food Chem 2015). Examples include:
·
VESISorb CoQ10 (SourceOne Global
Partners, Inc.), which consists of an oily core (triglycerides/orange
oil/CoQ10) that becomes encapsulated by surfactants (polysorbate/polyglycerol
esters). A small double-blind study that compared the bioavailability of a
single dose of 120 mg of VESISorb CoQ10 to the same dose of
other commercially available CoQ10 products (which were not named) showed that
the CoQ10 from VESISorb had 622% and 499% of the
bioavailability of an oil-based formula and of another solubilized formula,
respectively (Liu, Alt Ther 2009). The study was funded
by the maker of VESISorb. (VESISorb CoQ10 was not
included in this Review.)
·
NanoCell-Q, from Metagenics, is
promoted as having better absorption than standard CoQ10 based on a preliminary
study by Metagenics, but the study is not published and details of the study,
such as the dose used, are not available.
·
NanoCoQ10 (Pharmanex) is a
"nano" formula that utilizes cyclodextrin polysaccharides to improve
dispersion and claims to be up to "10 times more bioavailable" than
"powdered" CoQ10, but no research seems to be offered to support this
claim.
- Formulations designed to inhibit CoQ10/ubiquinol breakdown
Another approach to improving the bioavailability of CoQ10, as well as
ubiquinol, is taking it along with black pepper extract, also known
as piperine and sold as the branded ingredient Bioperine, which is also
frequently added to other supplements such as those containing turmeric or
curcumin. Piperine inhibits enzymes that breakdown CoQ10 and ubiquinol,
allowing you to achieve higher levels. A small clinical study showed that when
given daily for 30 days, adding 5 mg of piperine to 120 mg of CoQ10 (taken together
30 minutes after a fatty breakfast) resulted in a 30% increase in the amount of
CoQ10 in the blood compared to the same amount of CoQ10 taken without piperine
(Badmaev, J Nutr Biochem, 2000).
- Formulations that may not enhance absorption
If you see "crystal-free" CoQ10 formulations, such as CoQsol-CF and Q-Best (Best
Formulations), these are simply liquid CoQ10, meaning dry CoQ10 crystals have
been dissolved and, typically, combined with oil to enhance absorption. For
example, Q-Best contains liquid CoQ10 along with conjugated linoleic acid
(CLA), flaxseed oil and monoglycerides (a company-sponsored clinical trial
apparently showed improved absorption with this compared to dry CoQ10 powder,
although the results do not appear to have been published in a peer-reviewed
journal).
"Liposomal" formulations have sometimes been promoted
as improving absorption of CoQ10, but it is not clear that all of these
formulations provide a benefit. A liposomal formulation is one in which COQ10
or ubiquinol is encapsulated in small spheres. This is typically done by mixing
the CoQ10 or ubiquinol with a phospholipid, such as from the lecithin in
sunflower oil or soy oil. One study concluded that the bioavailability of a
such a liposomal formulation taken orally as a liquid was no better than from a
regular CoQ10 capsule when each was taken with a light breakfast (Vitetta, J Funct Biomater 2018). (For this reason we
have not classified all liposomal formulations as "bioavailability
enhanced" in this Review unless they include ingredients such as
polysorbate 80 or cyclodextrin).
Ubiquinol:
The CoQ10 found in most supplements is in the oxidized state
(ubiquinone), but once in the body it readily goes into the reduced state
(ubiquinol), which is its active, antioxidant form. Ubiquinol predominates in
the body. You can purchase supplements in which CoQ10 is already in the active
ubiquinol state. Ubiquinol is sometimes referred to as CoQH-10 or CoQH2-10 and
is marketed by a major supplier, Kaneka, as "QH."
Ubiquinol appears to have superior bioavailability to CoQ10. A
small study (funded by Kaneka) in healthy volunteers (ages 18 to 50) comparing
200 mg of each ingredient in identical softgel capsules found that, after 4
weeks of daily treatment, each significantly raised blood levels of total CoQ10
(i.e., the sum of ubiquinone and ubiquinol), but ubiquinol raised it 72% more
than CoQ10 (Langsjoen, Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 2014). Similarly, a small
study (also funded by Kaneka) in older men (average age 63) who took either 200
mg of CoQ10 or 200 mg of ubiquinol with a meal once daily for two weeks found
that only the ubiquinol supplement led to a statistically significantly
increase in average blood levels of total CoQ10, increasing it by 154% compared
to 63% with CoQ10, which was not considered statistically significant (Zhang, Food Funct 2018).
Ubiquinol is also sold by one company in solubilized and
stabilized forms as "Li-Q-Nol," "Quinogel,"
"Q-Nol" and "Carni-Q-Nol" (a formula that includes
L-carnitine). Another product like this is Qunol (as found in Qunol
Mega CoQ10 Ubiquinol). Like CoQ10, ubiquinol products may have better
absorption if they are "solubilized."
In the Results table below, products with bioavailability enhancers (excluding
small amounts of oil) are grouped separately and the second column of the table
indicates the specific enhancement compounds they claim to contain as well as
other ingredients.
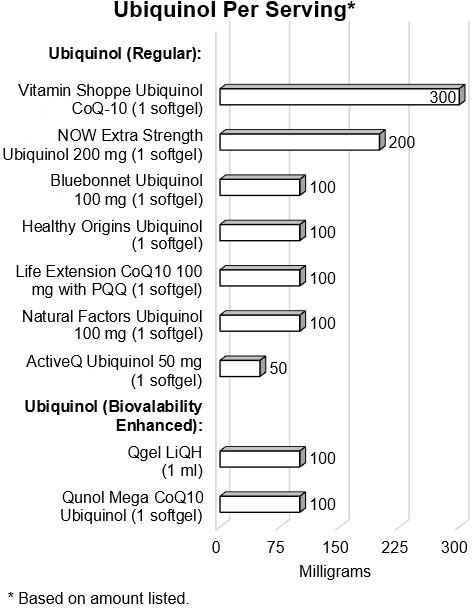
As shown below, the amount of ubiquinol per listed serving in
the products tested ranged from 50 to 300 mg, although considering the greater
bioavailability of ubiquinol over CoQ10, doses of 200 and, especially, 300 mg
seem rather high.
Considering the possible superior bioavailability of ubiquinol
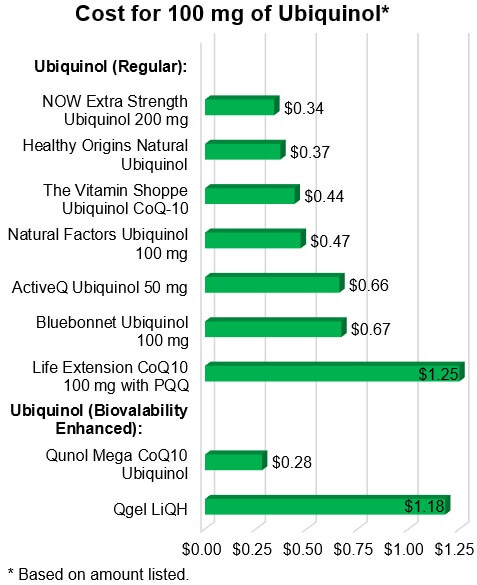
over regular CoQ10, the prices of most ubiquinol products were quite
reasonable, with the cost to obtain 100 mg ranging from just 28 cents
from Qunol Mega (which is bioavailability enhanced) to 67
cents from Bluebonnet, $1.18 from LiQH, (which is also
bioavailability-enhanced as well as a liquid formulation), and $1.25 from Life
Extension CoQ10 100 mg with PQQ — a combination of ubiquinol with PQQ
and a shilajit fulvic acid complex.
