Dark Chocolates, Cocoa & Cacao Powders, Nibs, and
Supplements Review -- Sources of Flavanols
Find the Best Dark
Chocolate, Cocoa Powder and Cocoa Supplements. Is Your Chocolate or Cocoa
Healthful or Toxic? Find Out Now!
Medically reviewed and
edited by Tod Cooperman, M.D. 
Last Updated![]() : 09/25/2021 | Initially Posted:
07/16/2017 | Expanded and Revised:
12/21/2019Latest Update: Dark Chocolate for Mood?
: 09/25/2021 | Initially Posted:
07/16/2017 | Expanded and Revised:
12/21/2019Latest Update: Dark Chocolate for Mood?


Table of Contents
Summary
·
What are the health benefits of dark chocolate and cocoa? Cocoa-based
products contain flavanols which are associated with modest potential benefits
regarding blood flow, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, exercise,
memory/cognition, skin wrinkles, and blood sugar control (See "What It Does")
·
Which dark chocolate and cocoa products are best? Be careful! Many
popular cocoa powders, cacao nibs, and some dark chocolates are contaminated
with high levels of cadmium, a toxic heavy metal (see What CL Found). Fortunately, we were able to
identify a few great products that minimize cadmium exposure, maximize
flavanols, offer superior value, and even minimize calories without sacrificing
flavor. See CL's Top Picks.
·
How much cocoa or dark chocolate do I need? Clinical studies
suggest the following total daily intakes of flavanols for the purposes noted below,
although further research is needed to confirm benefits and optimal dosing:
·
Cardiovascular health: About 200 to 900 mg per
day
·
Blood sugar/insulin improvement: About 200 mg
to 600 mg per day
·
Memory/cognitive function: About 500 to 900 mg
per day
·
Skin elasticity/wrinkles: 320 mg per day
To get these amounts look at the 3rd column in
the Results Table below. It will show you the
amount of flavanols in a serving of each product.
·
Dark chocolate and cocoa safety and side effects: Although cocoa and
chocolate products are generally safe, it may be best to limit consumption of
products due to contaminants as well as calories (See How much of a danger is cadmium from cocoa and chocolate?)
Be aware that the caffeine and theobromine in cocoa products may cause side
effects as well as interfere with the actions of certain drugs. Cocoa and
chocolate products may also trigger migraines in some people and may trigger
allergic contact dermatitis in nickel-sensitive individuals. People with milk
allergies should be aware that dark chocolate bars may contain milk (See Concerns and Cautions).
What It Is:
Cocoa
powder (also called cocoa solids) is made from cacao beans after removal of the
natural fats (cocoa butter). Cocoa powder is rich in antioxidant compounds
known as flavanols that also occur in grapes, apples, and teas. Flavanols can
exist as simple compounds (catechins monomers) or linked together (catechins
oligomers or polymers) as compounds known as proanthocyanidins
or PACs. (Note: Flavanols differ from flavonols,
such as quercetin, which contain a ketone group.)
Cocoa powder is used to make cocoa beverages, chocolate, chocolate syrup and
chocolate confectionaries. The amount of flavanols in a cocoa-based product
depends on multiple factors including plant genetics, where the plant is grown,
how the plant is harvested, how the cocoa is processed, and how the product is
prepared. For example, dark chocolate and milk chocolate are made with cocoa
powder and cocoa butter, however, dark chocolate has a much higher
concentration of flavanols because milk chocolate includes milk, and,
typically, a larger amount of sugar. [Be aware that the "% cocoa" or
"% cacao" in a chocolate reflects the total amount of cocoa powder
plus cocoa butter relative to all other ingredients. As sugar is the only other
ingredient in dark chocolate, "% cocoa" in dark chocolate tells you
the percent that is not sugar. However, as manufacturers typically don't
disclose the ratio of cocoa powder to cocoa butter in their chocolates, the
"% cocoa" is only a rough indicator of how much cocoa powder is in a
product and how flavanol-rich the chocolate may be.][Also be aware that the FDA
has found milk in some dark chocolates — see Concerns and Cautions.]
What It Does:
Cardiovascular:
Populations that consume higher amounts of flavanols from cocoa and other
sources tend to have lower rates of cardiovascular disease. In addition,
clinical studies have shown that the consumption of cocoa flavanols can
modestly improve vascular function and have favorable effects on cholesterol
levels, but long-term blood pressure lowering has not been
demonstrated in people with hypertension and the effects on cholesterol have
only been demonstrated in short-term studies of healthy individuals. Cocoa
flavanols may have a useful, short-term benefit in people with peripheral
artery disease.
Although no health claim about cardiovascular benefits can be made on cocoa
products in the U.S., in 2012 the European Food Safety Authority granted
permission to the maker of a dark chocolate product to claim on its product
label that, for the general population, "Cocoa flavanols help maintain
endothelium-dependent vasodilation, which contributes to normal blood flow."
In order to obtain the claimed effect, 200 mg of cocoa flavanols should be
consumed daily. This amount could be provided by 2.5 g of high-flavanol cocoa
powder or 10 g of high-flavanol dark chocolate, both of which can be consumed
in the context of a balanced diet (EFSA 2012). [You can check the amounts of
flavanols found by ConsumerLab.com in various products in Results table below.]
Studies that suggest cardiovascular benefits have tended to be of short
duration (up to 4 weeks) and in healthy individuals while longer studies (e.g.,
8 weeks), which are more meaningful, have shown more limited benefits or no
benefit.
A study among 100 healthy, middle-aged men and
women, consuming a flavored drink twice daily (providing a total of 900 mg
cocoa flavanols) for one month resulted in a small, but significant improvement
in blood vessel endothelial function (which contributes to normal
blood flow) compared to a placebo drink (which contained similar amounts of
caffeine and theobromine, but no cocoa flavanols). Those who drank the cocoa
flavanol drink also had small but significant reductions systolic and diastolic
blood pressure (4.4 mmHg and 3.9 mmHg, respectively) and total and LDL
"bad" cholesterol (approximately 8 mg/dL and 7 mg/dL, respectively),
as well as a slight increase in HDL "good" cholesterol (about 4
mg/dL). The researchers reported that these changes reduced the estimated risk
of death from cardiovascular disease over a projected 10-year period by 30%
compared to those who consumed the placebo drink. The flavanol drink, a powder
mixed with water and consumed with breakfast and dinner, was made with the same
extraction process (called CocoaPro)
as CocoaVia reviewed below and was
provided by MARS Inc., which sponsored the study (Sansone, Br J Nutr
2015). Similar improvements in
cholesterol levels were seen in a small study using a specially processed,
high-flavanol cocoa powder. In the study, healthy men and women who consumed 4
grams of the powder (providing 220 mg of flavanols, including 92 mg of
epicatechin) daily for one month had average decreases in blood levels of total
cholesterol (-12 mg/dL), LDL cholesterol (-14.98 mg/dL), oxidized LDL (-95.61
U/L) and triglycerides (-3.8 mg/dL), and an average increase in
"good" HDL of 3.37 mg/dL cholesterol compared to levels before
supplementation. People who took one-half or one-quarter of the dose did not
have significant changes in any of these measures. The study was funded by the
maker of the cocoa, Casa Luker S.A. Company of
Columbia, which claims to have developed a process allowing
for less oxidation and damage to cocoa polyphenols than traditional roasting (Danvinelli, J Nutr Biochem 2018).
A study in young, sedentary, but otherwise healthy women
in Texas found that daily consumption of 12.7 grams of a natural cocoa bar
(containing 309.6 mg of flavanols, including 48 mg of epicatechin) for 4 weeks
led to an 18% increase in HDL ("good") cholesterol and
a 60% decrease in EMPs (particles associated with blood vessel damage).
However, additional positive changes in blood markers were seen mainly with
obese women and not women of normal weight, suggesting a more positive effect
of cocoa on obese women than those who are not obese (McFarlin, J Nutri Biochem 2015).
Long-term studies in people with elevated cholesterol levels are needed to
better assess the true benefit of cocoa flavanols on cholesterol.
A small study in Italy found that within 2 hours of
consuming a bar (40 grams) of dark chocolate which was greater than 85% cocoa,
people with peripheral artery disease (due to atherosclerosis)
were able to walk 15% further than normally; eating a similar
amount of milk chocolate had no effect (Loffredo, J Am Heart Ass 2014). A
six-month study of 44 people with peripheral artery disease in Chicago who
consumed, as a beverage, 5 grams of cocoa providing 25 mg of epicatechin, or a
placebo, three times daily, also suggested improvement in walking distance,
indicating the cocoa increased six-minute walking distance 2.5 hours after the
final drink by 42.6 meters (about a 12% increase over baseline) compared to
placebo after adjusting for differences between the groups. It must be noted,
however, that much of this improvement was relative to a 15.3
meter decrease in the placebo group and other adjustments, as the actual
increase in the cocoa-treated group was very little -- only 8 meters. There was
no significant difference between the groups 24 hours after the final drink,
suggesting, no long-term benefit on walking distance (McDermott, Circ Research 2020).
Unfortunately, among people with mild hypertension,
cocoa has been of limited benefit. A placebo-controlled study in the U.S. among
people with stage 1 hypertension (blood pressure of 140-159/90-99 mm Hg),
failed to show reductions in blood pressure or other benefits from cocoa-based
products except among those also taking ACE inhibitors or beta blockers — among
whom blood pressure levels fell by roughly 2 to 5 mm Hg. However, blood
pressure rose (by about 5 mm Hg) among those taking diuretics who consumed the
cocoa-based products. The study (funded by Hershey) involved the daily
consumption of 10 grams of extra dark chocolate (89 mg of flavanols) and a
beverage containing 2.5 grams of cocoa powder (42 mg of flavanols), or twice
the amount of each for 8 weeks. (Njike, Clin Trials Reg Sci Cardiol 2016). Similarly,
a study in Finland among people ages 33 to 64 with mild hypertension found that
eating dark chocolate (49 grams daily -- 70% cocoa, providing 603 mg flavanols)
for 8 weeks had no significant effect on blood pressure or other cardiovascular
risk factors (such as arterial stiffness), compared to 8 weeks of refraining
from chocolate. During both periods subject were told to reduce snacking —
possibly explaining the loss of about 2 lbs. during the non-chocolate period of
the study, although this did not affect blood pressure (Koli,
Nutrition Journal, 2015).
Higher consumption of chocolate has been associated with
a lower risk of developing atrial fibrillation, which is the most
common type of irregular heartbeat and, itself, is associated with higher risk
of stroke, heart failure, cognitive decline, dementia, and mortality (death
over time). A large, 13.5 year study in Denmark found
that compared to people who ate no chocolate, the risk of having atrial
fibrillation was 10%, 17%, and 20% lower among those who ate, respectively, one
to three 1 oz. servings of chocolate per month, one serving per week, and two
to six servings per week after adjusting for calorie intake and other
variables. Unfortunately, the type of chocolate (dark or milk) was not
specified; however, chocolate in Europe is required to have higher
concentrations of cocoa than in the U.S: at least 30% for milk chocolate (vs.
10% in the U.S.) and 43% for dark chocolate (vs. 35% in the U.S.) (Mostofsky, Heart 2017). A
review of several studies found an association between moderate chocolate
consumption (1 to 3 servings per month) and a 23% lower risk
of heart failure compared to no regular chocolate consumption,
although consumption of one or more servings per day was associated with a
17% higher risk of heart failure. These associations, however,
were not deemed statistically significant and neither the form
of chocolate nor serving size was specified (Krittanawong, Eur Heart J Supplement 2018).
Cocoa flavanols appear to temporarily delay one measure
of platelet function according to a small study of healthy
young men who consumed 50 grams of a high-flavanol (90% cocoa) chocolate
(Lindt). A 14% delay in a measure of clotting (collagen/ADP-induced closure
time) occurred four hours after eating the chocolate, which coincided with the
appearance of cocoa flavanols in the men's blood. The researchers concluded
that dark chocolate may be beneficial for people at risk of thrombosis
(clot development) (Montagnana, Medicine 2018). However, the
researchers acknowledged that more study is needed, and a long-term
(three-month) study involving high-dose cocoa flavanols did not find
a significant effect on platelet function in healthy men and women (Ottaviani, Am J Clin Nutr 2015).
Some evidence suggests that cardiovascular effects of flavanols are due to
modulation of nitric oxide concentrations and that these effects may be based
on chemical properties other than the antioxidant properties of the ingested
compounds.
Blood Sugar, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes
A review of 8 clinical trials among men and women (many of whom had conditions
such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes) found, compared to
placebo, that a daily cocoa flavanol intake between 200 mg and 600 mg
significantly decreased fasting blood sugar levels (down 0.26 mmol/L), fasting
insulin (down 2.43 uIU/mL) and HOMA-IR, a measure of
insulin resistance (down 0.72 points). Higher daily intakes of cocoa flavanols
(at or above 600 mg) resulted in a greater decrease in HOMA-IR (down 1.05
points), but had less of an effect of fasting insulin (down 2.10 uIU/mL) and did not significantly decrease
fasting blood sugar levels (Lin, J Nutr 2016).
Note, however, that cocoa flavanols did not provide
additional benefit to people with diabetes and hypertension already
controlled with medication, as demonstrated in a 12-week,
placebo-controlled study using 2.5 grams per day of flavanol-rich cocoa powder
(ACTICOA, from Barry Callebaut) that contained a total of 207.5 mg of cocoa
flavanols (Dicks, Nutrients 2018).
A large, 13-year study of postmenopausal women found
that moderate consumption of chocolate (defined as 1 oz. 1.5
times per month but not more than 3 times per week) was associated with about a
10% lower risk of developing diabetes than consumption of 1 oz. of chocolate
less than once a month (type of chocolate not defined). This reduction,
however, was only statistically significant for those under 65 years of age or
less physically active; risk of diabetes was not reduced for women who consumed
1 oz. of chocolate 3 or more times per week (Greenberg, Eur J Clin Nutr 2017).
A study of 14 healthy postmenopausal women found that they
consumed an average of 100 fewer calories within 90 minutes
after eating 85 grams (about two regular servings) of 80% dark chocolate than
after eating similar amounts of white or milk chocolate. Blood glucose and
insulin concentrations were also higher after consuming milk or white chocolate
than after dark chocolate, suggesting greater blood sugar control with dark
chocolate. Dark and milk chocolate (both of which contain cocoa solids) led to
higher blood of levels of pancreatic polypeptide (which may help reduce
appetite), than white chocolate (which does not contain cocoa solids). These
results suggest that, given a choice, dark chocolate can help postmenopausal
women moderate overall energy intake better than milk and white chocolate (Marsh, Appetite 2017).
Improved glucose metabolism from cocoa flavanol intake has also been associated
with improved cognitive performance in healthy elderly men and women (See Memory section below).
Interestingly, 67 postmenopausal women in Spain who
consumed 10 grams of cocoa-rich chocolate ("99% cocoa," providing
65.4 mg of cocoa flavanols) once daily for 6 months lost about 1 lb of body fat, while a similar group of 61
women not given the chocolate gained nearly ½ lb on
average, although there were no significant differences between the groups in
terms of changes in overall weight or BMI, nor in serum insulin. The chocolate
maker Lindt & Sprungli supplied the chocolate but
was not involved in the study (Garcia-Yu, Br J Nutr 2020).
(The same study found a slight improvement in two measures of cognitive
function with chocolate, as discussed below.)