Top
Picks:
Considering our findings
for product quality, cost, and special features, below are our Top
Picks among the products.
CoQ10 Top Picks:
Regular CoQ10
If you are using a dose of 200 mg of CoQ10, our Top Pick is Puritan's
Pride Q-Sorb CoQ-10 200 mg, as it provides 200 mg for just 17 cents.
This works out to just 9 cents per 100 mg, which is the second lowest cost for
CoQ10 among the tested products. Although this product is called Q-Sorb, be
aware that it is not a bioavailability-enhanced formulation. Also be aware that
200 mg is a somewhat high dose for CoQ10, particularly if you are only taking
it to offset a decline in CoQ10 due to statins. A lower dose, such as 50 mg
twice daily may be sufficient. Unfortunately, none of the products with under
200 mg per unit were as inexpensive as this Puritan Pride's supplement.
Among the more
moderate-dose CoQ10 supplements that we reviewed, the lowest cost for just 100
mg was from a single VitaFusion CoQ10 gummy, costing 27
cents, although it comes with 12.5 Calories from added sugars. It is a soft
gummy with a nice peach flavor. If you want to spare the calories and want a
moderate dose, you will, unfortunately, have to pay more: Dr. Mercola
Liposomal CoQ10 provides 100 mg for 42 cents, Pure
Encapsulations CoQ10 60 mg provides 60 mg for 59 cents, and USANA
Coquinone 30 provides just 30 mg in a softgel for 68 cents. That's
right, the less you get, the more you have to pay with these particular
products!
Should you need a much
higher dose of CoQ10, Kirkland Signature [Costco] Maximum
Potency CoQ10 300 mg is a good choice and very well priced at 25 cents
per softgel (just 8 cents per 100 mg of CoQ10).
As noted earlier, these
products do not contain bioavailability enhancers, but as long as you take them
around the time of a meal containing a fair amount of oils or fats, this should
not matter.
Regular CoQ10 for Pets
We only tested one supplement marketed specifically for pets — VetriScience
Coenzyme Q10 10 mg — For Dogs and Cats. It passed our tests, providing its
claimed 10 mg per capsule, costing 12 cents. While this is not expensive for a
pill, it's actually a relatively expensive for just 10 mg and there is nothing
special about the capsules, which are similar to other cellulose-based
(vegetarian) capsules for people.
Bioavailability-Enhanced
CoQ10:
For those who can't time
their dosing to a meal and need to take CoQ10 with just water, it's best to use
a product that has been formulated to be water-soluble. The choices are
products that use either polysorbate 80 (in the ingredient QGel)
or cyclodextrin (in the ingredient HydroQsorb) to make the CoQ10 more water
soluble. Among the products we tested, the least expensive by far is Qunol
Ultra CoQ10, making it our Top Pick for
bioavailability-enhanced CoQ10. Qunol Ultra provides 100
mg of bioavailability-enhanced CoQ10 for just 25 cents per softgel, about ½ the
price of the other water-soluble CoQ10 supplements. Be aware that each softgel
also contains 68 mg of vitamin E, which is more than 4 times the daily
requirement for adults, but this is far below amounts that pose a concern. [link to
Concerns and Cautions section of Vitamin E Review] If you are taking this
supplement with just water (and not with a meal to boost CoQ10 absorption), it
would potentially double the amount of CoQ10 that you absorb versus taking
regular CoQ10.
Although not
water-soluble, even less expensive than Qunol Ultra is Doctor's Best
High Absorption CoQ10. It may help boost CoQ10 levels by about 30% due to
its inclusion of 5 mg of black pepper extract which interferes with the
breakdown of CoQ10. It costs just 23 cents per 200 mg capsule (12 cents per 100
mg). However, the black pepper extract can interact with other medications you
take (see Concerns and Cautions for black pepper extract).
Ubiquinol Top
Picks:
Regular Ubiquinol
Our Top Pick for regular ubiquinol is Healthy
Origins Natural Ubiquinol, providing 100 mg of ubiquinol in one softgel
for 37 cents. This product was also our Top Pick in our last two
reviews of this category, although the price has fallen from 55 cents in 2016
and 43 cents in 2019. NOW Extra Strength Ubiquinol (200 mg) is
a slightly less expensive source of CoQ10, but the 100 mg dose of Healthy
Origins gives the consumer more dosage flexibility.
Bioavailability-Enhanced
Ubiquinol:
If you want ubiquinol with an absorption enhancer, like polysorbate 80,
our Top Pick is Qunol Mega CoQ10 at
just 28 cents per softgel providing 100 mg of ubiquinol. This was also
our Top Pick for this category in 2019, when the price was a
little higher (34 cents per softgel). Interestingly, the current price makes
this the least expensive source of ubiquinol among all of the ubiquinol
products in this review, including those without an absorption enhancer.
Test Results by Product:
Listed
alphabetically below are the test results for 33 CoQ10 and ubiquinol
supplements. ConsumerLab.com selected 15 of these products. Eighteen others
(each indicated with a CL flask) were tested at the request of their manufacturers/distributors
through CL's voluntary Quality Certification Program and
are included for having passed testing.
Shown for each product is
the labeled amount of CoQ10 or ubiquinol per labeled serving, identified
bioavailability enhancers, and the daily serving size. The calculated cost to
obtain 100 mg of CoQ10 or ubiquinol is provided in the 4th column along with price information.
Notable features regarding allergens and significant amounts of other active
ingredients are noted in the 5th column, and the full list of ingredients for each product
is shown in the final column.
Pill sizes:
Due to the relatively large amounts of CoQ10 and ubiquinol in pills (typically
softgels or capsules), be aware that the pills tend be larger than for most
other supplements. In case you have trouble swallowing large pills, we've
included pill size information for each product in the 3rd column of the
results table, and the sizes are defined in a pop-up information box at the top
of that column. To give you a better idea of the sizes, below are examples
(from left to right) of a large softgel, medium/large softgel, and medium
softgel.

Jump to results for:
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of CoQ10 And Ubiquinol Supplements
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Approval Statusⓘ
Product Name
Claimed Amountⓘ of
CoQ10 or Ubiquinol Per Serving
Pill Sizeⓘ
Taste/Flavor
Suggested Serving on Label
Cost for Suggested Serving
[Price per 100 mg CoQ10 or Ubiquinol]
Price
Notable Features
Full List of Ingredients Per Serving
CoQ10 (Regular):
APPROVED
Dr. Mercola® Liposomal CoQ10
Dist. by NHP
1 capsule
100 mg
✔
Large capsule
Adults, take one (1) capsule daily with food and water.