Exercise and physical performance:
Cocoa flavanols can modestly improve physical performance in both young and old
people.
A small study in moderately-trained young men given 40 grams
of dark chocolate or white chocolate (which lacks flavanols) for 14 days found
the dark chocolate resulted in a modest (17%) but statistically
significant increase in the distance they could cycle in 2
minutes and reduced the oxygen cost of exercise, suggesting that it "may
be an effective ergogenic aid for short-duration moderate intensity
exercise." (Patel, J Int Soc Sport Nutr 2015). The benefit may be due to the
ability of epicatechin flavanols to dilate blood vessels by modulating nitrous
oxide production. Dove Dark Chocolate was used in the study on the researchers'
belief that it had a high concentration of the flavanol epicatechin, but they did
not test flavanol levels and it's likely that it actually has a low
concentration relative to other products as indicated by other research (Kaspar, U. Wisc. 2006) and the fact that it
is only 40% to 50% cocoa (according to Mars Chocolate customer care) and sugar
is listed as its primary ingredient.
Consuming large amounts of cocoa powder may modestly improve
physical performance in daily activities like walking, rising, and
gripping objects. This was shown in a study among older men and women in Mexico
(average age 76) which also showed the cocoa flavanols to reduce biochemical
markers of oxidative stress associated with frailty. In the study, which lasted
two months, every day before breakfast a group of participants consumed 5 grams
of cocoa powder (with 6 grams of added sugar) mixed in water while another
group had a placebo drink. Each serving of cocoa contained 179 mg of cocoa
flavanols while the placebo was an alkalized cocoa beverage that did not
contain flavonoids but contained the same amount of theobromine (Munguia, J Gerontol A Biol Sci
Med Sci 2019).
Memory and cognition:
Small clinical trials, typically using high-doses (500 mg
to 900 mg) of cocoa flavanols suggests that cocoa flavanols moderately improve
memory in older people with mild cognitive decline. In people with normal
cognition, improvements may also occur with lower (and, possibly, with lower
amounts (e.g. 86 mg) of flavanols and tend to be in
attention, processing speed and reduced mental fatigue.
A review of 14 small clinical studies examined the effects of cocoa flavanols
on cognition and memory and, while not all studies found a positive effect, the
authors concluded that supplementation with cocoa flavanols can be effective at
sustaining cognitive performance and memory. The greatest benefits were
found in older adults, those with only mild cognitive decline and those
consuming at least 500 mg per day of cocoa flavanols between 5 days to 3
months. However, the researchers also cautioned that due to the
limited number of studies in the review, differences in dosages, timing, and
the specific populations studied, more research is needed to confirm the
beneficial effects of flavanols on cognition and memory (Socci, Front Nutr 2017).
Several of the studies included in the review noted above used extracts which
were highly concentrated for cocoa flavanols produced by MARS. For example, a
study of healthy people ages 50 to 69 found that drinking a high-flavanol, hot
cocoa drink twice daily (providing 900 mg flavanols, including 138 mg
epicatechin) for 3 months enhanced brain functioning. Compared to people given
a similar, low-flavanol drink (10 mg flavanols, and less than 2 mg
epicatechin), those given the high-flavanol drink experienced improved recall
speed, comparable to individuals 30 years younger (Brickman, Nature Neuroscience 2014). It is not
known if lower doses of flavanols -- such as the 200 mg dose suggested for
cardiovascular benefit -- might work equally well for memory. The product used
in the study was provided by MARS, Inc., maker of CocoaVia powder,
which is reviewed below. Testing by ConsumerLab.com found that the ratio of
epicatechin to total flavanols in the study's product to be similar to that
of CocoaVia.
In a small study of healthy older adults (ages 50 — 65), drinking a high-
flavanol cocoa drink, also provided by MARS (494 mg flavanols, 89 mg
epicatechin) significantly increased blood flow to the brain 2 hours after
ingestion, an effect not observed after drinking a low-flavanol drink (29 mg
flavanols, 3 mg epicatechin). The study did not test cognitive function. (Lamport, Psychopharmacology 2015).
Another study showed cognitive benefits, and possible
cardiovascular and metabolic benefits, with high-flavanol hot cocoa drinks. In
the 2-month study, healthy individuals ages 60 to 85 were given one of three
drinks providing the following amounts of cocoa flavanols: (993 mg flavanols,
185 mg epicatechin), (520 mg flavanols, 95 mg epicatechin), or (48 mg
flavanols, 5 mg epicatechin). Those getting the higher flavanol drinks showed
moderate improvements in certain aspects of cognitive performance —
particularly processing speed. They also experienced reductions in blood
pressure ,
LDL ("bad") cholesterol, and glucose and insulin
levels, suggesting an association between glucose metabolism and improved
cognitive performance (Mastroiacovo, Am J
Clin Nutr 2014). The
drink, called CocoaPro, was also provided by MARS
Inc., which sponsored the study.
A study among 100 healthy, highly educated men and women
(ages 65 to 75) with normal cognition in Finland compared the effects of
consuming 50 grams daily of high-flavanol dark chocolate (Karl Fazer 70% Dark
Chocolate Pralines - containing 410 mg flavanols, 85 mg epicatechin) versus
low-flavanol dark chocolate (86 mg flavanols, 26 mg epicatechin) daily for two
months. Performance on cognitive testing improved equally in both groups (which
could have been due to experience with the tests over the course of the study),
but it was clear that there was no special benefit from high-dose flavanols in
people who were not experiencing cognitive decline. It's not known if consuming
the high-flavanol dark chocolate would have shown a benefit compared to no consumption
of cocoa flavanols (Suominen, Exp Gerontol 2020).
A study in Spain among postmenopausal women (average age 57)
found that consuming 10 grams of cocoa-rich chocolate ("99% cocoa,"
providing 65.4 mg of cocoa flavanols) once daily for six months modestly
improved cognitive flexibility and processing speed compared to similar women
in a control group who did not consume the chocolate. However, there were no improvements
in attention, verbal memory, or working memory compared to the control group (Garcia-Yu, Nutr Neurosci 2020). Note: These results would be
more meaningful had a placebo product been used as the control.
A placebo-controlled study of healthy adults in Australia,
ages 18 to 40, given a daily tablet providing 250 mg of cocoa flavanols found
short-term improvement in self-reported mental fatigue while
taking a mathematical test, but there were no effects on other aspects of
cognitive performance, mood, or cardiovascular functioning. Interestingly,
after one month, participants who had received the placebo reported feeling
significantly less stressed than those receiving the cocoa flavanols (Massee, Front Pharmacol 2015).
A small study among healthy, young men (average age 24)
found that consuming a high-flavonol, non-alkalized,
reduced-fat cocoa beverage (Natural Acticoa,
Barry Callebaut -- providing 681.4 mg total flavanols) two hours before
cognitive testing modestly improved performance on a highly demanding cognitive
task, but did not on less demanding cognitive tasks, compared to consuming a
low-flavonol cocoa beverage (providing 4.1 mg total
flavanols). Both beverages contained similar amounts of caffeine (about 19.4
mg). Additional testing in the study suggested that the findings may be
explained by an ability of cocoa flavanols to increase blood flow to the brain
when carbon dioxide levels are elevated (Gratton, Sci Rep 2020). Barry Callebaut
provided both cocoa beverages but did not fund the study.
Mood and Stress
A placebo-controlled study of healthy adults in the UK given
25 grams daily of dark chocolate containing 500 mg of cocoa flavonoids
(specific amount of flavanols, the predominant cocoa flavonoid, not listed),
for four weeks found that levels of cortisol (a stress hormone) in saliva were
significantly reduced (by 29%), compared to those given a low-flavonoid
chocolate. The high-flavonoid group also reported a greater improvement in mood
(a 5 point reduction on a 40 point-range
"negative affect" scale, which relates to anxiety) than the
low-flavonoid group (a 1.5 point reduction), but the between-group difference
was not statistically significant. There was also no significant difference
between the groups on "positive affect." (Tsang, Antioxidants 2019). As noted in the
"Memory" section above, a study in Australia also did not find an
overall effect of cocoa flavanols on mood.
A small study in
Korea among 48 healthy men and women ages 20 to 30 without depression found
that consuming 10 grams of "85% cocoa" dark chocolate (Weinrich
1895 Fine Dark Chocolate) providing 132 mg of polyphenols, three times
daily for three weeks modestly decreased self-reported indicators of negative
mood (i.e., feelings of irritability, hostility, guilt, etc.),
although it did not increase self-reported positive mood (i.e. feelings of
inspiration, enthusiasm, excitement, etc.) compared to a control group that did
not consume chocolate. Consumption of the same amount of dark chocolate made
with a lower percentage of cocoa (70% cocoa — providing 82.1 mg of polyphenols
per serving) had no effect on mood. Consumption of the 85% cocoa dark chocolate
led to changes in the presence and diversity of bacteria in the gut, that were
associated with the decrease in negative mood (Shin, J Nutr Biochem 2021).
A U.S. population study found that people who consumed dark
chocolate had 70% lower odds of reporting clinically relevant depressive
symptoms than those who did not consume dark chocolate. This association did
not exist for non-dark chocolate consumption (Jackson, Depress Anxiety 2019).
Skin
Cocoa flavanols may have a mild, beneficial effect on facial wrinkles and skin
elasticity according to a well-controlled study of 64 women in Korea (average
age 67) with moderate sun damage to the skin and visible wrinkles. After 24
weeks of consuming a low-fat cocoa beverage of 4 grams of processed cocoa
powder (providing 320 mg of cocoa flavanols) or placebo once daily for 24
weeks, the depth of "crow's feet" wrinkles increased
by 8 percent among those receiving placebo, but it barely changed in the cocoa
flavanol group. Skin elasticity improved by about 9% in the
cocoa flavanol group, while there was no improvement in the placebo group.
There was no significant effect on skin hydration. The women were not permitted
to consume other foods high in antioxidants around the time of the study. Among
a subgroup of the women who were exposed to artificial UV radiation at the end
of the study, those who drank the cocoa beverage required a higher dose of
radiation to induce skin damage, suggesting cocoa might have a protective
effect. The cocoa was provided by Barry Callebaut (Belgium) (Yoon, J Nutr
2015).
Vision
A small study found that adults in their 20's (with no eye disease) had greater
visual acuity when tested about two hours after eating a bar of dark chocolate
(Trader Joe's 72% Cacao Dark Chocolate) than after a bar of milk
chocolate (Trader Joe's Crispy Rice Milk Chocolate). Small-letter
contrast sensitivity was significantly greater with dark chocolate.
Large-letter contrast sensitivity was only slightly greater with dark chocolate
and this was not statistically significant. The study had several limitations
including a lack of comparison to baseline vision (i.e., before chocolate), the
investigators' knowledge of the identities of both bars, and self-reported
measures of visual acuity, i.e., participants read eye charts mounted on the
wall. The published study references ConsumerLab's
results (from this Review) for the cocoa flavanol level in the dark chocolate
bar (316.3 mg), which was much higher than in the milk chocolate (40 mg). The
researchers speculate that increased blood flow to the retina or brain might
explain the results (Rabin, JAMA Ophthalmol
2018). These results were later contradicted by a more
rigorous study that was double-blinded (neither the researchers nor
the participants knew which type of chocolate was consumed), included an
objective measure (a scan that measures blood flow in the eye), and measured
visual acuity at baseline (before chocolate consumption). This study found no
improvement in visual acuity or blood flow in the eye two hours after dark
chocolate (20 grams of dark chocolate providing 400 mg total flavanols) was
consumed compared to milk chocolate (7.5 grams containing 5 mg total
flavanols). The dark chocolate used in the study was Lavlé
Belgian Chocolate, by The Good Chocolate Company in Belgium (Siedlecki, JAMA Ophthalmol 2019).
Cancer
Flavonoids in chocolate have shown anticancer activity in laboratory studies.
Proposed mechanisms by which flavonoids may negatively affect cancer cells
include: (1) increasing immune response, (2) decreasing oxidative stress, (3)
reducing inflammation, (4) affecting proliferation and programmed cell death
(i.e., apoptosis) of cancer, (5) reducing the formation of blood vessels to
cancer (i.e., angiogenesis), and (6) reducing its spread (i.e., metastasis).
Despite the many ways by which chocolate flavonoids might target cancer, most
observational studies in humans have found that higher intake of
chocolate does not reduce cancer risk. Evidence from the Women's
Health Initiative Study, which included data on chocolate candy exposure for
114,281 women (average age 64), found that chocolate candy intake (type of
chocolate not specified) was not associated with the risk of invasive
total cancer or invasive breast cancer. Furthermore, the
risk of invasive colorectal cancer was 18% higher for women
who consumed an ounce (28.4 grams) of chocolate candy at least 1.5 times per
week compared to those who consumed an ounce of chocolate less than
once per month (Greenberg, J Acad
Nutr Diet 2020). Since frequent chocolate
consumption may contribute to adiposity (overweight/obesity), a risk factor for
colorectal and certain other cancers, and there's no strong evidence supporting
the benefit of chocolate for cancer prevention, it would not seem
beneficial to increase chocolate intake to lower cancer risk.
Intestinal Health
A placebo-controlled 27-day study in which a high-flavanol cocoa powder was fed
daily to young pigs (which have intestinal systems similar to those of humans)
found significant increases in beneficial bacteria L. casei and Bifidobacterium at
doses providing 205 mg to 410 mg of cocoa flavanols (from 10 grams to 20 grams
of Acticoa powder from Barry-Callebaut) (Jang, J Nutr 2016).
The results are similar to those from a study in healthy people in which
consumption of 494 mg of cocoa flavanols daily from a drink significantly
increased fecal levels of the same bacteria, while inhibiting potentially pathogenic Clostridium bacteria
(Tzounis, Am J Clin Nutr 2011).
These studies suggest that cocoa can have a "prebiotic" effect and
"support intestinal health," according to the researchers.
Caffeine and Theobromine
Naturally present in cocoa, caffeine and theobromine promote alertness (by
blocking cell receptors for adenosine — a hormone that promotes sleep) (Martinez-Pinilla, Front Pharmacol
2015). Theobromine can also relax blood vessels and have a diuretic
effect (increasing urination) and, in the past, was used as a heart medication
and for bronchodilation (to improve breathing). Taking theobromine decreased
LDL ("bad") cholesterol by 5.6% in a study in which 500 mg of
theobromine was taken daily by overweight but otherwise healthy men and women
for four weeks (Smolders, Clin Nutr
2017). The amount of theobromine used in this study is only slightly
more than the 300 to 400 mg ConsumerLab found in
single, 40-gram servings of dark chocolates (cocoa powders contained about 100
mg per 5-gram tablespoon).
Theobromine has been unsuccessfully tried as a cough suppressant in people with
chronic cough not due to illness or conditions such as COPD (Morice, J Thorac Dis 2017).
However, both compounds may also cause side effects (see Concerns and Cautions).
Quality Concerns and
Tests Performed:
As
noted above, there can be wide variation in the flavanol concentrations of
cocoa-based products. In addition, heavy metals can contaminate cocoa plants
and cocoa-based products. Consequently, ConsumerLab.com tested a variety of
cocoa and cacao products for their amounts of flavanols, as well as for the
heavy metals lead, cadmium, and arsenic. Although for many years there was
scientific uncertainty about how to properly measure flavanols in cocoa
products, in 2012 a validated method, using high performance liquid
chromatography (HPLC), was developed and published by the AOAC International,
allowing for more standardized measurement. This is the method utilized by
ConsumerLab.com. For more details about the testing, see How Products Were Evaluated.