$0.42/capsule
[$0.42]
$37.58/3 pack of 30 capsule bottles (90 capsules total)
Precaution: Contains Fish (Tilapia).
1 capsule
CoQ10 (Ubiquinone) 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium Chain Triglycerides, Calcium Carbonate, Sunflower
Lecithin, Capsule (Fish, Gelatin), Beeswax, Paprika Extract (for Color).
APPROVED
Finest Nutrition® [Walgreens] CoQ-10
Dist. by Walgreen Co.
1 softgel
200 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
As a dietary supplement for adults, take one (1) softgel daily with the meal of
your choice.
$0.47/softgel
[$0.24]
$28.35/60 softgels
No Yeast, No Wheat, No Gluten, No Milk Or Milk
Derivatives, No Lactose, No Sugar, No Preservatives, No Artificial Color,
Artificial Flavor, No Sodium.
Precaution: Contains soy ingredients.
1 softgel
Calories 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Coenzyme Q10 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Rice Bran Oil, Gelatin, Vegetable Glycerin. Contains <2%
of: Silica, Soy Lecithin.
APPROVED
Garden of Life™ Raw CoQ10 200 mg ![]()
Dist. by Garden of Life LLC
1 vegan capsule
200 mg
✔
Also tested and Approved for heavy metalsⓘ
Large vegan capsule
Adults take 1 capsule per day.
$0.58/vegan capsule
[$0.29]
$34.94/60 vegan capsules
RAW cold-pressed chia seed oil 444 mg, omega-3s
250 mg, omega-6s 71 mg, omega-9s 25 mg, RAW organic fruit & vegetable blend
30 mg & RAW probiotic blend 7 mg per vegan capsule
Kosher. Non GMO Project Verified seal, more...
1 vegan capsule
RAW Cold-Pressed Chia Seed Oil 444 mg, Omega-3s (as alpha-Linolenic Acid) 250
mg, Omega-6s (as Linoleic Acid) 71 mg, Omega-9s (as Oleic Acid) 25 mg, RAW
CoQ10 200 mg, RAW Organic Fruit & Vegetable Blend, more...
APPROVED
Kirkland Signature [Costco] Maximum Potency
CoQ10 300 mg ![]()
Dist. by Costco Wholesale Corporation
1 softgel
300 mg
✔
Large softgel
Take one (1) softgel daily or as directed by a physician.
$0.25/softgel
[$0.08]
$24.99/100 softgels
USP Dietary Supplement Verified® seal. No
Preservatives Added. No Artificial Colors. No Artificial Flavors. No Yeast or
Gluten. No Lactose.
Precaution: Contains: soy.
1 softgel
Calories 10, Total Fat 1 g, Coenzyme Q10 300 mg.
Ingredients: Soybean Oil, Coenzyme Q10 (Ubidecarenone), Gelatin (Bovine),
Glycerin, Soy Lecithin, Silica.
APPROVED
Mary Ruth's® CoQ10 Gummies - Raspberry
Dist. by Mary Ruth Organics LLC
2 gummies
120 mg
✔
Large heart-shaped gummy
Somewhat dry gummy, raspberry flavor
Adults 2 gummies per day as recommended by a physician or healthcare
professional.
$0.97/2 gummies
[$0.80]
$28.95/60 gummies
Sodium 20 mg per 2 gummies
Non-GMO. Gluten Free. No Gelatin. Vegan. Soy Free. Pectin based.
Precaution: Contains Nuts (Coconut Oil).
2 gummies
Calories 20, Total Carbohydrate 6 g, Total Sugars [Includes 2 g Added Sugars] 2
g, Sodium 20 mg, Coenzyme Q10 120 mg.
Other Ingredients: Organic Non-GMO Vegan Cane Sugar, more...
APPROVED
Nano Food Wonder Heart Liposomal CoQ10 -
Raspberry Flavor
Dist. by Codeage LLC
1 pouch [~10 ml]
100 mg
✔
Creamy but unpleasant flavor of rancid oil
Take 1 pouch daily or as directed by your healthcare provider.
$1.33/pouch
[$1.33]
$39.99/30 pouches
Does not contain: GMO, MSG, gluten, dairy,
wheat, soy, yeast, lactose or milk.
1 pouch
Calories 54, Total Fat 3 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Polyunsaturated Fat 0 g,
Monounsaturated Fat 3 g, Cholesterol Fat 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 5 g, Total
Sugars 0 g, CoQ10 as Ubiquinone 100 mg, more...
APPROVED
Nature's Bounty® CoQ-10 200 mg ![]()
Mfd. by Nature's Bounty, Inc.
1 softgel
200 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
For adults, take one (1) softgel daily, preferably with a meal.
$0.44/softgel
[$0.22]
$34.98/80 softgels
Non-GMO. No Artificial Color, No Artificial
Flavor, No Artificial Sweetener, No Preservatives, No Sugar, No Starch, No
Milk, No Lactose, No Gluten, No Wheat, No Yeast, No Fish. Sodium Free.
Precaution: Contains soy ingredients.
1 softgel
Calories 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Coenzyme Q10 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Rice Bran Oil, Gelatin, Vegetable Glycerin. Contains <2%
of: Silica, Soy Lecithin.
APPROVED
Also APPROVED for Fish Oil
Dist. by Ariix
1 softgel
20 mg
✔
Also tested and Approved for heavy metalsⓘ
Large softgel
Take 1 softgel twice daily, preferably with meals.
$1.26/softgel
[$6.31]
$70.70/56 softgels
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA - 295 mg, DHA - 235 mg)
530 mg
1 softgel
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA - 295 mg, DHA - 235 mg) 530 mg, Coenzyme Q10 20 mg.
Other Ingredients: Fish Oil, Gelatin, Glycerin, Extra Virgin Olive Oil, Lemon
Oil, Carob Bean Extract.
APPROVED
Premier Research Labs CardioVen™
Mfd. by Premier Research Labs, LP
1 plant-source capsule
50 mg
✔
Also tested and Approved for heavy metalsⓘ
Large plant-source capsule
Take 1 capsule, 3 times daily or as directed by a health professional.
$0.53/plant-source capsule
[$1.06]
$31.94/60 plant-source capsules
Cardio PhytoEssence™ 185 mg & Cardio Pro
Essentials™ 172 mg per plant-source capsule
Manufactured to avoid: added magnesium stearate (an undesirable excipient),
artificial colors, more...
1 plant-source capsule
Cardio PhytoEssence™ [Organic Blueberry (fruit), Organic Rice Fiber, Organic
Hawthorn Berry (Crataegus spp.), Organic Cayenne (fruit) (Capsicum
annuum), Organic Beet (root) (Beta vulgaris), more...
APPROVED
Pure Encapsulations® CoQ10 60 mg
Mfd. by Pure Encapsulations
1 capsule
60 mg
✔
Medium/large capsule
1 capsule, 1-2 times daily, with meals
$0.59/capsule
[$0.98]
$35.30/60 capsules
Gluten -free, Non-GMO & Hypoallergenic.