[Note: Due to popular interest in this category and the wide range
of products, the results reported are cumulative: they include those published
in July 2017, and most recently, in late 2019. The products are identified by
the year reported.
What CL Found:
Flavanols:
As shown with blue bars in the graph below, ConsumerLab.com found the
concentration of flavanols (measured in milligrams of flavanols per gram of
product) varied greatly among products, ranging from 3 mg to 14 mg per gram
among bars, 5 to 9 mg per gram among chips, 3 mg to 25 mg per gram among
powders, 12 mg to 23 mg per gram among nibs, and from virtually none to a
whopping 623 mg among supplements. Dutched (alkali
processed) cocoas and chocolates generally had lower flavanol concentrations,
as the Dutching process reduces flavanol levels.
Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic:
Concentrations of the toxic metal cadmium (shown with red bars) also ranged widely,
from less than 0.005 mcg per gram in some supplements and bars to as much as
1.2 mcg and 1.8 mcg per gram, respectively, in two powders. The highest level
in supplements and chips was 0.2 mcg/g, in nibs it was 0.5 mcg/g, and in bars
it was 0.7 mcg/g. Many products exceeded established limits for cadmium per
serving (indicated with red text). All of the values represented in the graph are also shown in
the Results table.
None of the products exceeded limits for lead or arsenic applied by
ConsumerLab.com.
Similar to CL's results in this Review, a study published in 2017 by
researchers from the U.S. FDA of 144 cocoa and chocolate products (not
identified by name) sold in the U.S. showed that the highest cadmium
concentrations were in cocoa powders (averaging 0.7 mcg/g). This was followed
by cocoa nibs (0.62 mcg/g), dark chocolates (0.27 mcg/g), and very low levels
in milk chocolates (0.06 mcg/g). Lead was also highest in cocoa powders (0.11
mcg/g) with only negligible amounts in other products — the lowest being cocoa
nibs (0.003 mcg/g) (Abt,
Food Add & Contam 2017).
A study of cadmium in cacao from plantations in Peru found that 57% of cacao
bean samples exceeded 0.8 mcg per gram, with the highest levels (up to 1.79 mcg
per gram) coming from northern Peru (Arevalo-Gardini, Sci Tot
Environ 2017). (Note that cadmium is found in the cocoa solids
and is not present in cocoa butter, nor, for the same reason, in white
chocolate).
It's interesting to note that "Organic" products were generally more
contaminated with cadmium than non-organic products — a phenomenon that
ConsumerLab.com has observed in the past and noted in other Reviews. Although
most products did not list the geographic source of their cacao beans (see 6th column of Results table), nearly all those that did
indicated areas in Central or South America. However, two products, both
from Chocolove, indicated a combination
of African and Caribbean sources and these products had lower than average
concentrations of cadmium, consistent with the above-mentioned study by U.S.
government researchers that found higher concentrations of cadmium in products
from Latin America than from Africa. Higher concentrations of cadmium were in
products from Latin America than from Africa. It was noted that although most
of the world's cocoa beans come from Africa, only the varieties from Latin
American produce the "fine cocas" (i.e., those having desirable
flavor and color) that are used to make specialty dark chocolates and many
cocoa powders (Abt,
Food Add & Contam 2017).
Getting cocoa flavanols and minimizing cadmium:
The most healthful products in terms of flavanols and cadmium are those with
the greatest ratio of flavanols to cadmium (i.e., more blue bar than red bar in
the graph below). Not surprisingly, highly concentrated extracts (in which
cadmium can be removed) such as CocoaVia and Futurebiotics had the best ratios of flavanols
to cadmium.
Among dark chocolates, the best ratio was for Montezuma's Dark
Chocolate Absolute Black with 14 mg per gram of flavanols but just
0.06 mcg of cadmium per gram of chocolate; in contrast, Pascha Organic
Dark Chocolate provided only 5 mg per gram of flavanols but more than
0.5 mcg of cadmium per gram of chocolate. Not surprisingly, chocolate chip
products fell within the range of dark chocolate bar products, and the chips
from Guittard had a somewhat better
ratio than those from Ghirardelli due to significantly more
flavanols per gram (9.6 mg vs. 5.3 mg per gram) although also slightly more
cadmium (0.23 mcg vs. 0.18 mcg per gram).
Nearly all of the cocoa powders had high concentrations of cadmium. Among those
that did not, Ghirardelli Chocolate Premium Baking Powder had
the best ratio of flavanols to cadmium, while Healthworks Cocoa Powder and Hershey's
Cocoa Special Dark had the worst; in fact, Healthworks had
the highest concentration of cadmium of any product tested and only a moderate
concentration of flavanols.
All three of the nibs had moderately high concentrations of cadmium — 0.29 to
0.45 mcg per gram, but Navitas Organic
Cacao had the best ratio of flavanols to cadmium.
Also included in the graph below is the amount of cadmium per serving,
which is written in text to the right of each bar. Products that exceed daily
cadmium limits are indicated in red font. However, because suggested serving
sizes differ across products within a category, the concentrations and ratios
discussed further above provide a more fair comparison
of products.
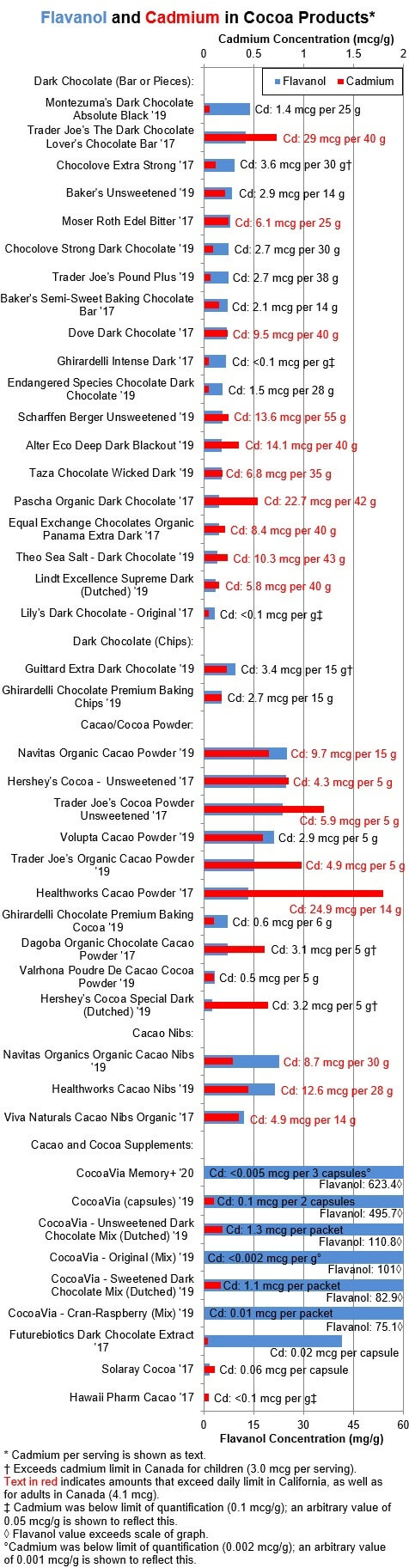
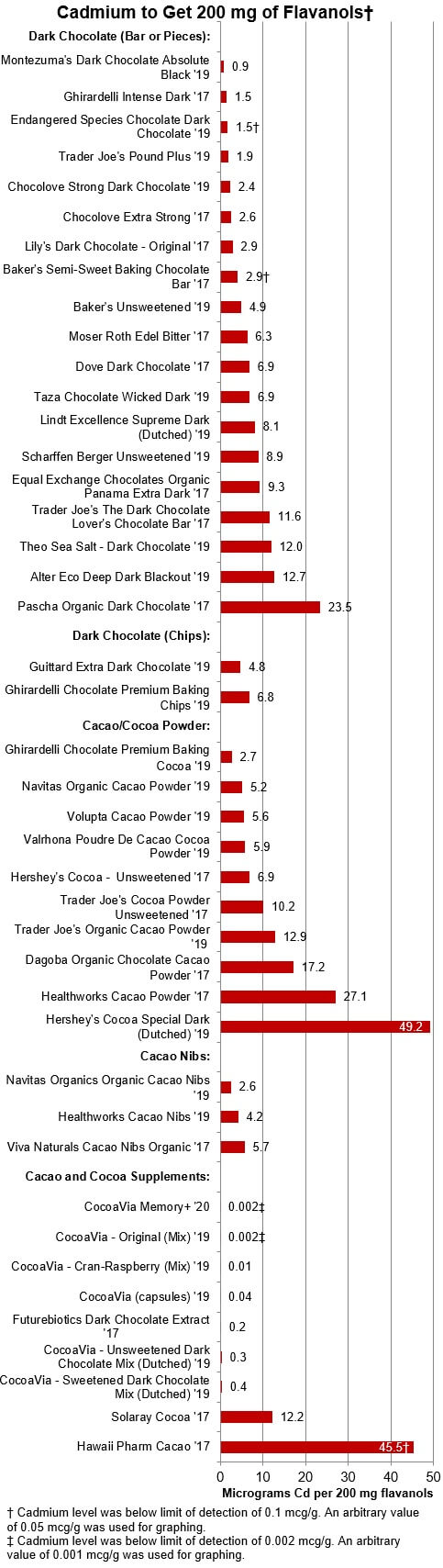
Another way to look at flavanols and cadmium is in terms of the amount of
cadmium exposure to get 200 mg of flavanols -- the minimum daily amount
associated with cardiovascular benefits, which is shown in the graph below.
Products with the longest red bars are the least favorable options for getting
flavanols while avoiding cadmium.
Calories:
Calories in cocoa and dark chocolate products come mainly from their cocoa
butter (9 Calories per gram) and added sugars (4 Calories per gram). As cocoa
supplements typically contain little to no sugar and minimal cocoa butter, they
provide few calories. Similarly, unsweetened cocoa powders contain no sugar and
generally little cocoa butter, so a tablespoon (about 5 grams) typically
provides only 10 to 20 Calories. Cocoa nibs naturally contain cocoa butter, so
a 3-tablespoon serving (15 grams) may provide about 7 grams of fat and 150
Calories. Dark chocolate typically includes the most cocoa butter and sugar, so
that a 40-gram serving will provide around 250 Calories -- or about 200
Calories if not sweetened with sugar. One of the products, Lily's,
was lower in calories (160 Calories per 40 grams) than the others because of
its use of non-sugar sweeteners, such as erythritol and stevia, and other
ingredients allowing for a reduction in cocoa butter.
Caffeine and Theobromine:
Note that that cocoa-based products will contain some caffeine — although
typically less than in a cup of coffee (about 100 mg). A 40-gram serving of
dark chocolate will generally contain about 25 to 85 mg of caffeine (see
amounts listed in the 4th column of the Results table). We didn't test other products
for caffeine in 2019 unless an amount was claimed, but, based on past testing,
a tablespoon of cocoa will contain about 10 to 20 mg of caffeine, supplements
will contain about 1 mg to 30 mg of caffeine, and 30 grams of nibs may contain
45 to 85 mg of caffeine.
Theobromine, which can cause some side effects, is also found in cocoa-based
products. We measured amounts in all dark chocolate bars, which ranged from 100
mg to over 600 mg per serving, and in supplements, which ranged from about 15
mg to 50 mg. These amounts are also listed in the 4th column of the Results table. Based on past testing, cocoa
powders contain about 100 to 120 mg of theobromine per tablespoon (but can be
much less if Dutched) and nibs contain about 300 mg
per three tablespoon serving.
Read about potential side-effects of caffeine and theobromine in the Concerns and Cautions section.
Top Picks:
In
choosing its Top Picks among the products "Approved"
for quality in this Review, ConsumerLab.com looked for those with a high
flavanol content and the lowest possible contamination, while also considering
cost and taste.
Overall
If you are just after flavanols, you'll generally get the most flavanols with
the least cadmium contamination and calories from supplements made from cocoa
extracts and, among these, the one with the highest concentration of flavanols
is CocoaVia Memory+ capsules.
This product promises 750 mg of flavanols in a daily serving of 3 capsules for
$1.50, and we found an even greater amount of flavanols (1,113.5 mg). This is a
reasonable cost for flavanols, with each 200 mg of flavanols costing 40 cents
(or just 27 cents based on the amount found), which is comparable to the cost
of flavanols from other Approved products -- such as Trader Joe's Pound
Plus 72% Cacao Dark Chocolate (27 cents) and about 10 cents more
than Volupta Cacao Powder (33
cents based on the amount of flavanols claimed and only 17
cents based on the higher amount of flavanols found). Some cocoa
powders provide flavanols at even lower cost but they were not Approved due to
cadmium levels. Exposure to cadmium with CocoaVia
Memory capsules is extremely low (0.005 mcg per gram).
Dark Chocolates
If you love strong dark chocolate, don't need it to be sweet, want plenty of
flavanols and minimal cadmium contamination, the clear winner, and a Top
Pick for dark chocolates, is Montezuma's Dark Chocolate
Absolute Black — 100% Cocoa. We found that each gram contains 14 mg of
flavanols and just 0.06 mcg of cadmium. Compare this with Trader Joe's
The Dark Chocolate Lover's Chocolate Bar — 85% Cacao (tested in 2017)
which had the next highest concentration of flavanols (12.6 mg per gram)
but 12 times as much cadmium (0.73 mcg per gram) — the most
cadmium in any dark chocolate we tested. Montezuma's, which is from
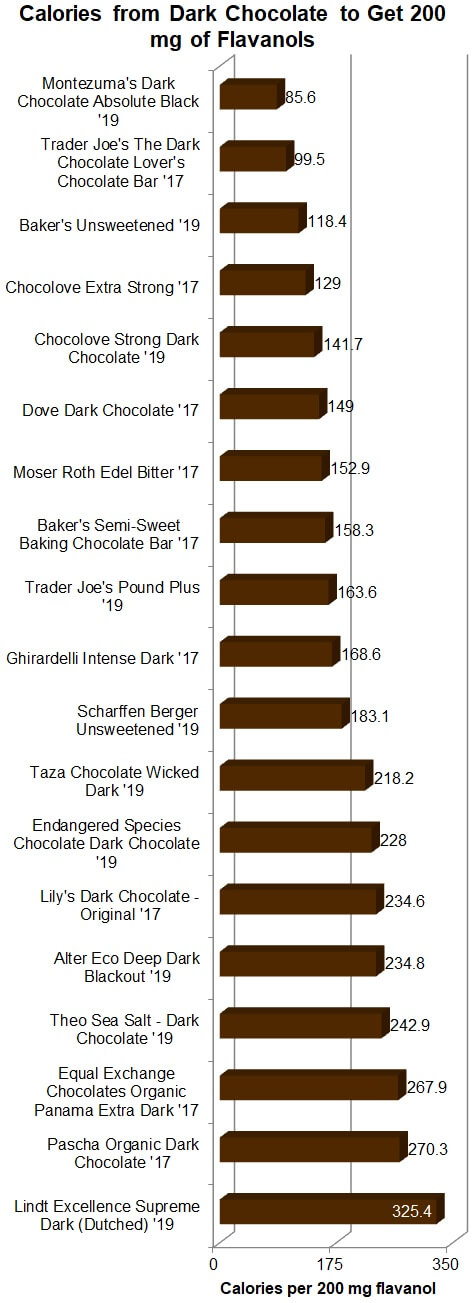
England, is a bit pricey at $4.30 for a large (100 gram) bar, but, in terms of getting flavanols, it's among the lowest
cost bars and it has the fewest calories — just 85.6 Calories per 200 mg of
flavanols, as shown in the graph below.
Although Trader Joe's Dark Chocolate Lover's bar was a cadmium
disaster and the two Trader Joe's cocoa powders in this Review
were also among the worst in terms of cadmium, this is not the case with Trader
Joe's Pound Plus — 72% Cacao Dark Chocolate, which is our
other Top Pick for dark chocolates — for people who like dark
chocolate a little sweet. In addition to being the least expensive dark
chocolate by far ($4.99 for a huge, 500 gram, 1.1
pound, bar), it, like Montezuma's, was among the lowest in cadmium
at just 0.07 mcg per gram and fairly high in flavanols (7.4 mg per gram).
Despite containing sugar, it provides fewer Calories (163.3) per 200 mg of
flavanols than many other bars, as shown in the graph below. Keep in mind that,
due to added cocoa butter (which has twice the calories of sugar) and sugar
itself, dark chocolate bars have more calories than cocoa powder, so, to get
200 mg of flavanols, you will consume about 100 to 250 or more Calories from a
bar versus only about 30 calories from a (non-Dutched)
powder.
Be aware that you can't always rely on the "% cocoa" or "%
cacao" claims on dark chocolate bars to inform you of their flavanol
concentrations: ConsumerLab.com has frequently found that bars claiming 80 to
85% cacao contain lower concentrations of flavanols than bars claiming
flavanols in the 70% range. In the current Review, for example, Taza Chocolate Wicked Dark — 95% Dark had
a lower flavanol concentration (5.5 mg per gram) than the Trader Joe's
72% bar (7.4 mg per gram). One reason why you can't rely on the
"% cacao" as an indicator of flavanol content is that the
confectionery industry has defined this as the sum of the cocoa liquor, cocoa
powder, and cocoa butter in the formulation — and cocoa butter does not contain
flavanols. Products claiming a high "% cacao" but which CL found to
be relatively low in flavanols likely contain relatively high concentrations of
cocoa butter.
Chocolate Chips
Our Top Pick among dark chocolate chips is Guittard Extra Dark Chocolate Baking
Chips — 63% Cacao because these chips provide 81% more flavanols
per gram than Ghirardelli Chocolate Premium Baking Chips — 60% Cacao (9.6
mg vs. 5.3 mg) and cost a bit less (20 cents vs. 25 cents per 15 grams). However, Guittard does contain a bit more cadmium per
gram (0.23 mcg vs. 0.18 mcg), making a 15-gram serving exceed the limit in
Canada for children, but not for adults. For children, the Ghirardelli chips
may be preferable. (Note that the Ghirardelli chips are about
twice the size of the Guittard chips
due a much wider base.)
Cocoa Powders
A conundrum with cocoa/cacao powders is that those with the highest flavanol
concentrations tend to be the most contaminated with cadmium (and are,
consequently, Not Approved by us). Conversely, those with little cadmium
contamination (and are Approved by us) tend have low flavanol levels. And then
there is the worst of both worlds, a product very low in
flavanols but relatively high in cadmium, as exemplified by Hershey's
Cocoa Special Dark, which we found to provide only 13.1 mg of flavanols per
tablespoon (the lowest level among cocoa powders) but 3.2 mcg of cadmium, which
is over the limit for children in Canada and just 0.9 mcg below the limit for
adults.
Fortunately, there is a middle ground, which is where we found our Top
Pick: Ghirardelli Chocolate Premium Baking Cocoa — 100% Cocoa.
Per tablespoon, Ghirardelli has only 0.6 mcg of cadmium yet
provides 44 mg of flavanols and costs just 13 cents. In fact, it is the only
cocoa powder we tested that would not cause a child or adult to exceed daily
cadmium limits if trying to get 200 mg of flavanols (which would take 4.5
tablespoons of Ghirardelli, as noted in the 5th column of the Results table). It has a moderate, although
slightly bitter, chocolate flavor. If you want a less bitter cocoa powder while
still minimizing cadmium, you need to sacrifice flavanols and go with the
French product, Valrhona Poudre De Cacao Cocoa Powder, which, per
tablespoon, provides just 17 mg of flavanols and costs 33 cents — 2½ times as
much as Ghirardelli. Interestingly, both Valrhona and Hershey's
Special Dark are Dutch processed -- which removes bitterness but also
reduces flavanols -- but the concentration of cadmium in Valrhona is
only one-sixth that of Hershey's.
If you are an adult and still want to use one of the cocoa powders that is high
in flavanols but also high in cadmium, it may be best to limit consumption to
one tablespoon per day. None of the high-flavanol powders would be appropriate
for children.
Cacao Nibs
Unfortunately, all three brands of nibs (bits of broken, roasted cocoa bean)
tested by CL were Not Approved due to cadmium contamination. However, the best
option among them is Navitas
Naturals Cacao Nibs because it had the highest concentration of
flavanols — a whopping 677.1 mg per 3 tablespoons (30 grams), which was even
more than its listed amount of 480 mg, and the lowest concentration of cadmium.
Although the suggested 3 tablespoon serving size would put you at more than
double the daily adult limit for cadmium, if you wanted just 200 mg of
flavanols, you could eat a little less than one tablespoon per day and stay
below the daily cadmium limit. Keep in mind that although nibs don't have
sugar, about half their weight is fat, so they are not low in calories, and
most of the fat is saturated fat.
Cocoa Supplements
For the same reasons that made it our "Overall" Top Pick for
getting flavanols, CocoaVia
vegetarian capsules is also one of our two Top Picks among
supplements.
Our other Top Pick among
supplements is CocoaVia Dark
Chocolate — Unsweetened, which is a powder that comes in packets that
provide 450 mg of flavanols. It is a good option for someone who wants to enjoy
a chocolaty drink providing hundreds of milligrams of cocoa flavanols with
little cadmium.
We tested several powdered CocoaVia products
of varying flavors — each listing 450 mg of flavanols per packet. The powder is
to be added to drinks, such as milk or coffee, or to foods, like oatmeal or
yogurt. All of the products passed our testing and we found the powders to mix
easily into liquids. There are two Dark Chocolate versions (Sweetened
and Unsweetened) and each was found to contain about 1 mcg of cadmium per
packet, which is relatively low considering their enormous flavanol content.
The Original flavor (which is a bit bitter) and Cran-Raspberry (which is tart and sweet)
do not have a chocolate flavor but contain virtually no cadmium (0.01 mcg or
less per packet). The Dark Chocolate versions have a rich dark
chocolate taste. The Unsweetened version is a bit bitter, but
we found it to pack a whopping 753.5 mg of flavanols per packet, which made it
our Top Pick. The Sweetened version, which
includes sucralose (which is non-caloric), is mildly sweet and was found to
provide 497.1 mg of flavanols, which is still quite impressive.
Be aware that some cocoa supplements contain little or no flavanols. Hawaii
Pharm Cacao (a liquid) contained little and, in our 2014 testing we
found NuNaturals Pure Liquid™ Cocoa
Bean Extract contained virtually no flavanols despite the claim on its
label that it was "a highly concentrated extract and should not be
confused with less potent powdered herbs or extracts."
How much of a danger is cadmium and lead from
cocoa and chocolate?
As discussed above, many of the tested cocoa powders and nibs, and some of the
dark chocolates, exceeded established limits for cadmium and represent
significant and unnecessary exposure to cadmium.
Cadmium is a probable carcinogen (i.e., cancer-causing agent), can be toxic to
the kidneys, can soften the bones -- causing bone pain, and may affect fetal
development. Cadmium accumulates in the body due to its long biological
half-life in humans of 10 to 35 years. It has been conservatively estimated
that an adult weighing 150 lbs can tolerate total ongoing
daily exposure to cadmium (that is, from all sources of
exposure — food, drink, air) of up to 25 mcg, while a child of half that weight
can tolerate about 12 mcg (EFSA 2011).
The concentrations of cadmium in plant-based foods that are normally considered
"high" in cadmium, such as peanuts and sunflower seeds, have been
found to range from 0.05 to 0.12 mcg per gram; which means that the cadmium
concentrations in many cocoa powders tested by ConsumerLab.com were 10
to 20 times higher than in these cadmium-rich foods (ATSDR 2012). In addition, a daily serving of
many cocoa products exceeds the limit in California of 4.1 mcg, above
which a warning is to appear on the label, and the limit in Canada where a
daily serving of a natural health product must contain no more than 6 mcg of
cadmium for an individual weighing 150 lbs and 3 mcg
for a 75 lb individual, such as a child.
Unfortunately, the U.S. government has not set a limit for cadmium in
supplements or foods. The European Union has established a
cadmium limit of 0.6 mcg per gram of cocoa powder, which most
cocoa powders tested in this review would violate.
The European limit on cadmium in
chocolates with 30% to 50% cacao is 0.3 mcg per gram and, for chocolate over
50% cacao, i.e., most dark chocolates, is 0.8 mcg per gram. None of the tested
chocolate bars exceeded these European concentration limits, although Trader
Joe's 85% Cacao came close at 0.73 mcg of cadmium per gram. It should
be noted that the European cadmium limit on high-flavanol dark chocolate is
lenient and likely considers the potential economic impact on cocoa producers
of stricter limits. Its limit for milk chocolate is just 0.1 mcg per gram due
to particular concern for children, who tend to eat more milk chocolate than
dark chocolate and have a lower daily tolerance for cadmium due to smaller body
size.
In May, 2021, it was proposed by the Codex Committee on
Contaminants in Food that the European limit for chocolate be reviewed for
adoption by the Codex Alimentarius, the international food standards agency
that includes the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and
the World Health Organization (WHO). This review is scheduled for November 2021
(FAO 2021).
Since cadmium, as well as lead, compete for absorption with
other metals, you may be able to reduce their absorption by making sure that
you're getting adequate calcium, iron, and zinc in your diet (Nawrot, Biometals 2010).
Test Results by Product:
Listed
alphabetically below are the test results for 43 cocoa/cacao-based products.
Thirty-seven were selected by ConsumerLab.com and six supplements (each
indicated with a CL flask) are included for having passed the same evaluation
through ConsumerLab.com's voluntary Quality Certification Program.
Products listed as "Approved" contained the cocoa-related compounds
based on their label claims and expected minimum amounts and met requirements
regarding heavy metals and proper labeling (see Passing Score). Flavanol amounts found and
listed calories are shown in the third column; amounts of cadmium found are
shown in the fourth column — along with some caffeine and theobromine levels;
price and cost comparisons are in the fifth column; notable features are in the
sixth column, and the full list of ingredients is available for each product in
the last column.
Results of
ConsumerLab.com Testing of COCOA PRODUCTS
(Click arrows or swipe left or right to see all columns)
Product Name
(Suggested Serving on Label)
Cacao or Cocoa Claimed Per Serving
Taste
Flavanolsⓘ and
Calories
Calories Per 200 mg Flavanols
Heavy Metalsⓘ,
Caffeine and Theobromine Found
Cost Per Serving
[Cost Per 200 mg Flavanols]
Product Price
Cacao/Cocoa Source
Notable Features
Full List of Ingredients Per Serving
Dark Chocolate (Bar or Pieces):
NOT APPROVED
2019
Alter Eco® Deep Dark Blackout
Dist. by Alter Eco Foods
5 sections [40 g]
34 grams cocoa (based on claimed "85% cocoa")
Bittersweet, earthy chocolate flavor
5 sections [40 g]
Flavanols: 221.5 mg (5.5 mg per g) found
Calories: 260 [6.5 Cal/gram] claimed
234.8 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
5 sections [40 g]
Found 14.1
mcg cadmium per serving (0.35 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 50 mg
Theobromine: 375.6 mg
$1.85/5 sections
[$1.67 based on amount found; about 4.5 sections]
$44.28/twelve 2.82 oz [80 g] bar (approx. 24 servings)
Source: Ecuador
Non GMO Project Verified seal. International
Fairtrade Certification seal. Vegan. Gluten-Free.
Precaution: May contain milk, hazelnuts, almonds, coconut, and soy.
5 sections
Calories 260, Calories from Fat 200, Total Fat 22 g, Saturated Fat 13 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 11 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 6 g, Protein 4 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, more...
APPROVED
2017
Baker's Semi-Sweet Baking Chocolate Bar - 56%
Cacao
Dist. by Kraft Foods Group, Inc.
2 pieces [14 g]
7.8 grams cacao (based on claimed "56% cacao")
Mild, sweet
2 pieces [14 g]
Flavanols: 101.1 mg (7.2 mg per g) found
Calories: 80 [5.7 Cal/gram] claimed
158.3 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2 pieces [14 g]
✔
Found 2.1 mcg cadmium per serving (0.15 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 10.8 mg
Theobromine: 100.6 mg
$0.31/2 pieces
[$0.62 based on amount found; about 4 pieces]
$2.50/4 oz [113 g] bar (approx. 8 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: Contains: Soy. Manufactured On Equipment That Processes
Milk.
2 pieces
Calories 80, Calories from Fat 45, Total Fat 5 g, Saturated Fat 3 g, Trans Fat
0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 8 g, Dietary Fiber 1 g,
Sugars 6 g, Protein <1 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 6%, more...
APPROVED
2019
Baker's Unsweetened - 100% Cacao
Dist. by Kraft Heinz Foods
2 pieces [14 g]
14 grams cacao (based on claimed "100% cacao")
Slightly bitter, rich chocolate flavor
2 pieces [14 g]
Flavanols: 118.4 mg (8.5 mg per g) found
Calories: 70 [5 Cal/gram] claimed
118.4 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2 pieces [14 g]
✔
Found 2.9 mcg cadmium per serving (0.21 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 18.3 mg
Theobromine: 171.6 mg
$0.35/2 pieces
[$0.59 based on amount found; about 3 pieces]
$2.79/4 oz [113 g] bar (approx. 8 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: May Contain: Milk.
2 pieces
Calories 70, Total Fat 7 g, Saturated Fat 4.5 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 4 g, Dietary Fiber 3 g, Total Sugars [Includes
0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein 2 g, Vit. D 0 mcg, Calcium 0 mg, Iron 2.8 mg, Potas. 150 mg, more...
APPROVED
for Adults
2017
Chocolove® Extra Strong - 77% Cocoa
Content
Dist. by Chocolove
1/3 bar [30 g]
23.1 gram cocoa (based on claimed "77%
cocoa")
Sweet, slightly fruity
1/3 bar [30 g]
Flavanols: 279.3 mg (9.3 mg per g) found
Calories: 180 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
129 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/3 bar [30 g]
✔
Note: Found 3.6 mcg cadmium per serving (0.12 mcg per g), which is over the
Health Canada limit for children (3.0 mcg per serving)
Caffeine: 29.9 mg
Theobromine: 304.8 mg
$0.86/1/3 bar
[$0.62 based on amount found; about 2/9 of a bar]
$2.59/3.2 oz [90 g] bar (approx. 3 servings)
Source: African and Caribbean
Kosher.
Precaution: May Contain Traces Milk, Wheat, Peanuts Or Other Nuts.
1/3 bar
Calories 180, Fat Cal. 130, Total Fat 14 g, Sat Fat 9 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest. 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb. 12 g, Fiber 4 g,
Sugars 6 g, Protein 2 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 25%.