1 capsule
Coenzyme Q10 60 mg.
Other Ingredients: Hypoallergenic plant fiber (cellulose), vegetarian capsule
(cellulose, water).
APPROVED
Top Pick
for 200 mg CoQ10
Puritan's Pride® Q-Sorb™ CoQ-10 200 mg ![]()
Mfd. by Puritan's Pride, Inc.
1 softgel
200 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
For adults, take one (1) softgel one to two times daily, preferably with meals.
$0.17/softgel
[$0.09]
$123.98/6 bottlesⓘ of
120 capsules (720 capsules total)
Non-GMO. No Artificial Color, Flavor, Sweetener,
No Sugar, No Starch, No Milk, No Lactose, No Gluten, No Wheat, No Yeast, No
Fish. Sodium Free.
Precaution: Contains soy ingredients.
1 softgel
Calories 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Coenzyme Q10 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Rice Bran Oil, Gelatin, Vegetable Glycerin. Contains <2%
of: Silica, Soy Lecithin.
APPROVED
Spring Valley™ [Walmart] CoQ10 200 mg ![]()
Dist. by Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.
1 softgel
200 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
Adults, take one softgel daily, preferably with a meal.
$0.31/softgel
[$0.16]
$18.64/60 softgels
No Gluten, Yeast, Wheat, Milk or Milk
Derivatives, Lactose, Sugar, Preservatives, Artificial Color, Artificial
Flavor, Sodium (less than 5 mg per serving).
Precaution: Contains Soy.
1 softgel
Calories 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Coenzyme Q10 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Rice Bran Oil, Gelatin, Glycerin. Contains <2% of:
Silica, Soy Lecithin.
APPROVED
Mfd. by USANA Health Sciences, Inc.
1 soft gel capsule
30 mg
✔
Medium/large soft gel capsule
Take one (1) or two (2) capsules daily, preferably with food.
$0.68/soft gel capsule
[$2.26]
$37.95/56 soft gel capsules
Alpha-lipoic acid 13 mg per soft gel capsule
Precaution: Contains: Soy.
1 soft gel capsule
Coenzyme Q10 30 mg, Alpha-Lipoic Acid 13 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium Chain Triglycerides, Gelatin, Glycerin Monooleate,
Soy Lecithin, Glycerin, Purified Water, Annatto Seed Extract (Color), Titanium Dioxide.
APPROVED
Top Pick
for 100 mg CoQ10
Vitafusion™ CoQ10 - Natural Peach Flavor
Dist. by Church & Dwight Co., Inc.
2 gummies
200 mg
✔
Medium/large gummy
Very soft gummy, nice peach flavor
Adults take two (2) gummy supplements per day.
$0.53/2 gummies
[$0.27]
$15.99/60 gummies
No Artificial Flavors or Sweeteners. No Gluten.
No High Fructose Corn Syrup. No Dairy. No Synthetic Dyes.
Precaution: Contains: tree nuts (coconut), more...
2 gummies
Calories 25, Total Carbohydrate 5 g, Total Sugars [Includes 4 g Added Sugars] 4
g, Coenzyme Q10 (as ubiquinone) 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Glucose syrup, sugar, water, gelatin, more...
CoQ10 (Regular for Pets):
APPROVED
VetriScience® Coenzyme Q10 10 mg - For Dogs +
Cats
Dist. by VetriScience® Laboratories
1 capsule
10 mg
✔
Medium/large capsule
Give 1 capsule daily per 10 lbs of body weight. If giving more than 1 capsule,
divide between AM and PM.
$0.12/capsule
[$1.15]
$11.50/100 capsules
NASC Quality Seal.
Precaution: For use in dogs and cats only.
1 capsule
Coenzyme Q10 10 mg.
Inactive Ingredients: Cellulose, maltodextrin, silicon dioxide, vegetable
cellulose (capsule), vegetarian leucine.
CoQ10 (Bioavailability Enhanced):
APPROVED
Mfd. by Tishcon Corp.
1 chewtab
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: HydroQsorb® (a solubility enhancer to
make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Medium/large circular chewtab
Easy to chew tablet, light orange flavor
Chew one (1) chewtab with or after a meal as a dietary supplement, or as
recommended by your healthcare professional.
$0.63/chewtab
[$0.63]
$37.95/60 chewtabs
Free of: milk or milk by-products, egg or egg
by-products, fish or fish by-products, shellfish or shellfish by-products, tree
nuts, wheat or wheat by-products, peanuts or peanut by-products, soybeans or
soy by-products, more...
1 chewtab
Calories 5, Total Carbohydrates 1 g, Coenzyme Q10 (ubidecarenone USP) 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Xylitol, gamma cyclodextrin, S.D. orange, flavor, gum acacia, more...
APPROVED
Doctor's Best® High Absorption CoQ10 With
BioPerine®
Dist. by Doctor's Best, Inc.
1 veggie cap
200 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Black pepper extract (a solubility
enhancer to make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Large veggie cap
Take 1 capsule daily preferably with food for maximum absorption, or as
recommended by a nutritionally-informed physician.
$0.23/veggie cap
[$0.12]
$41.42/180 veggie caps
Black pepper extract 5 mg per veggie cap
Non-GMO / Gluten Free / Soy Free / Vegan.
1 veggie cap
Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone) 200 mg, Black Pepper Ext. (Piper nigrum) (fruit)
(standardized to contain 95% Piperine) (BioPerine®) 5 mg.
Other Ingredients: Rice powder, hypromellose (vegetarian capsule), silicon
dioxide, magnesium stearate (vegetable source).
APPROVED
Dist. by Healthy Directions
2 softgels
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: HydroQsorb® (a solubility enhancer to
make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Also tested and Approved for heavy metalsⓘ
Very large softgel
Take 2 softgels once daily with a meal.
$2.00/2 softgels
[$2.00]
$59.99/60 softgels
Vitamin B6 30 mg, folate 680 mcg DFE, vitamin
B12 500 mcg, chromium 400 mcg, CalaMarine® oil concentrate [DHA 350 mg, EPA 200
mg] 1,250 mg, L-carnitine fumarate 174 mg, HydroCurc® 125 mg & trans
resveratrol 30 mg per 2 softgels, more...
2 softgel
Calories 20, Total Fat 1.5 g, Cholesterol <5 mg, Vitamin B6 (as pyridoxine
hydrochloride, pyridoxal-5-phosphate) 30 mg, Folate 680 mcg DFE, Vitamin B12
(as cyanocobalamin) 500 mcg, more...
APPROVED
Mfd. by Health Thru Nutrition
1 vegecap
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: HydroQsorb® (a solubility enhancer to
make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Large vegecap
Adults, take one (1) to three (3) VegeCaps daily with a meal, or as directed by
a qualified healthcare practitioner.
$0.53/vegecap
[$0.53]
$32.01/60 vegecaps
Free of: milk or milk by-products, egg or egg
by-products, fish or fish by-products, shellfish or shellfish by-products, tree
nuts, wheat or wheat by-products, peanuts or peanut by-products and soybean or
soy by-products.