Ingredients: Cocoa Liquor, more...
APPROVED
2019
Chocolove Strong Dark Chocolate -
70% Cocoa Content
Dist. by Chocolove
1/3 bar [30 g]
21 grams cocoa (based on claimed "70% cocoa")
Sweet, fairly smooth flavor, slightly waxy
1/3 bar [30 g]
Flavanols: 225.9 mg (7.5 mg per g) found
Calories: 160 [5.3 Cal/gram] claimed
141.7 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/3 bar [30 g]
✔
Found 2.7 mcg cadmium per serving (0.09 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 31.8 mg
Theobromine: 304.5 mg
$0.79/1/3 bar
[$1.08 based on amount found, about 4/9 of a bar]
$2.36/3.2 oz [90 g] bar (approx. 3 servings)
Source: African and Caribbean
Non GMO Project Verified seal. Kosher.
Rainforest Alliance Certified seal.
Precaution: Contains Soy. May Contain Traces Of
Milk, Wheat, Peanuts Or Other Nuts.
1/3 bar
Calories 160, Fat Cal. 110, Total Fat 13 g, Sat Fat 8 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest. 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb. 14 g, Fiber 3 g,
Sugars 9 g, Protein 2 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 30%.
Ingredients: Cocoa Liquor, more...
NOT APPROVED
2017
Dove® Dark Chocolate
Dist. by Mars Chocolate North America, LLC
5 pieces [40 g]
% cocoa not listed
Sweet, smooth, no bitterness
5 pieces [40 g]
Flavanols: 281.3 mg (7.0 mg per g) found
Calories: 210 [5.3 Cal/gram] claimed
149 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
5 pieces [40 g]
Found 9.5
mcg cadmium per serving (0.24 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 25.0 mg
Theobromine: 263.8 mg
$0.88/5 pieces
[$0.63 based on amount found; about 3.5 pieces]
$5.29/8.87 oz [251.5 g] bag (approx. 6 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: Allergy Information: Contains Milk And
Soy.
5 pieces
Calories 210, Fat Cal. 120, Total Fat 13 g, Sat. Fat 8 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest. 5 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb. 24 g, Fiber 3 g,
Sugars 19 g, Protein 2 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 6%, more...
APPROVED
2019
Endangered Species™ Chocolate Strong + Velvety
Dark Chocolate - 88% Cocoa
Dist. by Endangered Species Chocolate, LLC
1/3 bar [28 g]
24.6 grams cocoa (based on claimed "88% cocoa")
Bittersweet
1/3 bar [28 g]
Flavanols: 157.9 mg (5.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 180 [6.4 Cal/gram] claimed
228 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/3 bar [28 g]
✔
Found 1.5 mcg cadmium per serving (0.05 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 32.5 mg
Theobromine: 321.2 mg
$1.16/1/3 bar
[$1.47 based on amount found; about 2/5 of a bar]
$3.49/3 oz [85 g] bar (approx. 3 serving)
Source: Not listed
Non GMO Project Verified seal. International
Fairtrade Certification seal. Kosher. Certified Vegan Vegan.org seal.
Gluten-Free.
Precaution: Allergens: Contains Soy. Produced On Equipment That
Also Processes Products Containing Milk, Peanuts And
Tree Nuts.
1/3 bar [28 g]
Calories 180, Total Fat 13 g, Sat. Fat 8 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest.
0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb. 11 g, Total Sugars [Incl. 3 g Added Sugars] 3 g,
Protein 3 g, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 0 mg, Iron 1.5 mg, Potassium 260 mg.
Ingredients: Bittersweet Chocolate (Chocolate Liquor, Sugar, Soy Lecithin,
Vanilla).
NOT APPROVED
2017
Equal Exchange Chocolates Organic Panama Extra
Dark - 80% Cacao
Dist. by Equal Exchange
12 pieces [40 g]
32 gram cacao (based on claimed "80% cacao")
Mild, slightly waxy
12 pieces [40 g]
Flavanols: 179.2 mg (4.5 mg per g) found
Calories: 240 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
267.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
12 pieces [40 g]
Found 8.4
mcg cadmium per serving (0.21 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 54.3 mg
Theobromine: 434.4 mg
$2.37/12 pieces
[$2.64 based on amount found; about 13 pieces]
$28.39/six 2.8 oz [80 g] bar (approx. 12 servings)
Source: Panama
USDA Organic Seal. Kosher.
Precaution: May Contain Milk, Peanuts, Hazelnuts, Almonds &
Coconut.
12 pieces
Calories 240, Fat Cal. 170, Total Fat 19 g, Sat. Fat 12 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest. 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb 15 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 8 g, Protein 4 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A
0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 40%.
Ingredients: Organic Chocolate Liquor, more...
APPROVED
2017
Ghirardelli® Intense Dark 86% Cacao
Mfd. by Ghirardelli Chocolate Company
4 sections [45 g]
38.7 gram cacao (based on claimed "86%
cacao")
Not much flavor, waxy
4 sections [45 g]
Flavanols: 296.6 mg (6.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 250 [5.6 Cal/gram] claimed
168.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
4 sections [45 g]
✔
Found <0.1 mcg cadmium per gram
Caffeine: 35.3 mg
Theobromine: 435.8 mg
$1.23/4 sections
[$0.83 based on amount found; about 2.5 sections]
$2.46/3.17 oz [90 g] bar (approx. 2 servings)
Source: Not listed
Precaution: May contain tree nuts and milk.
4 sections
Calories 250, Calories from Fat 220, Total Fat 25 g, Saturated Fat 15 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 15 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 5 g, Protein 3 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A
0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 25%, more...
APPROVED
2017
Lily's™ Dark Chocolate - Original - Stevia
Sweetened 55% Cocoa
Dist. by Lily's Sweets, LLC
1/2 bar [40 g]
22 gram cocoa (based on claimed "55% cocoa")
Smooth, not bitter. No aftertaste despite non-sugar sweeteners
1/2 bar [40 g]
Flavanols: 136.4 mg (3.4 mg per g) found
Calories: 160 [4 Cal/gram] claimed
234.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/2 bar [40 g]
✔
Found <0.1 mcg cadmium per gram
Caffeine: 24.8 mg
Theobromine: 322.9 mg
$2.20/1/2 bar
[$3.22 based on amount found; about 7/10 of a bar]
$4.39/3 oz [85 g] bar (approx. 2 servings)
Source: Not listed
Fair Trade Seal. Certified Gluten Free. No Sugar Added. Not a low calorie food.
Precaution: Produced on equipment that also processes product
containing peanuts and tree nuts.
1/2 bar
Calories 160, Calories from Fat 130, Total Fat 15 g, Saturated Fat 9 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol less than 5 mg, Sodium 0 g, Total Carbs 22 g, Dietary
Fiber 12 g, Sugars less than 1 g, Erythritol 6g, Protein 2 g, Percent of
recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 20%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Lindt Excellence Supreme Dark - 90% Cocoa
Mfd. by Lindt & Sprungli
(USA) Inc.
4 squares [40 g]
36 grams cocoa (based on claimed "90% cocoa") (Dutched
- alkali processed)
Slightly sweet, mild chocolate flavor, waxy
4 squares [40 g]
Flavanols: 147.5 mg (3.7 mg per g) found
Calories: 240 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
325.4 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
4 squares [40 g]
Found 5.8
mcg cadmium per serving (0.15 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 42.4 mg
Theobromine: 474 mg
$1.68/4 squares
[$2.27 based on amount found; about 1/2 of a bar]
$4.19/3.5 oz [100 g] bar (approx. 2.5 servings)
Source: Not listed
Precaution: May contain traces of peanuts/ soybeans/ tree nuts/
milk.
4 squares
Calories 240, Calories from Fat 190, Total Fat 22 g, Saturated Fat 13 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 10 mg, Total Carbohydrate 12 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 3 g, Protein 4 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A
0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 4%, Iron 15%, more...
APPROVED
2019
Top Pick
for Dark Chocolate (Bar or Pieces)
Montezuma's® Dark Chocolate Absolute Black -
100% Cocoa![]()
Mfd. by Montezuma's Chocolates
1/4 bar [25 g]
25 grams cocoa (based on claimed "100% cocoa")
Strong chocolate flavor, slightly bitter
1/4 bar [25 g]
Flavanols: 350.5 mg (14 mg per g) found
Calories: 150 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
85.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/4 bar [25 g]
✔
Found 1.4 mcg cadmium per serving (0.06 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 85.3 mg
Theobromine: 604.5 mg
$1.08/1/4 bar
[$0.61 based on amount found; about 3/20 of a bar]
$25.82/six 100 g bar (approx. 24 servings)
Source: Not listed
Vegan. Free From Gluten, Soya, Colourings,
Preservatives & GM.
Precaution: May Contain Traces Of Dairy,
Nuts, Peanuts & Sesame Seeds.
1/4 bar
Energy 160 kcal, Fat [of which: saturates 8 g] 13 g, Carbohydrates [of which:
Sugars <0.1 g] 2 g, Protein 3 g, Fibre 4 g, Salt
<0.01 g.
Ingredients: Dark Chocolate (Cocoa Mass 100%).
NOT APPROVED
2017
Moser Roth Edel Bitter
85% Cacao
Dist. by Moser Roth GmbH
1 bar [25 g]
21.3 mg cacao (based on claimed "85% cacao")
Rich chocolate taste, smooth
1 bars [25 g]
Flavanols: 197.5 mg (7.9 mg per g) found
Calories: 151 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
152.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 bars [25 g]
Found 6.1
mcg cadmium per serving (0.25 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 25.5 mg
Theobromine: 253 mg
$1.50/1 bar
[$1.52 based on amount found; about 1 bar]
$5.99/4 bars [100 g] (approx. 4 servings)
Source: Not listed
Precaution: Can also contain portions of milk, hazelnut, almond,
peanuts and other nuts.
1 bars
Calories 151, Total Fat 12.5 g, Saturated Fat 7.7 g, Carbohydrate 5.1 g, Sugars
3.5, Protein 2.8 g, Salt 0.07 g.
Ingredients: Cocoa mass, cocoa butter, sugar, lean cocoa, emulsifier lecithin
(soya), vanilla extract.
NOT APPROVED
2017
Pascha™ Organic Dark Chocolate - 85% Cacao
Dist. by Pascha Chocolate Company
10 pieces [42 g]
35.7 gram cacao (based on claimed "85%
cacao")
Bitter
10 pieces [42 g]
Flavanols: 192.4 mg (4.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 260 [6.2 Cal/gram] claimed
270.3 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
10 pieces [42 g]
Found 22.7
mcg cadmium per serving (0.54 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 58.9 mg
Theobromine: 454.4 mg
$1.60/10 pieces
[$1.66 based on amount found; about 10 pieces]
$3.99/3.5 oz [100 g] bar (approx. 2.5 servings)
Source: Peru
USDA Organic Seal. Non GMO Project Verified.
Kosher. Free From Peanuts, Nuts, Dairy, Soy, Eggs, Wheat & Gluten. Fair
Trade Certified Seal.
10 pieces
Calories 260, Calories from Fat 170, Total Fat 19 g, Saturated Fat 12 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 15 mg, Total Carbohydrate 16 g, Dietary Fiber
4 g, Sugars 7 g, Protein 5 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A
0%, Vitamin C 8%, Calcium 4%, Iron 10%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Scharffen Berger® Unsweetened - 99%
Cacao
Mfd. by Scharffen
Berger Chocolate Maker
1 block [55 g]
54.5 grams cacao (based on claimed "99% cacao')
Bitter, earthy chocolate flavor
Note: Large, thick, block for baking
1 block [55 g]
Flavanols: 305.9 mg (5.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 280 [5.1 Cal/gram] claimed
183.1 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 block [55 g]
Found 13.6
mcg cadmium per serving (0.25 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 79.2 mg
Theobromine: 628.7 mg
$1.92/1 block
[$1.25 based on amount found; about 1/10 of a bar]
$9.58/9.7 oz [275 g] bar (approx. 5 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
1 block
Calories 280, Calories from Fat 250, Total Fat 30 g, Sat. Fat 19 g, Trans Fat 0
g, Cholest. 0 mg, Sodium 5 mg, Total Carb. 14 g,
Dietary Fiber 9 g, Sugars <1 g, Protein 8 g, Percent of recommended daily
intake: Vitamin A 0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 2%, Iron 20%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Taza Chocolate® Wicked Dark® -
95% Dark
Mfd. by Taza Chocolate
1/2 bar [35 g]
33.3 grams cacao (based on claimed "95% cacao")
Mildly sweet, earthy chocolate flavor, slightly grainy
1/2 bar [35 g]
Flavanols: 192.5 mg (5.5 mg per g) found
Calories: 210 [6 Cal/gram] claimed
218.2 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/2 bar [35 g]
Found 6.8
mcg cadmium per serving (0.19 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 67.2 mg
Theobromine: 414.4 mg
$1.69/1/2 bar
[$1.75 based on amount found; about 1/2 of a bar]
$3.37/2.5 oz [70 g] bar (approx. 2 servings)
Source: Not listed
USDA Organic seal. Non GMO Project Verified seal.
Gluten Free. Dairy Free. Soy Free. Vegan. Kosher.
Precaution: Contains traces of almonds, cashews, coconut, hazelnuts
and pecans.
1/2 bar
Calories 120, Total Fat 14 g, Sat Fat 10 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg,
Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb. 14 g, Dietary Fiber 8 g, Total Sugars [Incl. 2 g Added
Sugars] 2 g, Protein 5g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin D 0%,
Calcium 2%, Iron 6%, Potassium 6%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Theo Sea Salt - 70% Dark Chocolate
Dist. by Theo Chocolate
1/2 bar [43 g]
30.1 grams cocoa (based on claimed "70% cocoa")
Mildly sweet and salty, smooth chocolate flavor
1/2 bar [43 g]
Flavanols: 172.9 mg (4 mg per g) found
Calories: 210 [4.9 Cal/gram] claimed
242.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1/2 bar [43 g]
Found 10.3
mcg cadmium per serving (0.24 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 52.5 mg
Theobromine: 427.4 mg
$1.73/1/2 bar
[$2.00 based on amount found; about 3/5 of a bar]
$3.46/3 oz [85 g] bar (approx. 2 servings)
Source: Not listed
Non GMO Project Verified seal. USDA Organic
seal. Soy Free. Kosher. Fair For Life Fair Trade seal.
Precaution: Allergy Information: Manufactured on shared equipment
with products containing milk, eggs, wheat, peanuts & tree nuts.
1/2 bar
Calories 210, Fat Cal. 150, Total Fat 17 g, Sat. Fat 10 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholest. 0 mg, Sodium 150 mg, Total Carb. 20 g, Fiber 4 g,
Sugars 13 g, Protein 3 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 4%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2017
Trader Joe's® The Dark Chocolate Lover's
Chocolate Bar - 85% Cacao
Dist. by Trader Joe's
2/3 bar [40 g]
34 grams cacao (based on claimed "85% cacao")
Slightly fruity, bitter
2/3 bar [40 g]
Flavanols: 502.4 mg (12.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 250 [6.3 Cal/gram] claimed
99.5 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2/3 bar [40 g]
Found 29
mcg cadmium per serving (0.73 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 74.4 mg
Theobromine: 439.2 mg
$0.56/2/3 bar
[$0.22 based on amount found; about 1/5 of a bar]
$1.69/2 1.75 oz. [50 g] bars (approx. 3 servings)
Source: Colombia
Our Venders Follow Good Manufacturing Practices To
Segregate Ingredients To Avoid Cross Contact With Allergens.