1 vegecap
Coenzyme Q10 (ubidecarenone USP, as HydroQsorb® 100% water soluble CoQ10) 100
mg.
Other Ingredients: Gamma-cyclodextrin and hypromellose.
APPROVED
Dist. by Tishcon Corp.
1 ml
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Add 1 ml to 6 to 8 ounces of your favorite
juice, smoothie or milk shake for a delicious treat supplying 100 mg of
hydrosoluble CoQ10.
$0.76/ml
[$0.76]
$129.00/170 ml bottle [approx. 170 servings]
Sugar-Free.
Precaution: Contains soy.
1 ml
Coenzyme Q10 (Liposomal) 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Purified water, medium chain triglycerides, soy lecithin,
polysorbate 80, citric acid, potassium sorbate and alpha tocopherol.
APPROVED
Dist. by Epic
1 scoop [1 g]
200 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: HydroQsorb® (a solubility enhancer to
make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Mix one (1) to two (2) scoops daily with your
favorite drink, water or pudding, as a dietary supplement or as directed by
your health care professional.
$1.07/scoop
[$0.53]
$79.95/75 g container (approx. 75 servings)
Free of: milk, egg, fish, shellfish, tree nuts,
wheat, peanuts and soybeans. Non GMO, Gluten Free, Soy Free.
1 scoop
Calories 3, Calories From Fat 0, Total Fat 0 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Trans Fat 0
g, Cholesterol 0 g, Sodium 0 g, Potassium 0 g, Total Carbohydrate 0.7 g,
Dietary Fiber 0 g, Total Sugar 0 g, Sugar Alcohol 0 g, more...
APPROVED
Qgel® 200 Double Strength Coenzyme Q10 200 mg![]()
Dist. by Gel-Tec, Division of Tishcon Corp.
1 softgel
200 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Large softgel
Take one (1) softgel daily as a dietary supplement or as directed by your
healthcare professional.
$1.10/softgel
[$0.55]
$66.00/60 softgels
Vitamin E 40.50 mg per softgel
Free of: milk or milk by-products, egg or egg by-products, fish or fish
by-products, shellfish or shellfish by-products, wheat or wheat by-products,
peanuts or peanut by-products and soybeans or soy by-products and gluten.
1 softgel
Calories 5, Vitamin E (as DL-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate) 40.50 mg, Coenzyme Q10
200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Polysorbate 80, D-Limonene, gelatin, medium chain
triglycerides, glycerin, sorbitol, more...
APPROVED
Dist. by Tishcon Corp.
1 softgel
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Medium/large softgel
Adults: Take one (1) softgel daily as a dietary supplement or as recommended by
your healthcare professional.
$0.56/90 softgels
[$0.56]
$49.99/90 softgels
Free of: milk or milk byproducts, egg or egg
byproducts, fish or fish byproducts, shellfish or shellfish byproducts, wheat
or wheat byproducts, peanuts or peanut byproducts, and soybeans and soy
byproducts.
1 softgel
Coenzyme Q10 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Polysorbate 80, D-Limonene, gelatin, medium chain
triglycerides, glycerin, sorbitol, purified water and annatto suspension in
sunflower oil.
APPROVED
Top Pick
for bioavailability-enhanced CoQ10
Dist. by Quten Research Institute, LLC
1 softgel
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make CoQ10 water soluble)
✔
Large softgel
Adults take one (1) softgel, once per day with food, or as recommended by your
healthcare professional.
$0.25/softgel
[$0.25]
$29.97/120 softgels
Vitamin E 68 mg per softgel
Free Of: Milk or milk by-products, egg or egg by-products, fish or fish
by-products, shellfish or shellfish by-products, wheat or wheat by-products and
peanuts or peanut by-products, more...
1 softgel
Calories 7, Vitamin E (as dl-alpha tocopheryl acetate) 68 mg, Coenzyme Q10
(Ubiquinone USP Grade) 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Polysorbate 80, medium chain triglycerides (palm oil),
gelatin, more...
Ubiquinol (Regular):
APPROVED
ActiveQ® Ubiquinol 50 mg
Mfd. by Gel-Tec, Division of Tishcon Corp.
1 softgel
50 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
Adults: Take one (1) to two (2) softgels daily with meals as a dietary
supplement or as directed by your healthcare professional.
$0.33/softgel
[$0.66]
$33.00/100 softgels
Non-GMO, Free of: milk or milk by-products, egg
or egg by-products, fish or fish by-products, shellfish or shellfish
by-products, tree nuts, wheat or wheat by-products, peanuts or peanut
by-products, soybeans or soy by-products and gluten.
1 softgel
Ubiquinol (Kaneka Ubiquinol™) [active form of Coenzyme Q10] 50 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium chain triglycerides, gelatin, glycerin, ascorbyl
palmitate, purified water, white beeswax, more...
APPROVED
Bluebonnet Ubiquinol 100 mg
Dist. by Bluebonnet Nutrition Corporation
1 vegetarian softgel
100 mg
✔
Medium/large vegetarian softgel
Take one vegetarian softgel daily, preferably with a meal or as directed by a
healthcare practitioner.
$0.67/vegetarian softgel
[$0.67]
$39.96/60 vegetarian softgels
Non GMO. Soy Free. Free of milk, egg, fish,
crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat and soybeans. Also free of
gluten, barley, rice, sodium and sugar.
1 vegetarian softgel
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium chain triglycerides, vegetarian capsule (soluble food
starch, glycerin, sea vegetable extract, purified water, lycopene, more...
APPROVED
Top Pick
for regular ubiquinol
Healthy Origins Natural Ubiquinol
Dist. by Healthy Origins®
1 softgel
100 mg
✔
Large softgel
Take one (1) softgel once or twice daily with food, or as directed by a
physician.
$0.37/softgel
[$0.37]
$22.13/60 softgels
Not manufactured with wheat, gluten, soy, milk,
egg, fish, shellfish, peanut or tree nut derived ingredients. Non GMO.
1 softgel
Kaneka Ubiquinol™ 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium Chain Triglycerides, Kosher Gelatin, Glycerin
(Vegetarian), Ascorbyl Palmitate, Purified Water, more...
APPROVED
Also Approved for PQQ
Life Extension® CoQ10 100 mg with PQQⓘ![]()
Dist. by Quality Supplements and Vitamins, Inc.
1 softgel
100 mg
✔
Also tested and Approved for heavy metalsⓘ
Medium/large softgel
Take one (1) softgel daily with food, or as recommended by a healthcare
practitioner.
$1.25/softgel
[$1.25]
$37.50/30 softgels
Shilajit fulvic acid complex 100 mg & PQQ
disodium salt 10 mg per softgel
Gluten Free. Non GMO.
1 softgelCalories 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Ubiquinol (as Kaneka
Ubiquinol™) 100 mg, PrimaVie® Shilajit fulvic acid complex 100 mg, PQQ
(pyrroloquinoline quinone) disodium salt 10 mg.Other Ingredients: Medium chain
triglycerides, gelatin, glycerin, purified water, beeswax, sunflower lecithin,
annatto color, rosemary extract.