Precaution: Made On Shared Equipment With Milk.
2/3 bar
Calories 250, Calories from Fat 180, Total Fat 20 g, Saturated Fat 10 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 13 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 6 g, Protein 4 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A
0%, Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 6%, Iron 6%, more...
APPROVED
2019
Top Pick
for Dark Chocolate (Bar or Pieces)
Trader Joe's® Pound Plus - 72% Cacao Dark
Chocolate
Dist. by Trader Joe's
3 squares [38 g]
27.4 grams cacao (based on claimed "72% cacao")
Sweet, slightly bitter, smooth chocolate flavor
3 squares [38 g]
Flavanols: 281.2 mg (7.4 mg per g) found
Calories: 230 [6.1 Cal/gram] claimed
163.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
3 squares [38 g]
✔
Found 2.7 mcg cadmium per serving (0.07 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 47.1 mg
Theobromine: 508.4 mg
$0.38/3 squares
[$0.27 based on amount found; about 2 squares]
$4.99/17.6 oz [500 g] bar (approx. 13 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: Contains Soy. May Contain Traces Of
Wheat, Milk, Eggs, Tree Nuts.
3 squares
Calories 230, Calories from Fat 130, Total Fat 15 g, Saturated Fat 9 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 19 g, Dietary Fiber
5 g, Sugars 10 g, Protein 3, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 40%, more...
Dark Chocolate (Chips):
APPROVED
2019
Ghirardelli® Chocolate Premium Baking Chips -
60% Cacao Bittersweet Chocolate
Mfd. by Ghirardelli Chocolate Company
16 chips [15 g]
(wide, flat shape)
9 grams cacao (based on claimed "60% cacao")
Slightly sweet, very slightly bitter, smooth chocolate flavor
16 chips [15 g]
Flavanols: 79.2 mg (5.3 mg per g) found
Calories: 80 [5.3 Cal/gram] claimed
202 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
16 chips [15 g]
✔
Found 2.7 mcg cadmium per serving (0.18 mcg per g)
$0.25/16 chips
[$0.64 based on amount found; about 35 chips]
$4.79/10 oz [283 g] bag (approx. 19 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: May contain milk.
16 chips
Calories 80, Calories from Fat 50, Total Fat 6 g, Sat Fat 3.5 g, Trans Fat 0 g,
Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 8 g, Dietary Fiber 1 g,
Sugars 6 g, Protein 1 g. Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 6%, more...
APPROVED
for Adults
2019
Top Pick
for Dark Chocolate (Chips)
Guittard Extra Dark Chocolate
Baking Chips - 63% Cacao
Dist. by Guittard
Chocolate Company
30 pieces [15 g]
(little "kiss-shaped" chips)
9.5 grams cacao (based on claimed "63% cacao")
Moderately sweet, smooth chocolate flavor
30 pieces [15 g]
Flavanols: 143.6 mg (9.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 80 [5.3 Cal/gram] claimed
111.5 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
30 pieces [15 g]
✔
Note: Found 3.4 mcg cadmium per serving (0.23 mcg per g), which is over the
Health Canada limit for children of 3.0 mcg per serving
$0.20/30 pieces
[$0.28 based on amount found; about 40 pieces]
$4.49/11.5 oz [326 g] bag (approx. 22 servings)
Source: Not listed
Organic. Made In A Peanut-Free, Tree-Nut Free,
& Gluten-Free Manufacturing Facility. International Fairtrade Certification
seal. Non GMO Project Verified seal.
Precaution: Made On Equipment Also Used To Make Milk Chocolate; Not
Suitable For Individuals With Milk Allergies.
30 pieces
Calories 80, Total Fat 5 g, Saturated Fat 3 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg,
Sodium 0 mg, Total Carb 8 g, Dietary Fiber 3 g, Total Sugars [Including 5 g
Added Sugars] 6 g, Protein, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 10 mg, Iron 2 mg,
Potassium 84 mg.
Ingredients: Cacao Beans, Sugar, Sunflower Lecithin And
Vanilla.
Cacao/Cocoa Powder:
APPROVED
for Adults
2017
Dagoba® Organic Chocolate Cacao Powder
Mfd. by Dagoba Organic Chocolate a division of
The Hershey Company
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cocoa powder
1 tbsp [5 g]
Total Flavanols: 35.5 mg (7.1 mg per g) found
Calories: 10 [2 Cal/gram] claimed
56.3 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
✔
Note: Found 3.1 mcg cadmium per serving (0.61 mcg per g), which is over the
Health Canada limit for children of 3.0 mcg per serving
Caffeine: 15.1 mg
Theobromine: 128.5 mg
$0.17/1 tbsp
[$0.95 based on amount found; about 5.5 tbsp]
$45.60/6 pack of 8 oz [226 g] containers (total 48 oz [1,356 g]) (approx. 270
servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher. USDA Organic Seal. Rainforest Alliance Certified.
Precaution: May Contain tree nuts, wheat, soy, dairy and egg.
1 tbsp
Calories 20, Calories from Fat 10, Total Fat 1.5 g, Saturated Fat 0.5 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2
g, Sugars 0 g, Protein 1 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 15%.
Ingredients: Cocoa.
APPROVED
2019
Top Pick
for Cacao/Cocoa Powders
Ghirardelli® Chocolate Premium Baking Cocoa -
100% Cocoa
Dist. by Ghirardelli Chocolate Company
1 tbsp [6 g]
6 gram cocoa powder
Moderate chocolate flavor, slightly bitter
1 tbsp [6 g]
Flavanols: 44 mg (7.3 mg per g) found
Calories: 15 [2.5 Cal/gram] claimed
68.2 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [6 g]
✔
Found 0.6 mcg cadmium per serving (0.1 mcg per g)
$0.13/1 tbsp
[$0.60 based on amount found; about 4.5 tbsp]
$4.99/8 oz [227 g] bag (approx. 38 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
Precaution: May contains tree nuts, wheat, soy, milk and egg.
1 tbsp
Calories 15, Total Fat 1.5 g, Saturated Fat 1 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Total Sugars
[Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein 1 g, Vit. D 0 mcg, Calcium 6 mg, Iron
3 mg, Potas. 108 mg.
Ingredients: Cocoa.
NOT APPROVED
2017
Healthworks Cacao Powder
Dist. by Healthworks
2.5 tbsp [14 g]
14 gram cocoa powder
2.5 tbsp [14 g]
Flavanols: 185.9 mg (13.3 mg per g) found
Calories: 60 [4.3 Cal/gram] claimed
64.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2.5 tbsp [14 g]
Found 24.9
mcg cadmium per serving (1.8 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 38.2 mg
Theobromine: 255.4 mg
$0.33/2.5 tbsp
[$0.36 based on amount found; about 2.5 tbsp]
$10.63/16 oz [454 g] container (approx. 32 servings)
Source: Latin America
USDA Organic Seal.
2.5 tbsp
Calories 60, Calories from Fat 10, Total Fat 1.5 g, Saturated Fat 1 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 10 mg, Total Carbohydrate 9 g, Dietary Fiber
4 g, Sugars 0 g, Protein 3 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2017
Hershey's Cocoa - 100% Cacao Natural Unsweetened
Dist. by The Hershey Company
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cocoa powder
1 tbsp [5 g]
Flavanols: 123.7 mg (24.7 mg per g) found
Calories: 10 [2 Cal/gram] claimed
16.2 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
Found 4.3
mcg cadmium per serving (0.85 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 10.4 mg
Theobromine: 121.7 mg
$0.09/1 tbsp
[$0.15 based on amount found; about 1.5 tbsp]
$4.19/8 oz [226 g] container (approx. 45 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher, NO gluten, artificial colors, preservatives.
1 tbsp
Calories 10, Calories from Fat 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Trans Fat
0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g,
Sugars 0 g, Protein <1 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%,
Vitamin C 0%, Calcium 0%, Iron 2%, more...
APPROVED
for Adults
2019
Hershey's Cocoa Special Dark - 100% Cacao
Dist. by The Hershey Company
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cocoa powder (Dutched
- alkali processed)
Smooth, moderate chocolate flavor. Very dark color.
1 tbsp [5 g]
Flavanols: 13.1 mg (2.6 mg per g) found
Lowest in flavanols among cocoa powders
Calories: 10 [2 Cal/gram] claimed
152.7 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
✔
Note: Found 3.2 mcg cadmium per serving (0.64 mcg per g) ,
which is over the Health Canada limit for children of 3.0 mcg per serving
$0.10/1 tbsp
[$1.46 based on amount found; about 15 tbsp]
$4.29/8 oz [226 g] container (approx. 45 servings)
Source: Not listed
No Artificial Flavors. No Artificial Colors. No Preservatives. Gluten Free.
Kosher. Non GMO Project Verified seal.
1 tbsp
Calories 10, Total Fat 0.5 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Total Sugars
[Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 10 mg, Iron
2.1 mg, Potassium 250 mg, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Navitas™ Organic Cacao Powderⓘ
Dist. by Navitas
Organics
2.5 tbsp [15 g]
15 gram cacao powder
Somewhat smooth, mild chocolate flavor, very slightly bitter
2.5 tbsp [15 g]
700 mg flavanols
Flavanols: 374.4 mg (25 mg per g) (53.5% of listed amount)
Calories: 60 [4 Cal/gram] claimed
32.1 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2.5 tbsp [15 g]
Found 9.7
mcg cadmium per serving (0.65 mcg per g)
$0.62/2.5 tbsp
[$0.18 based on amount claimed]
[$0.33 based on amount found; about 1.25 tbsp]
$9.34/8 oz [227 g] bag (approx. 15 servings)
Source: Peru
USDA Organic seal. Non GMO Project Verified seal. Kosher.
BPA Free. International Fairtrade Certification seal.
2.5 tbsp
Calories 60, Total Fat 1.5 g, Saturated Fat 1 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 8 g, Dietary Fiber 5 g, Total Sugars
[Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein 4 g, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 35 mg, more...
NOT APPROVED
2017
Trader Joe's® Cocoa Powder Unsweetened
Dist. by Trader Joe's
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cocoa powder
1 tbsp [5 g]
Flavanols: 118.1 mg (23.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 10 [2 Cal/gram] claimed
16.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
Found 5.9
mcg cadmium per serving (1.2 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 19.6 mg
Theobromine: 123.2 mg
$0.05/1 tbsp
[$0.08 based on amount found; about 1.5 tbsp]
$2.49/9 oz [255 g] container (approx. 51 servings)
Source: Columbia
Precaution: May Contain Traces Of Soy.
1 tbsp
Calories 10, Calories from Fat 5, Total Fat 0.5 g, Sodium 0 mg, Total
Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Protein less than 1 g, Percent of
recommended daily intake: Iron 4%, Magnesium 6%.
Ingredients: Tumaco Cocoa Powder.
NOT APPROVED
2019
Trader Joe's® Organic Fair Trade Cacao Powder
Dist. by Trader Joe's
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cacao powder
Somewhat bitter/sour, mild chocolate flavor
1 tbsp [5 g]
Flavanols: 76 mg (15.2 mg per g) found
Calories: 20 [4 Cal/gram] claimed
52.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
Found 4.9
mcg cadmium per serving (0.98 mcg per g)
$0.09/1 tbsp
[$0.23 based on amount found; about 2.5 tbsp]
$3.99/8 oz [227 g] bag (approx. 45 servings)
Source: Peru
Kosher. Quality Assurance International Certified Organic seal. USDA Organic
seal. International Fairtrade Certification seal.
1 tbsp
Calories 20, Total Fat 0.5 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Total Sugars
[Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein 1 g, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 10 mg,
Iron 0.6 mg, Potassium 100 mg, more...
APPROVED
2019
Valrhona Poudre De Cacao Cocoa Powder - 100%
Cacao
Dist. by Valrhona
5 gⓘ
5 gram cacao powder (Dutched - alkali processedⓘ)
Smooth, earthy moderate chocolate flavor. Very dark color.
5 gⓘ
Flavanols: 17 mg (3.4 mg per g) found
Calories: 22.5 [4.5 Cal/gram] claimed
264.7 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
5 gⓘ
✔
Found 0.5 mcg cadmium per serving (0.1 mcg per g)
$0.33/5 gⓘ
[$3.88 based on amount found; about 10 g]
$16.50/8.82 oz [250 g] container (approx. 50 servings)
Source: Not listed
Kosher.
5 gⓘ
Calories 22.5, Calories from Fat 10, Total Fat 1.125 g, Saturated Fat 1.5 g,
Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 1.25 mg, Total Carbohydrate 2 g,
Dietary Fiber 1.375 g, Sugars 0.125 g, Protein 1.125 g, Percent of recommended
daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, Vitamin C 0%, more...
APPROVED
2019
Volupta Cacao Powder
Dist. by Volupta, LLC
1 tbsp [5 g]
5 gram cacao powder
Slightly bitter, moderate chocolate flavor
1 tbsp [5 g]
55 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 105.6 mg (21.1 mg per g) found
Calories: 20 [4 Cal/gram] claimed
37.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 tbsp [5 g]
✔
Found 2.9 mcg cadmium per serving (0.59 mcg per g)
$0.09/1 tbsp
[$0.33 based on amount claimed]
[$0.17 based on amount found; about 2 tbsp]
$32.99/2 pack of 32 oz [907 g] bags (total 64 oz [1,814 g]) (approx. 362
servings)
Source: Peru, Ecuador
USDA Organic seal. Non GMO Project Verified seal.
International Fairtrade Certification seal. Kosher. Vegan.
Precaution: Processed In A Facility That
Also Handles Egg, Dairy, Soy, Wheat, Tree Nut, Fish.
Prop 65 Warning for Reproductive Health.
1 tbsp
Calories 20, Total Fat 0.5 g, Saturated Fat 0 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Polyunsaturated
Fat 0 g, Monounsaturated Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total
Carbohydrate 3 g, Dietary Fiber 2 g, Total Sugars [Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0
g, Protein 1 g, Vitamin D 0 mcg, more...
Cacao Nibs:
NOT APPROVED
2019
Healthworks® Cacao Nibs
Dist. by Healthworks
1 oz [28 g]
28 gram cacao nibs (small-sized)
Very crunchy, slightly bitter, mild chocolate flavor
1 oz [28 g]
Flavanols: 596.8 mg (21.3 mg per g) found
Calories: 130 [4.6 Cal/gram] claimed
43.6 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
1 oz [28 g]
Found 12.6
mcg cadmium per serving (0.45 mcg per g)
$0.75/1 oz
[$0.25 based on amount found; about 1/3 of an ounce]
$11.99/16 oz [454 g] bag (approx. 16 servings)
Source: Latin America
USDA Organic seal.
1 oz
Calories 130, Calories from Fat 110, Total Fat 14 g, Saturated Fat 8 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 10 g, Dietary Fiber
8 g, Sugars 0 g, Protein 4 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, more...
NOT APPROVED
2019
Best Option
Among Nibs
Navitas™ Organics Organic Cacao
Nibs
Dist. by Navitas Organics
3 tbsp [30 g]
30 gram cacao nibs (small- and medium-sized)
Very crunchy, slightly bitter, mild chocolate flavor
3 tbsp [30 g]
480 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 677.1 mg (22.6 mg per g) found
Calories: 190 [6.3 Cal/gram] claimed
56.1 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
3 tbsp [30 g]
Found 8.7
mcg cadmium per serving (0.29 mcg per g)
$0.87/3 tbsp
[$0.36 based on amount claimed]
[$0.26 based on amount found; about 1 tbsp]
$6.99/8 oz [227 g] bag (approx. 8 servings)
Source: Peru
USDA Organic seal. Non GMO Project Verified seal.
Kosher. BPA Free. International Fairtrade Certification seal.
3 tbsp [30 g]
Calories 190, Total Fat 15 g, Saturated Fat 9 g, Trans Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0
mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 11 g, Dietary Fiber 8 g, Total Sugars
[Includes 0 g Added Sugars] 0 g, Protein 4 g, Vitamin D 0 mcg, Calcium 26 mg,
Iron 1 mg, Potassium 255 mg, Magnesium 84 mg, more...
NOT APPROVED
2017
Viva Naturals® Cacao Nibs Organic
Dist. by Viva Naturals Inc.
2 tbsp [14 g]
14 gram cacao nibs
Crunchy
2 tbsp [14 g]
Flavanols: 170.1 mg (12.2 mg per g) found
Calories: 90 [6.4 Cal/gram] claimed
105.8 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
2 tbsp [14 g]
Found 4.9
mcg cadmium per serving (0.35 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 20.5 mg
Theobromine: 135.4 mg
$0.38/2 tbsp
[$0.45 based on amount found; about 2 tbsp]
$12.29/1 lb [454 g] container (approx. 32 servings)
Source: Peru
Non GMO Project Verified. Quality Assurance
International Certified Organic. Kosher. Vegan. Gluten-Free.
2 tbsp
Calories 90, Calories from Fat 60, Total Fat 7 g, Saturated Fat 4.5 g, Trans
Fat 0 g, Cholesterol 0 mg, Sodium 0 mg, Total Carbohydrate 4 g, Dietary Fiber 3
g, Sugars 0 g, Protein 2 g, Percent of recommended daily intake: Vitamin A 0%, more...
Cacao and Cocoa Supplements:
APPROVED
2019
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
2 capsules
1,100 mg cocoa extract
2 Capsules Daily With Food.
2 capsules
450 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 600.4 mg (495.7 mg per g) found
Calories: 5 [4.1 Cal/gram] claimed
1.7 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Large vegetarian capsuleⓘ
2 capsules
✔
Found 0.1 mcg cadmium per serving (0.1 mcg per g)
20 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 19.5 mg
Theobromine: 55.7 mg
$1.33/2 capsules
[$0.59 based on amount claimed]
[$0.44 based on amount found]
$120.00/3 pack of 60 capsule bottles (total 180 capsules)
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 20 mg Naturally-Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
2 capsules
Calories 5, Total Carbohydrate <1 g, Cocoa Extract (bean) [Cocoa Flavanols
450 mg] 1,110 mg.
Other Ingredients: Hypromellose Capsule, Silicon Dioxide, Magnesium Stearate.
APPROVED
2019
CocoaVia™ - Cran-Raspberry
(Mix)ⓘ![]()
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
1 packet [5.9 g]
1,200 mg cocoa extract
Add 1 packet to a beverage or food of choice.
Purple powder, mixes easily; Tart, sweet, cranberry/raspberry flavor;
slightly astringent, slight lingering sweetness
1 packet [5.9 g]
450 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 443 mg (75.1 mg per g) found
Calories: 20 [3.4 Cal/gram] claimed
9.1 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Powder in packet
1 packet [5.9 g]
✔
Found 0.01 mcg cadmium per serving (0.002 mcg per g)
25 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 16.3 mg
Theobromine: 54.6 mg
$1.17/packet
[$0.52 based on amount claimed]
[$0.53 based on amount found]
$35.00/30 packets
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 25 mg Naturally-Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
Contains Bioengineered Food Ingredients.
1 packet
Calories 20, Total Carbohydrate 5 g, Cocoa Extract (bean) [Cocoa Flavanols 450
mg] 1,200 mg.
Other Ingredients: Maltodextrin, Citric Acid, Natural Flavors, Sucralose.
APPROVED
2019
CocoaVia™ - Original (Mix)ⓘ![]()
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
1 packet [4 g]
1,130 mg cocoa extract
Add 1 packet to a beverage or food of choice.
Dark brown powder, mixes easily; Little flavor, slightly bitter and
astringent
1 packet [4 g]
450 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 404 mg (101 mg per g) found
Calories: 15 [3.8 Cal/gram] claimed
7.5 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Powder in packet
1 packet [4 g]
✔
Found <0.008 mcg cadmium per serving (<0.002 mcg per g)
25 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 14.8 mg
Theobromine: 14.8 mg
$1.17/packet
[$0.52 based on amount claimed]
[$0.58 based on amount found]
$35.00/30 packets
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 25 mg Naturally-Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
Contains A Bioengineered Food Ingredient.
1 packet
Calories 15, Total Carbohydrate 3 g, Cocoa Extract (bean) [Cocoa Flavanols 450
mg] 1,130 mg.
Other Ingredients: Maltodextrin.
APPROVED
2019
CocoaVia™ - Sweetened Dark
Chocolate Mixⓘ![]()
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
1 packet [6 g]
1,130 mg cocoa extract (Dutched - alkali processed)
Add 1 packet to a beverage or food of choice.
Very dark brown powder, mixes easily; Dark chocolate flavor, mildly sweet,
slight lingering sweetness
1 packet [6 g]
450 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 497.1 mg (82.9 mg per g) found
Calories: 20 [3.3 Cal/gram] claimed
8 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Powder in packet
1 packet [6 g]
✔
Found 1.1 mcg cadmium per serving (0.2 mcg per g)
30 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 20.6 mg
Theobromine: 114.6 mg
$1.17/packet
[$0.52 based on amount claimed]
[$0.47 based on amount found]
$35.00/30 packets
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 30 mg Naturally-Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
Contains A Bioengineered Food Ingredient.
1 packet
Calories 20, Total Carbohydrate 4 g, Dietary Fiber <1 g, Protein <1 g,
Iron 0.7 mg, Potassium 170 mg, Cocoa Extract (bean) [Cocoa Flavanols 450 mg]
1,130 mg.
Other Ingredient: Cocoa Powder (Processed With
Alkali), Maltodextrin, Sunflower Lecithin, Sucralose.
APPROVED
2019
Top Pick
CocoaVia™ - Unsweetened Dark
Chocolate Mix![]()
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
1 packet [6.8 g]
1,500 mg cocoa extract (Dutched - alkali processed)
Add 1 packet to a beverage or food of choice.
Very dark brown powder, mixes easily; Dark chocolate flavor, moderately
bitter
1 packet [6.8 g]
450 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 753.5 mg (110.8 mg per g) found
Calories: 20 [2.9 Cal/gram] claimed
5.3 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Powder in packet
1 packet [6.8 g]
✔
Found 1.3 mcg cadmium per serving (0.19 mcg per g)
30 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 20.7 mg
Theobromine: 154.6 mg
$1.67/1 packet
[$0.74 based on amount claimed]
[$0.44 based on amount found]
$50.00/30 packets
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 30 mg Naturally-Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
Contains A Bioengineered Food Ingredient.
1 packet
Calories 20, Total Fat 0.5 g, Total Carbohydrate 4 g, Dietary Fiber 1 g,
Protein <1 g, Iron 0.9 mg, Potassium 180 mg, Cocoa Extract (bean) [Cocoa
Flavanols 450 mg] 1,500 mg.
Other Ingredients: Cocoa Powder (Processed With
Alkali), Maltodextrin, Sunflower Lecithin.
APPROVED
2020
Top Pick
CocoaVia™ Memory+ⓘ![]()
Dist. by Mars Symbioscience,
A Division Of Mars, Inc.
3 capsules
1,650 mg
cocoa extract
3 Capsules Once Daily With Food.
3 capsules
750 mg flavanols
✔
Flavanols: 1,113.5 mg (623.4 mg per g) found
Calories: 5 [2.8 Cal/gram] claimed
0.9 Calories per 200 mg flavanols
Large capsuleⓘ
3 capsules
✔
Found <0.009 mcg cadmium per serving (<0.005 mcg per g)
30 mg caffeine listed
✔
Caffeine: 26.1 mg
Theobromine: 75.6 mg
$1.50/3 capsules
[$0.40 based on amount claimed]
[$0.27 based on amount found]
$135.00/3 bottles of 90 capsules (270 capsules total)
Source: Not listed
Precaution: 30 mg Naturally Occurring Caffeine Per Serving.
3 capsules
Calories 5, Total Carbohydrate 1 g, Cocopro® Cocoa
Extract (bean) [Cocoa Flavanols (including 105 mg (-)-epicatechin) 750 mg]
1,650 mg.
Other Ingredients: Hypromellose Capsule, Ascorbyl
Palmitate, Silicon Dioxide.
APPROVED
2017
Futurebiotics Dark Chocolate Extract 500
mg
Mfd. by Futurebiotics®
1 capsule
500 mg Violetamine™ dark chocolate bean extract
As a dietary supplement for adults, take 1 capsule daily or as recommended by a
healthcare professional.
1 capsule
Flavanols: 24.5 mg (41.4 mg per g) found
Calories not listed
Large vegetarian capsuleⓘ
1 capsule
✔
Found 0.02 mcg cadmium per serving (0.04 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 2.1 mg
Theobromine: 14.2 mg
$0.38/1 vegetarian capsule
[$3.13 based on amount found]
$22.98/60 vegetarian capsules
Source: Not listed
100% Vegetarian. Contains no added yeast, sugar, salt, starch, soy, wheat,
gluten, dairy, artificial colors, preservatives or animal products.
1 capsule
Violetamine™ Dark Chocolate bean extract (contains
polyphenols) 500 mg.
Other Ingredients: Modified cellulose (vegetarian capsule), microcrystalline
cellulose, silica, vegetarian stearate.
NOT APPROVED
2017
Hawaii Pharm Cacao
Dist. by Hawaii Pharm LLC
20 drops [0.9 mlⓘ]
1,100 mg cacao extract
Take about 20-30 drops in juice, water, tea or as desired up to four times per
day.
20 drops [0.9mlⓘ]
Flavanols: 0.23 mg (0.22 mg per g) found
Calories not listed
20 drops [0.9mlⓘ]
✔
Found <0.1 mcg cadmium per gram
Caffeine: 9.2 mg
Theobromine: 55.7 mg
$0.30/20 drops
[$262.85 based on amount found]
$19.95/2 fl oz. [60 ml] bottle (approx. 66 servingsⓘ)
Source: Not listed
Non-GMO. Contains No Alcohol. Contains NO
gluten, artificial colors, pesticides, preservatives, heavy metals.
20 drops
Dry herb/menstruum ratio: 1:3.
Ingredients: Certified Organic Cacao (Theobroma Cacao) raw beans. Other
Ingredients: Vegetable palm glycerin, crystal clear artesian Hawaiian water.
NOT APPROVED
2017
Solaray® Cocoa
Mfd. by Nutraceutical Corp.
1 capsule
500 mg cacao extract
Take one vegetarian capsule with a meal or glass of water.
1 capsule
Total Flavanols: 0.95 mg (1.8 mg per g)
Calories not listed
Large vegetarian capsuleⓘ
1 capsule
✔
Found 0.06 mcg cadmium per serving (0.11 mcg per g)
Caffeine: 0.65 mg
50 mg theobromine listed
✔
Theobromine: 65.9 mg
$0.15/1 vegetarian capsule
[$32.60 based on amount found]
$9.29/60 vegetarian capsules
Source: Not listed
1 capsule
Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) (bean extract) (Guaranteed to contain 50 mg
[10%] Theobromine) 500 mg.
Other Ingredients: Vegetable Cellulose Capsule, Maltodextrin, Rice Hull
Concentrate and Rice Bran Extract.
Unless otherwise noted, information about the
products listed above is based on the samples purchased by ConsumerLab.com (CL)
for this Product Review. Manufacturers may change ingredients and label
information at any time, so be sure to check labels carefully when evaluating
the products you use or buy. If a product's
ingredients differ from what is listed above, it may not necessarily be of the
same quality as what was tested.
The information contained in this report is
based on the compilation and review of information from product labeling and
analytic testing. CL applies what it believes to be the most appropriate
testing methods and standards. The information in this report does not reflect
the opinion or recommendation of CL, its officers or employees. CL cannot
assure the accuracy of information.
Copyright ConsumerLab.com, LLC, 2021 All
rights reserved. Not to be reproduced, excerpted, or cited in any fashion
without the express written permission of ConsumerLab.com LLC
ConsumerTips™:
As shown in the test
results above, the flavanol content of cocoa and cacao products can vary
tremendously and most products do not list their flavanol content. Use the
information in the third column to compare the amounts found. Be aware that
caffeine levels also range widely: Some products contain little while others
provide more caffeine than a cup of coffee. Use the information in the fourth
column of the table above to compare amounts of caffeine in products. An effective dose of flavanols from cocoa products has not
been established for any specific purpose, although positive results have been
seen with dosages ranging from about 50 mg to 200 mg or more per day. As noted
above, in Europe, cocoa-based products providing at least 200 mg of total
flavanols per day are permitted to claim an effect which may promote normal
blood flow. To get 200 mg of flavanols from a natural or raw, unsweetened cocoa
powder, you would need about 1 to 1¼ tablespoons of powder. Some products,
however, are made to contain higher concentrations of flavanols. Products
made from cocoa powder which has been Dutched
(alkaline processed) -- which lowers the bitterness and darkens the
color of cocoa powder -- have lower concentrations of flavanols: light Dutching reduces levels by about 60%, medium Dutching by about 75%, and heavy Dutching
by about 90% according to one study (Miller, J Agric Food Chem 2008). Dutched cocoa powders and chocolates sold in the U.S. must
include the statement "Processed with alkali" or identify the
specific alkali used, e.g., "Processed with sodium bicarbonate."
However, they need not specify whether a light, medium or heavy Dutching process was used. It is not clear if alkaline
processing has an effect on heavy metal contamination.
It is interesting to note that although the CocoaVia mix (powder) tested in this Review
includes cocoa powder "processed with alkali," this powder is
combined with a high-flavanol cocoa extract, so the resulting product is high
in flavanols. According to a communication received by ConsumerLab
(on 8/25/17) from Mars, maker of CocoaVia,
the alkalized cocoa is added to provide a richer taste and darker color to the
extract which is made from fresh cocoa beans (using the "Cocoapro process") that are higher in flavanols than
the fermented and roasted beans traditionally used to make cocoa powders.
Are cocoa and chocolate good sources of iron?
Like cadmium and lead, iron (and other minerals like calcium, magnesium and
zinc) is absorbed from the soil as cacao plants grow (Aikpokpodion, J Agri Sci 2010). The amount of iron
in a particular cocoa powder or chocolate will vary, but is estimated to be
about 1 or 2 mg in a 5 gram tablespoon of cocoa powder
and about 3 milligrams in a 40 gram serving of dark chocolate. However, not all
the iron in cocoa and chocolate products is absorbed (Yokoi, Br J Nutr
2009). The type of iron found in plants is absorbed only about half
as well as iron from animal sources. Additionally, polyphenols in cocoa and
chocolate can interfere with iron absorption (Natsume, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2000;Hurrell, Br J Nutr
1999). One clinical study in children found that iron absorption
from a chocolate flavored drink containing 158 mg of polyphenols was very low,
but was significantly improved when vitamin C (known to increase iron absorption)
was added to the drink (Davidsson, Am J Clin Nutr 1998). So while cocoa and chocolate
provide some iron, don't count on them to significantly contribute to the daily
recommended intake, which generally ranges from 7 mg to 18 mg depending on your
age and gender and is 27 mg for pregnant women (See the Iron Review for more about iron
requirements) — and you don't need to worry about it causing you to exceed the
tolerable daily intake level for iron, which is 40 to 45 mg.