APPROVED
Natural Factors® Ubiquinol Active CoQ10 100 mg![]()
Mfd. by Natural Factors Canada
1 softgel
100 mg
✔
Medium/large softgel
1 softgel 1-3 times per day or as directed by a health professional.
$0.47/softgel
[$0.47]
$55.97/120 softgels
Organic flaxseed oil 295 mg per softgel
Contains no artificial colors, preservatives, or sweeteners; no dairy,
starch, sugar, wheat, gluten, yeast, soy, corn, egg, fish, shellfish, salt,
tree nuts, or GMOs.
1 softgel
CoQ10 Ubiquinol Form (as Kaneka Q+) 100 mg, Organic Flaxseed Oil (Linum
usitatissimum) 295 mg.
Other Ingredients: Softgel (gelatin, glycerin, purified water, carob), yellow
beeswax, sunflower lecithin (non-GMO), vitamin E (non-GMO) sunflower oil.
APPROVED
NOW® Extra Strength Ubiquinol 200 mg
Dist. by Now Foods
1 softgel
200 mg
✔
Large softgel
Take 1 softgel daily with a fat-containing meal.
$0.68/softgel
[$0.34]
$40.87/60 softgels
Not manufactured with wheat, gluten, soy, milk,
eggs, fish or shellfish ingredients. Produced in a GMP facility that processes
other ingredients containing these allergens, more...
1 softgel
Ubiquinol (Kaneka Ubiquinol™) (Reduced Form CoQ10) 200 mg.
Other Ingredients: MCT Oil (medium chain triglycerides), Softgel Capsule, more...
APPROVED
The Vitamin Shoppe® Triple Strength Ubiquinol
CoQ-10
Dist. by Vitamin Shoppe, Inc.
1 softgel
300 mg
✔
Large softgel
Take one (1) softgel daily, preferably with a meal.
$1.33/softgel
[$0.44]
$39.99/30 softgels
Gluten Free. Dairy Free. Nut Free. Soy Free.
1 softgel
Calories 10, Total Fat 1 g, Ubiquinol (Kaneka Ubiquinol™) 300 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium chain triglycerides, gelatin, ascorbyl palmitate,
glycerin, purified water, sunflower lecithin, white beeswax, more...
Ubiquinol (Bioavailability Enhanced):
APPROVED
Dist. by Tishcon Corp.
1 ml
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make ubiquinol water soluble)
✔
Add 1 mL to 6 to 8 ounces of your favorite
juice, smoothie or milk shake for delicious treat supplying 100 mg of
hydrosoluble™ Ubiquinol.
$1.18/ml
[$1.18]
$199.95/170 ml bottle [approx. 170 servings]
Precaution: Contains soy.
1 ml
Ubiquinol (Kaneka Ubiquinol™) [active form of Coenzyme CoQ10) 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Purified water, medium chain triglycerides, non-GMO soy
lecithin, more...
APPROVED
Top Pick
for bioavailability-enhanced ubiquinol
Dist. by Quten Research Institute, LLC
1 softgel
100 mg
Bioavailability enhancement: Polysorbate 80 (a solubility enhancer
to make ubiquinol water soluble)
✔
Large softgel
Adults take one (1) softgel daily, with or after a meal, or as recommended by
your healthcare professional.
$0.28/softgel
[$0.28]
$33.99/120 softgels
Gluten Free. Free Of: Milk or milk by-products,
egg or egg by-products, fish or fish by-products, shellfish or shellfish
by-products, tree nuts, wheat or wheat by-products, peanuts or peanut
by-products, and soybeans or soy by-products.
1 softgel
Calories 6, Vitamin C (as ascorbyl palmitate) 6 mg, Ubiquinol (Kaneka
Ubiquinol®) [active form of Coenzyme Q10] 100 mg.
Other Ingredients: Medium chain triglycerides (palm oil), polysorbate 80,
gelatin, glycerin, more...
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's ingredients differ from what is
listed above, it may not necessarily be of the same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
ConsumerTips™:
Dosage:
CoQ10:
The suggested daily dosage of CoQ10 products varies widely. In this review
alone, it ranged from 20 mg to 300 mg of CoQ10 or ubiquinol among products for
people. It is probably better to determine your dosage based on amounts that
have shown to be clinically effective (as described below) and based on the
recommendation of your health care provider.
Using CoQ10 to
treat congestive heart failure should be considered an adjunct
to, not a replacement for, other medications. A daily dose of 100 mg to 300 mg
of CoQ10 is generally used. Be aware that improvement in symptoms may take more
than one month. Don't suddenly stop taking CoQ10, because symptoms may worsen.
Tapering off the supplement is recommended.
Taking 300 mg to 400 mg
of CoQ10 (in 2- 3 divided doses) daily may reduce the frequency, duration,
and/or severity of migraines. Be aware it may take one to three
months of supplementation to achieve these benefits (Sandor, Neurology 2005; Nattagh-Eshtivania, Eur J Integr
Med 2018).
For reducing muscle
pain associated with statin use, a dose of 50 mg twice daily may be helpful
(Skarlovnik, Medical Science Monitor 2014).
CoQ10 can be taken at the same time as statin medication (Bargossi, Int J Clin Lab Res 1994).
Additionally, CoQ10 taken at the same time as lovastatin has been reported to
reduce statin-related muscle pain in patients with cancer (Thibault, Clin Cancer Res 1996). People who
take their statin medication in the evening may prefer to take CoQ10 earlier in
the day, as taking CoQ10 in the evening may cause insomnia in some individuals
(see Concerns and Cautions). Also, keep in mind
that CoQ10 is best absorbed with foods that contain fats or oils. If your
statin must be taken without food, take CoQ10 at a different time along with
food.
For other diseases, the
following daily doses have been used, although optimal dosage levels have not
been determined: For reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia during
pregnancy 200 mg (Teran, Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2009); for hypertension 120
to 200 mg; for angina 150 mg; for reducing the likelihood of future
heart problems in people who've had a first heart attack 120 mg;
for HIV/AIDS 200 mg; for muscular dystrophy 100
mg; for mitochondrial encephalomyopathies 150 to 160 mg and
sometimes higher; for increasing sperm motility 200 to 300 mg
(Safarinejad, J Urol 2009);
for increasing ubiquinol ratios in children with trisomy 21, 10 mg
of ubiquinol (liquid form) per kilogram of body weight.
A very small Japanese
study of eleven healthy elderly subjects given 100 mg per day of ubiquinol
showed increases in self-assessed "vitality" and "mental
health". This dose increased plasma concentrations of ubiquinol by
four-fold and increased the ratio of ubiquinol to CoQ10. Interestingly, the
effects were correlated with the increased ratio rather than the increased
concentration.
A study in veterans with
Gulf War illness found that taking 100 mg of CoQ10 (in oil from a softgel)
daily for 3 to 4 months appeared to improve physical functioning and, among
men, general self-rated health (Golomb, Neural Computation 2014).