What about the fat in dark chocolate bars?
While cocoa powder contains only cocoa solids, chocolate bars contain both
cocoa solids and cocoa butter — the fat from cocoa beans. The majority of the
fat in cocoa butter, about 65% or so, is saturated fat, mostly palmitic acid
and stearic acid. Cocoa butter contains smaller amounts of the unsaturated fats
oleic acid (30%) and linoleic acid (3%) (Liendo, Food Res Int 1997). Dark chocolate
does not contain trans-fat. Since cocoa butter is a relatively expensive
ingredient, some chocolate manufacturers replace a portion of the fat in cocoa
butter with less expensive, "replacement" fats, such as palm or
soybean oil, but, in the U.S. such products must be
labeled as "chocolate flavored" rather than "chocolate."
Acrylamide in cocoa and chocolate — a concern?
Acrylamide is a neurotoxin and probable carcinogen produced when cocoa beans
are roasted (part of typical processing). FDA tests in 2002 found amounts of
acrylamide in various cocoa powders and chocolate bars to range from 0.29 mcg
to 4.5 mcg per serving (see table below), although other foods, particularly
potato-based products like fries, cookies, crackers, and coffee generally
contribute higher amounts to the daily diet — estimated to be about 35 mcg for
an adult. Dutched (alkalized) and milk chocolate have
lower concentrations of acrylamide — but also lower levels of flavanols.
Nevertheless, it's best to minimize intake of acrylamide when possible. Even a
small amount of acrylamide may slightly increase the risk of tumors, leading
the state of California to
require a warning label on foods containing more than 0.2 mcg (micrograms) of
acrylamide per daily serving, although there is little risk of neurotoxicity
with exposure to less than 140 mcg per day according to the EPA.
Acrylamide in Cocoa and Chocolate
|
Cocoa or Chocolate |
Parts per Billion |
Per Serving |
|
Hershey's Cocoa |
909 |
4.5 mcg |
|
Hershey's European Style Dutch Processed Cocoa |
58 |
0.29 mcg |
|
Ghirardelli Unsweetened Cocoa |
316 |
1.58 mcg |
|
Ghirardelli Bittersweet Chocolate Baking Bar |
93 |
3.7 mcg |
|
Baker's Bittersweet Baking Chocolate Squares |
104 |
4.2 mcg |
|
Hershey's Milk Chocolate Bar |
Not detectable |
N/A |
Source: FDA Acrylamide in Food Survey Data
2002
Child labor and cocoa production
Be aware that, despite promises to eradicate the unethical practice, cocoa
sourced from West Africa, and possibly other countries, may be the product of child labor.
Several organizations help to provide oversight and set standards for ethically
responsible cocoa farming and production, including Fair Trade International, Fair for Life, and
the Rainforest Alliance.
Cocoa products and chocolate bars that meet these standards, which include no
use of forced or child labor, may bear these organizations' seals on their
labels. ConsumerLab lists these seals, as well as the
country of origin (when available) for cocoa products tested in this review in
the sixth column, "Notable Features," of the Results table.
Concerns and Cautions:
Cocoa
and chocolate products are generally safe. In a
3-month study of healthy men and women, a dose of up to 1,000 mg of cocoa
flavanols from a cocoa extract taken twice a day with meals was found to be
safe and well-tolerated, with no significant changes in blood pressure,
platelet function, cholesterol, or heart rate (Ottaviani, Am J Clin Nutr 2015).
Bear in mind that some cocoa-based products, particularly chocolate, contain
high amounts of added sugars and fats and contribute a significant number of
calories. These should be used in moderation, as excessive intake of sugars,
fats, and calories may negate any positive benefits of flavanols.
Caffeine and Theobromine
While the amounts of caffeine and theobromine found in typical
servings of cocoa and chocolate are generally well-tolerated, they can cause
side effects such as heartburn, gastritis, insomnia, anxiety, and heart
arrhythmias in some people, as well as interfere with the actions of drugs used
for these conditions and with stimulant drugs and MAO inhibitors. In the study
noted above, gastrointestinal side effects were more frequent when cocoa extract
was taken on an empty stomach than with meals.
Higher intakes of theobromine can cause
other side effects in some people. For example, daily intake of 50 - 100 grams
of cocoa (providing 800 mg to 1,500 mg of theobromine) has
been associated with sweating, trembling and severe headache (IARC 2018). Theobromine
has also been reported to cause nausea and vomiting in some individuals taking
a very high dose (1000 mg per day -- equivalent to the amount of theobromine in
three to five 40-gram bars of dark chocolate) (Baggott, Psychopharmacology (Berl)
2013). High amounts of theobromine might also be an issue
for people who need to control blood sugar levels. Results of a study
in which 500 mg of theobromine was taken daily by overweight but otherwise
healthy men and women for four weeks found that blood glucose rose
significantly more after eating as compared to responses in the same people
when theobromine was not taken. As noted earlier, moderate consumption of cocoa
flavanols as well as chocolate intake may help control blood sugar and reduce
the risk of diabetes, but not higher levels. If blood sugar control is an issue
for you, it would seem wise to limit intake of dark chocolate to no more than two
servings per week.
Caffeine and theobromine are toxic to dogs and cats. See
a Chocolate Toxicity Calculator for
estimates of toxicity based on the weight of the animal and the amount and type
of chocolate consumed. Initial signs of caffeine/theobromine intoxication in
pets are extreme thirst, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distention, and
restlessness, which can progress to hyperactivity, increased urination,
rigidity, tremors, fast, slow or irregular heartbeat, high or low blood
pressure, seizures, coma and even death. Dark chocolate is more toxic than milk
chocolate.
Migraine?
Consumption of cocoa and/or chocolate has been reported to trigger migraines in
some people, however, the evidence for this is mixed, and it is unclear exactly
how cocoa may trigger migraines. Cocoa contains the amino acids
phenylethylamine and tyramine (approximately 0.1 - 2.8 mcg/g and 3.6 - 8.3
mcg/g, respectively), which are also found in foods such as wine and cheese and
which people with migraines are often advised to avoid. However, clinical
studies of the effects of these amino acids in people with migraine have
yielded mixed results, with some finding an increase in the incidence in
migraine and others finding no increase (Hannington, Br Med J 1967; Moffet, J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry 1972; Sandler, Nature 1974). Cocoa also contains
histamine, a substance which can dilate blood vessels and cause allergic
reactions such as rash and headache in some people (Kovacova-Hanuskova, Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 2015). Cocoa ingestion has been shown
in one clinical study to increase blood flow to the brain, which,
theoretically, might trigger migraine in some people (Lamport,Psychopharmacology 2015). Interestingly, however,
double-blind clinical studies of chocolate consumption, a single serving of
chocolate between 44 and 62 grams has not found an increased risk of migraine
in people with a history of migraine, compared to placebo; a review of these
and other studies concluded that there was no reliable scientific basis to
support the recommendation that people with migraines avoid chocolate and
cocoa-containing foods (Lippi, Acta Biomed 2014).
In addition, animal studies have found cocoa and cocoa extract to have
anti-inflammatory effects on the trigeminal nerve (inflammation of which is
associated with migraine) and surrounding tissues, suggesting a possible
benefit for migraine — although this has not been studied yet in people (Abbey, J Ethnopharmacol 2008; Cady, Mol Nutr Food Res 2013).
Kidney stones
The National Kidney Foundation advises
individuals who are prone to developing calcium oxalate kidney stones (the
most common type of kidney stone) to avoid cocoa and chocolate because they
contain high amounts of oxalates — naturally occurring compounds that bind with
calcium and form kidney stones in some people. In a small study among women
(who were not noted to have a history of kidney stones) consuming 68 grams
(about 12 pieces) of dark chocolate (Whittaker's dark Ghana chocolate,
72% cocoa) increased urinary oxalate output by an average of 69% over a
six-hour period compared to when chocolate was not consumed (Schroder, J Food Compost Anal 2011).
Cocoa powder contains higher concentrations of oxalates than chocolate, as
chocolate includes other ingredients, such as cocoa fat, that don't contribute
oxalates. In the same study above, the researchers also analyzed the oxalate
content of 15 cocoa powders and 34 dark/bitter chocolate bars. The powders
averaged 729 mg of total oxalates per 100 grams while the dark chocolates
averaged about one-third of that amount -- 254 mg total oxalates per 100 grams.
Among the five dark chocolate bars purchased in the U.S., Newman's Own
Super Dark Chocolate contained the lowest concentration of total
oxalates (169 mg/100 grams) and Ghirardelli Unsweetened Chocolate contained
the highest (322 mg/100 grams). Bars containing higher % cocoa tended to
contain higher concentrations of oxalates, but not in all cases, suggesting
that other factors, such as differences in cocoa bean varieties and processing
methods may also affect oxalate content. A recommended low-oxalate diet may
limit daily oxalate intake to 50 to 80 mg or less. Based on the average amounts
found in this study, amounts of total oxalates in typical servings of cocoa
powder (about 36 mg per 1 tablespoon) or dark chocolate (about 100 mg per 50-gram
bar) would be close to, or exceed, this limit.
Acne
Although some studies using chocolate bars have not found chocolate to
worsen acne, a small, double-blind, placebo-controlled study giving
100% cocoa powder (i.e., pure chocolate) to men ages 18 to 35 found a positive
association between the number of pimples they developed and the use of cocoa.
The men, who had a history of acne, were given a single serving ranging from 0
to 170 mg of cocoa powder in capsules and were followed for one week. Although
some men given cocoa did not develop pimples during the week, and some men
given placebo did, overall there was a modest but positive correlation between
the amount of cocoa consumed and the number of pimples developed (Caperton, J Clin Aesthet
Dermatol 2014).
Allergies
People with milk allergies should be aware that dark chocolate bars may contain
milk. Tests published in 2020 by the FDA of
119 dark chocolate bars and chips specifically claiming to be
"dairy-free" or "milk-free" showed that approximately 10%
of these products contained milk. The FDA reported similar findings in 2015,
which included finding milk in a bar labeled as "allergen-free."
Nickel
Cocoa powder and chocolate (and related products, like
chocolate syrup) are among foods which have relatively high concentrations of
nickel and may trigger allergic contact dermatitis (eczema) in
nickel-sensitive individuals. This typically occurs when ingesting large
portions or in conjunction with ingestion of large amounts of other high-nickel
foods (such as peas and beans, canned foods, shellfish, oats (including
granola), peanuts, hazelnuts, walnuts, and sunflower seeds) (Pizzutelli, Eur Ann All Clin Immunol, 2011). One
case report involved four children in the U.S. with known nickel sensitivity
who binged on chocolate Easter eggs (Jacob, Ped Derm 2014).
The U.S. FDA provides a listing of the amounts of nickel in
common foods.
In response to a possible allergic reaction to nickel reported to
ConsumerLab.com by a CL member who had used CocoaVia,
CL purchased the latest formulation of CocoaVia
Unsweetened Dark Chocolate Mix and tested it for nickel in January
2016. For comparison, CL also tested a cocoa powder and a dark chocolate. The
highest concentration of nickel was in the cocoa powder (Hershey's Cocoa —
Natural Unsweetened) -- 9.0 mcg/g. This was followed by CocoaVia -- 5.85 mcg/g and Endangered
Species Natural Dark Chocolate 88% Cocoa -- 5.56 mcg/g. These are
higher levels than the FDA has reported in other foods, the highest of which
was 3 mcg/g in sunflower seeds, followed by 2 mcg/g in an oat-based cereal, and
1 mcg/g in milk chocolate. The listed serving of 43 grams (half a bar) of Endangered
Speciesdark
chocolate therefore contained 239 mcg of nickel. This is similar to all the
nickel in an adult daily diet, which has been reported to range from 200 to 300
mcg (Grandjean, IARC Sci Publ 1984). As the suggested serving sizes
are smaller for CocoaVia (6.8 grams)
and Hershey's Cocoa Powder (5 grams), total nickel per serving
from these was 40 mcg and 45 mcg, respectively.
The take home message about nickel: Natural cocoa powder has more nickel
per gram than CocoaVia (a cocoa
extract) or dark chocolate (which, in turn, has much more nickel than milk
chocolate), but the relatively large serving size of chocolate means higher
total nickel exposure. However, at their suggested serving sizes, none of these
exceeds the daily tolerable upper intake level for nickel, which is 1,000 mcg
(1 mg) — a limit based on nickel toxicity (IOM, 2001), not nickel allergy which can occur
with lower amounts.
Ochratoxin A
Cocoa beans can become contaminated with fungi which produce toxins,
particularly during drying and storage. Ochratoxin A (OTA), a potential
carcinogen and kidney toxin, is one of the most common fungal toxins to occur
in cocoa beans. However, most OTA is found in the shell of the bean, which is
removed during processing. An analysis of 85 cocoa and chocolate products sold
in Canada between 2011 and 2012 found that two cocoa powders exceeded proposed
European limits (which was never established), although the levels of OTA were
still below 5 ppb, the European limit for OTA in roasted coffee (Turcotte, Mycotoxin Res 2013). For this
reason, ConsumerLab.com did not include OTA testing in this Review.
Information on this site
is provided for informational purposes only. It is not an endorsement of any
product nor is it meant to substitute for the advice provided by physicians or
other healthcare professionals. The information contained herein should not be
used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease. Consumers should
inform their healthcare providers of the dietary supplements they take.
Latest Clinical Research Updates for Cocoa Powders, Dark
Chocolate, Extracts, Nibs & Supplements
9/25/2021
A recent study
investigated the effects of consuming dark chocolate on mood. The effect
depended on cocoa level. See the results in the Mood and Stress section of our Dark
Chocolate and Cocoa Review. Also see our Top Picks among dark chocolate bars and cocoa products.
12/02/2020
A new study suggests that
cocoa may improve some aspects of cognitive function in healthy people and
sheds some light on how this may work. See the details in the Memory and Cognition section
of the Dark Chocolate and Cocoa Review. Also see our Top Picks among dark
chocolates, cocoa powders and supplements.
11/22/2020
Does eating chocolate
improve cognition in postmenopausal women? See what a new study found in
the Memory and Cognition section
of the Dark Chocolate and Cocoa Review. Also see our Top Picks for dark chocolate,
cocoa powders and supplements based on their flavanol content
and purity.
Undeclared Milk in Dark Chocolates
10/03/2020
If you're allergic to
milk, be aware that about 10% of "dairy free" dark chocolate bars and
chips were recently found to contain milk. Learn more in the Concerns and Cautions section
of our Dark Chocolates Review. Also see our Top Picks for dark chocolate.
Chocolate to Improve Body Composition?
8/11/2020
Can eating a small amount
of chocolate every day help improve body composition? Find out what a recent
study showed in the What It Does section
of the Dark Chocolates, Cocoa & Cacao Powders, Nibs, and Supplements
Review. Also see our Top Picks for dark chocolate, chocolate chips and
cocoa powders.