Divided dosing (taking two or
three equally divided smaller doses instead of one large dose a day) is
recommended when the total daily dose exceeds 100 mg. It is also recommended
that you take CoQ10 with fatty meals to help increase
absorption.
See the discussion of
"Absorption and Bioavailability Enhancers"
in the What CL Found section above.
After age 60, the body
may be less efficient at converting CoQ10 to its active form, ubiquinol
(see What It Is). For this reason, people
over the age of 60 may want supplement with ubiquinol rather than
CoQ10.
Natural vs. Synthetic: Naturally formed CoQ10 is 100% in the
"trans" isomer form. Synthetically formed material is also
predominantly in the "trans" form with a small amount in the
"cis" form. Since the fermentation process using bacteria or yeast is
much cheaper than chemical synthesis and provides 100% natural (trans) CoQ10,
most, but not all, CoQ10 found in the marketplace today is made by a
fermentation process. This is sometimes (but not always) indicated on the label
with terms such as "yeast fermentation;" branded CoQ10 ingredients
known to be natural include Kaneka QH and Q-Gel (Tishcon).
A
compound called idebenone is a somewhat similar compound to CoQ10. It can be a
by-product of improperly made CoQ10, which is why ConsumerLab.com has tested
for idebenone as a contaminant in CoQ10 supplements in the past. Interestingly,
some evidence suggests that idebenone could be helpful for slowing cognitive
decline in Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia (Voronkova, Neurosci 2009; Weyer, Neuropsychobiology, 1997) but not all
studies have found a benefit (Thal, Neurology 2003).
Another compound,
mitoquinone (MitoQ) is marketed as a more "effective" form of
CoQ10 because the ubiquinone molecule is altered to carry a positive charge
that allows it to be better absorbed into the mitochondria of cells — and
consequently, can be taken at lower doses than regular CoQ10. MitoQ products
were not included in this Review.
In animal studies, MitoQ has been shown to be
absorbed into heart, brain, liver and kidney cells and appeared to reduce
oxidative damage in the mitochondria of some of these cells, after ingestion (Smith, Ann NY Acad Sci 2010). However, it should also be noted that MitoQ was
shown in a laboratory study to cause acute swelling in the mitochondria of
animal kidney tubule cells and to damage kidney tissue in mice, possibly due to
its ability to increase the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane. The
researchers advised that "caution should be exercised before using this
compound in renal patients," i.e., patients with kidney disease (Gottwald, Physiol Rep 2018). Testing in people
shows that MitoQ has an oral bioavailability of about 10%
(compared to about 2% for regular CoQ10 without an absorption-enhanced
formula). Doses of 40 mg and 80 mg of MitoQ have been shown to
reduce certain measures of liver damage in individuals with hepatitis C, but
had no beneficial effect in Parkinson's disease. Side-effects were similar to
those that may be experienced with high doses of CoQ10, such as headache and
nausea, although vomiting was also reported (Gane, Liver Int 2010; Snow, Mov Discord 2010).
A small
study among healthy older adults (aged 60 to 70 years) with impaired
endothelial function (i.e., stiffer arteries) found that 20 mg of MitoQ taken
daily for six weeks increased flow-mediated dilation of the brachial artery by
42% compared to those who took placebo. There was no significant effect on
blood pressure -- although the study participants did not have high blood
pressure. Levels of oxidized "bad" LDL cholesterol decreased by 13%
in those who took MitoQ, while there was no significant decrease in
those who took placebo. The researchers speculated that MitoQ be
might be effective in treating conditions affecting vascular function (Rossman, Hypertension 2018).
A
company-funded study among 16 recreational male cyclists (average age 44) found
that 20 mg of MitoQ taken daily 30 minutes before breakfast
for 28 days resulted in very slight, but statistically significant
improvements in exercise performance. Aerobic fitness (as determined by VO2peak, a measure of oxygen consumption) improved by
4.4%, and the time it took to complete a 5-mile timed cycling trial decreased
(12.91 vs. 13.09 minutes to completion) with MitoQ compared to
placebo, although MitoQ did not decrease perceived exertion (Broome, J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2021).
Tests for measuring CoQ10 levels in the blood
CoQ10 levels can be measured by a blood test, and may help to guide dosing for
individuals with CoQ10 deficiency, heart disease, or who are taking statin
drugs, which are known to lower blood levels of CoQ10. The test, usually
referred to as "Coenzyme Q10," "Coenzyme Q10, Total," or
"Ubiquinone 50" is available through well-known laboratories such as
Quest Diagnostics and LabCorp. The normal reference range for CoQ10 levels
using these tests is 0.5 - 1.7 micromol/L (Molyneux, Clin Biochem Rev 2008), or 0.44 -
1.64 mg/L. For people with heart disease, a therapeutic target range of 2 mg/L
or greater is sometimes recommended.
CoQ10 levels in the blood
do not necessarily reflect the levels found in tissue, such as heart and
skeletal muscle but are still considered a useful measure of CoQ10 status.
(While some studies have shown that supplementation may increase CoQ10 levels
in heart tissue in people with heart disease (Keith, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2008; Rosenfeldt, Biogerontology 2002; Folkers, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985), the
evidence is mixed. Additionally, because measuring CoQ10 levels in tissue
requires taking a tissue sample, or biopsy, this is not considered a practical
test for most people.)
Concerns and Cautions:
CoQ10
is generally safe and well-tolerated when taken by adults in appropriate amounts.
A study involving over 100 people with cardiomyopathy taking CoQ10 (100 mg
daily, divided into three doses) for several years (some as long as 6 years)
concluded that CoQ10 was safe — although the study had no control group (Langsjoen, Am J Cardiol, 1990). Doses as high
as 1,200 mg per day (divided into four doses taken with meals and at bedtime)
were used in a placebo-controlled study lasting 16 months which found CoQ10 to
be safe and well tolerated (Shults, Arch Neurol 2002).
Gastrointestinal side
effects such as loss of appetite, heartburn, nausea, and diarrhea have
been reported in about 1% of individuals taking CoQ10 in clinical trials;
rarely, headache, fatigue, irritability and skin rash have
also been reported (Hidaka, Biofactors 2008; Bonackdar Am Fam Physician 2005).
Gastrointestinal side effects may be minimized by taking smaller, divided doses
(Shinde, Internet J Nutr Wellness 2004).
CoQ10's safety has not
been evaluated for pregnant or breast-feeding women.
CoQ10 has been used
safely in children, under medical supervision, in doses up to 10 mg/kg/day for
up to nine months.
Although
some studies have found CoQ10 to lower elevated blood pressure, a
critical review of these studies concluded that CoQ10 does not have a
clinically significant effect in lowering blood pressure (Ho, Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016).
Certain medications,
including some cholesterol-lowering "statin" drugs,
beta-blockers, antidepressants, and antipsychotics may decrease the
body's natural production of CoQ10; therefore, the CoQ10 dosage for individuals
taking any of these drugs should possibly be higher than generally recommended.
Taking CoQ10 might interfere with the blood-thinning
effect of warfarin. There have been reports of CoQ10 decreasing the
blood-thinning effect, which could necessitate an increase in warfarin dosage (Spigset, Lancet 1994).
Interestingly, CoQ10 is chemically similar to vitamin K2, which can also
decrease the effectiveness of warfarin. However, a population-based study
suggested the opposite — an increased risk of bleeding with CoQ10 for people on
warfarin (Shalansky, Pharmacother 2007), and another
study suggested no effect in people with a stable INR (Engelsen, Ugeskr Laeger 2003). In any event,
it would seem prudent to inform your doctor if you wish to use CoQ10 with
warfarin, so that you are properly monitored. It is unclear whether CoQ10
interacts with the drug clopidogrel (Plavix), which works through a
different mechanism than warfarin.
A dose
of 100 mg or more of CoQ10 taken in the evening may cause mild insomnia in
some individuals (Pepping, Coenyzme Q10. AJHP 1999).
Even if taken during the day, high-dose CoQ10 (300 mg) may also cause sleep
problems, as suggested by a small study of veterans with Gulf War illness: 74%
reported sleep problems before the study. This fell to 64% among those given
100 mg of CoQ10 daily but increased to 83% among those given 300 mg (Golomb, Neural Computation 2014 —-
see What It Does, above, for more about this
study). If CoQ10 seems to cause insomnia, take it well before dinner time and
consider reducing the dose.
Thyroid hormones can affect CoQ10 levels in the body; in
hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) CoQ10 levels have been found to be the
lowest discovered in human diseases, while in hypothyroidism (underactive
thyroid), CoQ10 levels tend to be elevated (Mancini, Int J Mol Sci 2013). Treatment of
hyperthyroidism in children with methimazole (Tapazole) has been shown to
normalize CoQ10 levels in the body (Mancini, Int J Mol Sci 2011). However, it is
not known whether CoQ10 supplementation affects thyroid hormone levels and
interactions between CoQ10 and medication for hypothyroidism, such as
levothyroxine (Synthroid) have not been reported.
Use of CoQ10 (and other
antioxidant supplements) before or during chemotherapy treatment have been
associated with an increased risk of cancer recurrence or death in
women receiving treatment for breast cancer (Ambrosone, J Clin Oncol 2020). A study in mice
suggests that CoQ10 may also reduce the effectiveness of cancer
radiotherapy (Lund, Folia Microbio, 1998).
A case
of insulin autoimmune syndrome (IAS) possibly caused by CoQ10
was reported in 52-year-old woman Japan who had taken CoQ10 for 3 months. Her
symptoms resolved after stopping CoQ10 (Kusano, J Rural Med 2019). Symptoms of IAS
include sweating, shakiness, and weakness due to hypoglycemia.
People of Japanese ancestry may be more predisposed to IAS than others. Many
cases of IAS due to alpha-lipoic acid have
been reported in Japan, but this is the first reported case associated with
CoQ10.
Some products (including several in this review) include polysorbate
80 to help solubilize CoQ10 or ubiquinol. Although the FDA considers
polysorbate to be generally safe, some people may be sensitive to it and there
is a limit as to how much polysorbate 80 you should ingest daily. The FDA limits polysorbate 80 in
supplements to 175 to 475 mg per daily serving depending on other ingredients,
and the World Health Organization (WHO)
recommends that adults not consume more than a total 1,750 mg
(25 mg per kg of body weight) daily of polysorbate 80, which is also found in
food products such as frozen gelatin. Amounts of polysorbate 80 in supplements
are not listed on labels, but ConsumerLab.com estimates that amounts over 100
mg may be present in CoQ10 and ubiquinol supplements, particularly when the
ingredient appears early in the list of "Other ingredients." There
are isolated reports of people who have had anaphylactoid reactions to polysorbate
80 from medication given subcutaneously (Price, Allergy Asthma Proc 2007) or
intravenously (Coors, Ann Allergy Asthma Immol
2005), but not by mouth. There is theoretical concern that it may be
harmful to people with Crohn's disease (Roberts, Gut 2010).
Formulas
containing black pepper extract (piperine, Bioperine): Although in people,
there do not appear to be any reported adverse effects when these are taken at
typical doses and Bioperine® is self-affirmed GRAS (generally recognized as
safe) (FDA 2013), piperine
inhibits specific enzymes in the lining of the gut (such as "CYP"
enzymes) which otherwise break down certain compounds, and it may also affect
the permeability of the intestine. It would be best to avoid formulas
containing a black pepper extract if you are taking medications known to be
metabolized by CYP enzymes such as phenytoin, rifampin, propranolol
theophylline, felodipine, amlodipine and nevirapine. Piperine (at a dose of 20
mg) may increase the bioavailability of the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine
(Tegretol, Carbatro) (Pattanaik, Phytother Res 2009).
Laboratory evidence suggests that piperine may have anti-platelet effects. It
should be used with caution in people taking blood-thinning medication (Raghavendra, Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids 2009). They may also have diuretic properties
(increasing urine output) and stimulate the production of stomach acid (Meghwal, Scientific Reports 2012).
One animal study found lower doses of both black pepper extract and piperine to
have a laxative effect, while higher doses were found to slow intestinal
motility and have an antidiarrheal effect — although in these studies both
doses were significantly higher than amounts typically use supplements (Mehmood, J Med Food 2010).
Information on this site
is provided for informational purposes only. It is not an endorsement of any
product nor is it meant to substitute for the advice provided by physicians or
other healthcare professionals. The information contained herein should not be
used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease. Consumers should
inform their healthcare providers of the dietary supplements they take.
Latest Clinical Research Updates for CoQ10 and Ubiquinol
Supplements
11/30/2021
Can supplementing with
ubiquinol, the active form of CoQ10, improve heart function in people with
heart failure? See what a new study found in the What It Does section of our CoQ10 and
Ubiquinol Supplements Review. Also see our Top Picks among CoQ10 and ubiquinol supplements.
Supplement for Better Exercise Performance?
8/25/2021
Can taking a modified
form of CoQ10 known as mitoquinone improve exercise performance in middle-aged men?
See what a recent study found in our CoQ10 and Ubiquinol Supplements Review,
which also includes information about a potential concern with mitoquinone.
Ubiquinol (CoQ10) for Cognitive Function?
1/31/2021
Does taking ubiquinol,
the active form of CoQ10, improve cognition in people with mild cognitive
impairment? See what a new study found in the What It Does section of our CoQ10 and
Ubiquinol Supplements Review. Also see our Top Picks for CoQ10 and ubiquinol.
8/04/2020
Ubiquinol (the active
form of CoQ10) can have a beneficial effect on ailing hearts, but can taking it
protect the heart around the time of aortic valve replacement? Find out what a
recent study showed in the What It Does section
of the CoQ10 and Ubiquinol Supplements Review. Also see our Top Picks for Ubiquinol and CoQ10.
6/02/2020
Does taking ubiquinol
(the active form of CoQ10) help men and women who are experiencing fatigue in
daily life? Find out what a recent study showed in the What It Does section
of the CoQ10 and Ubiquinol Supplements Review. Also see our Top Picks for CoQ10 and ubiquinol.